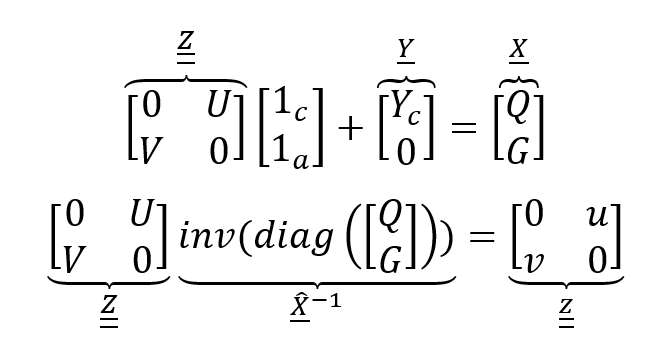The repository is complementing what is described in the paper A multi-disciplinary approach to estimate the medium-term impact of COVID-19 on the energy system: a case study for Italy for what concerns the meso-economic modelling.
In this folder the EUROSTAT Supply and Use Table (SUT) for Italy are reported in row format (in 'Database/EUROSTAT' where also the consumption_trend.py module for extrapolating trends in final demand shares on the basis of 2010-2016 values can be found) and CVX_SUT format (the excel files in 'Database' for 2014, 2015 and 2016 which are used for feeding the Leontief Kantorovich optimiztion model) are present. In this folder one can also find the Aggregation.xlsx file, which can be used for aggregating the results on the basis of any aggregation choice. Here two aggregation are used for presenting results, one based on the sectors adopted in the Energy Model (Integration), one for a detailed analysis of results (Analysis) and the last one as the one adopted in the main paper (Paper).
In this folder the module for managing input-output model and its dedicated readme file can be found. This step of the work is taking advantage of REP_CVX, a python module developed by REP research group in Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei with the aim to provide an open-source tool for performing Input-Output analysis based on the Supply and Use Framework. The approach is grounded on the use of Supply and Use Framework as described by Lenzen and Rueda-Cantuche in A note on the use of supply-use tables in impact analyses. In this case, input-output coefficients have been obtained by simply multiplying supply (V) and use (U) matrices (collectively identifiable as Z) by the inverse of the diagonalized resulting vector of total outputs of commodities (Q) and industrial activities (G). In this way, industry related assumption (i.e. input-structure of an industry is invariant irrespective of its product-mix) is implicitly assumed, as here shown:
Where:
- 1c and 1a are two row summation sub-vectors, one for commodity (c) and one for activities (a);
- Yc is the demand, which is clearly expressed by means of commodities;
- u and v form the supply and use coefficient matrices: u is called the (product-by-industry) use coefficients matrix (input structures), and v is called the (industry-by-product) market share matrix. In this way it is possible to express the represented economy by means of coefficients which are showing the following: from the one hand how much inputs of commodity are required to produce one unit of industrial activity (u) and, from the other hand, how much activity production is needed by each industrial activity for every one unit of a certain commodity (v). Getting coefficients from the other matrices is straightforward: all of them are get from the same vector of total output (X).
Note that a variable with one underline identifies a vector, while one with double underline identifies a matrix. A variable in capital letters has absolute units (e.g. M€), while one in small letters has specific units (e.g. M€/M€).
In this folder the results are stored. Each run generates 4 htlm charts and 1 excel files. For each aggregation a dedicated folder can be found. Note that the model is also run assuming a fixed share of final demand, which is resulting in a trivial redistribution of GDP on the basis of 2016 allocation of value added among industries. Nevertheless, this set of results can be helpful in investigating how the model is working.
In this folder an excel file for managing the non-database exogenous parameters for the Leontief model is present. In the README sheet a detailed presentation of the sheets is presented.
Here a conceputal highly aggregated model is presented in an Excel file. OpenSolver add-in for Excel is required for running the model (see https://opensolver.org/).
Here the main code of the repository is stored. A for loop around years and scenarios is performed as described in the paper. The user has the possibility of selecting among different running options (e.g. running with fixed final demand shares or with projected trends, which is the mode adopted in the study) and printing modes.