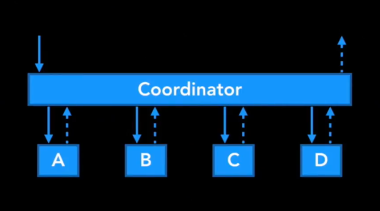
Coordinator and FlowController
onmyway133 opened this issue · 16 comments
Every new architecture that comes out, either iOS or Android, makes me very excited. I'm always looking for ways to structure apps in a better way. But after some times, I see that we're too creative in creating architecture, aka constraint, that is too far away from the platform that we're building. I often think "If we're going too far from the system, then it's very hard to go back"
I like things that embrace the system. One of them is Coordinator which helps in encapsulation and navigation. Thanks to my friend Vadym for showing me Coordinator in action.
The below screenshot from @khanlou 's talk at CocoaHeads Stockholm clearly says many things about Coordinator
But after reading A Better MVC, I think we can leverage view controller containment to do navigation using UIViewController only.
Since I tend to call view controllers as LoginController, ProfileController, ... and the term flow to group those related screens, what should we call a Coordinator that inherits from UIViewController 🤔 Let's call it FlowController 😎 .
The name is not that important, but the concept is simple. FlowController was also inspired by this Flow Controllers on iOS for a Better Navigation Control back in 2014. The idea is from awesome iOS people, this is just a sum up from my experience 😇
So FlowController can just a UIViewController friendly version of Coordinator. Let see how FlowController fits better into MVC
«UIViewController is the center of the universe.»
— Elvis Nuñez (@3lvis) 6. oktober 2017
— @onmyway133
1. FlowController and AppDelegate
Your application starts from AppDelegate, in that you setup UIWindow. So we should follow the same "top down" approach for FlowController, starting with AppFlowController. You can construct all dependencies that your app need for AppFlowController, so that it can pass to other child FlowController.
AppDelegate is also considered Composition Root
Here is how to declare AppFlowController in AppDelegate
struct DependencyContainer: AuthServiceContainer, PhoneServiceContainer, NetworkingServiceContainer,
LocationServiceContainer, MapServiceContainer, HealthServiceContainer {
let authService: AuthServiceProtocol
let phoneService: PhoneService
let networkingService: NetworkingService
let locationService: LocationService
let mapService: MapService
let healthService: HealthService
static func make() -> DependencyContainer {
// Configure and make DependencyContainer here
}
}
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
var appFlowController: AppFlowController!
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
appFlowController = AppFlowController(
dependencyContainer: DependencyContainer.make()
)
window = UIWindow(frame: UIScreen.main.bounds)
window?.rootViewController = appFlowController
window?.makeKeyAndVisible()
appFlowController.start()
return true
}
}Here are some hypothetical FlowController that you may encounter
- AppFlowController: manages UIWindow and check whether to show onboarding, login or main depending on authentication state
- OnboardingFlowController: manages
UIPageViewControllerand maybe ask for some permissions - LoginFlowController: manages
UINavigationControllerto show login, sms verification, forget password, and optionally startSignUpFlowController - MainFlowController: manages
UITabBarControllerwith each tab serving main features- FeedFlowController: show feed with list of items
- ProfileFlowController: show profile
- SettingsFlowController: show settings, and maybe call logout, this will delegates up the
FlowControllerchain.
- OnboardingFlowController: manages
The cool thing about FlowController is it makes your code very self contained, and grouped by features. So it's easy to move all related things to its own package if you like.
2. FlowController as container view controller
In general, a view controller should manage either sequence or UI, but not both.
Basically, FlowController is just a container view controller to solve the sequence, based on a simple concept called composition. It manages many child view controllers in its flow. Let' say we have a ProductFlowController that groups together flow related to displaying products, ProductListController, ProductDetailController, ProductAuthorController, ProductMapController, ... Each can delegate to the ProductFlowController to express its intent, like ProductListController can delegate to say "product did tap", so that ProductFlowController can construct and present the next screen in the flow, based on the embedded UINavigationController inside it.
Normally, a FlowController just displays 1 child FlowController at a time, so normally we can just update its frame
final class AppFlowController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLayoutSubviews() {
super.viewDidLayoutSubviews()
childViewControllers.first?.view.frame = view.bounds
}
}3. FlowController as dependency container
Each view controller inside the flow can have different dependencies, so it's not fair if the first view controller needs to carry all the stuff just to be able to pass down to the next view controllers. Here are some dependencies
- ProductListController: ProductNetworkingService
- ProductDetailController: ProductNetworkingService, ImageDowloaderService, ProductEditService
- ProductAuthorController: AuthorNetworkingService, ImageDowloaderService
- ProductMapController: LocationService, MapService
Instead the FlowController can carry all the dependencies needed for that whole flow, so it can pass down to the view controller if needed.
struct ProductDependencyContainer {
let productNetworkingService: ProductNetworkingService
let imageDownloaderService: ImageDownloaderService
let productEditService: ProductEditService
let authorNetworkingService: AuthorNetworkingService
let locationService: LocationService
let mapService: MapService
}
class ProductFlowController {
let dependencyContainer: ProductDependencyContainer
init(dependencyContainer: ProductDependencyContainer) {
self.dependencyContainer = dependencyContainer
}
}
extension ProductFlowController: ProductListControllerDelegate {
func productListController(_ controller: ProductListController, didSelect product: Product) {
let productDetailController = ProductDetailController(
productNetworkingService: dependencyContainer.productNetworkingService,
productEditService: dependencyContainer.productEditService,
imageDownloaderService: dependencyContainer.imageDownloaderService
)
productDetailController.delegate = self
embeddedNavigationController.pushViewController(productDetailController, animated: true)
}
}Here are some ways that you can use to pass dependencies into FlowController
4. Adding or removing child FlowController
Coordinator
With Coordinator, you need to keep an array of child Coordinators, and maybe use address (=== operator) to identify them
class Coordinator {
private var children: [Coordinator] = []
func add(child: Coordinator) {
guard !children.contains(where: { $0 === child }) else {
return
}
children.append(child)
}
func remove(child: Coordinator) {
guard let index = children.index(where: { $0 === child }) else {
return
}
children.remove(at: index)
}
func removeAll() {
children.removeAll()
}
}FlowController
With FlowController, since it is UIViewController subclass, it has viewControllers to hold all those child FlowController. Just add these extensions to simplify your adding or removing of child UIViewController
extension UIViewController {
func add(childController: UIViewController) {
addChildViewController(childController)
view.addSubview(childController.view)
childController.didMove(toParentViewController: self)
}
func remove(childController: UIViewController) {
childController.willMove(toParentViewController: nil)
childController.view.removeFromSuperview()
childController.removeFromParentViewController()
}
}And see in action how AppFlowController work with adding
final class AppFlowController: UIViewController {
func start() {
if authService.isAuthenticated {
startMain()
} else {
startLogin()
}
}
private func startLogin() {
let loginFlowController = LoginFlowController(
loginFlowController.delegate = self
add(childController: loginFlowController)
loginFlowController.start()
}
fileprivate func startMain() {
let mainFlowController = MainFlowController()
mainFlowController.delegate = self
add(childController: mainFlowController)
mainFlowController.start()
}
}and with removing when the child FlowController finishes
extension AppFlowController: LoginFlowControllerDelegate {
func loginFlowControllerDidFinish(_ flowController: LoginFlowController) {
remove(childController: flowController)
startMain()
}
}5. AppFlowController does not need to know about UIWindow
Coordinator
Usually you have an AppCoordinator, which is held by AppDelegate, as the root of your Coordinator chain. Based on login status, it will determine which LoginController or MainController will be set as the rootViewController, in order to do that, it needs to be injected a UIWindow
window = UIWindow(frame: UIScreen.main.bounds)
appCoordinator = AppCoordinator(window: window!)
appCoordinator.start()
window?.makeKeyAndVisible()You can guess that in the start method of AppCoordinator, it must set rootViewController before window?.makeKeyAndVisible() is called.
final class AppCoordinator: Coordinator {
private let window: UIWindow
init(window: UIWindow) {
self.window = window
}
func start() {
if dependencyContainer.authService.isAuthenticated {
startMain()
} else {
startLogin()
}
}
}FlowController
But with AppFlowController, you can treat it like a normal UIViewController, so just setting it as the rootViewController
appFlowController = AppFlowController(
window = UIWindow(frame: UIScreen.main.bounds)
window?.rootViewController = appFlowController
window?.makeKeyAndVisible()
appFlowController.start()6. LoginFlowController can manage its own flow
Supposed we have login flow based on UINavigationController that can display LoginController, ForgetPasswordController, SignUpController
Coordinator
What should we do in the start method of LoginCoordinator? Construct the initial controller LoginController and set it as the rootViewController of the UINavigationController? LoginCoordinator can create this embedded UINavigationController internally, but then it is not attached to the rootViewController of UIWindow, because UIWindow is kept privately inside the parent AppCoordinator.
We can pass UIWindow to LoginCoordinator but then it knows too much. One way is to construct UINavigationController from AppCoordinator and pass that to LoginCoordinator
final class AppCoordinator: Coordinator {
private let window: UIWindow
private func startLogin() {
let navigationController = UINavigationController()
let loginCoordinator = LoginCoordinator(navigationController: navigationController)
loginCoordinator.delegate = self
add(child: loginCoordinator)
window.rootViewController = navigationController
loginCoordinator.start()
}
}
final class LoginCoordinator: Coordinator {
private let navigationController: UINavigationController
init(navigationController: UINavigationController) {
self.navigationController = navigationController
}
func start() {
let loginController = LoginController(dependencyContainer: dependencyContainer)
loginController.delegate = self
navigationController.viewControllers = [loginController]
}
}FlowController
LoginFlowController leverages container view controller so it fits nicely with the way UIKit works. Here AppFlowController can just add LoginFlowController and LoginFlowController can just create its own embeddedNavigationController.
final class AppFlowController: UIViewController {
private func startLogin() {
let loginFlowController = LoginFlowController(
dependencyContainer: dependencyContainer
)
loginFlowController.delegate = self
add(childController: loginFlowController)
loginFlowController.start()
}
}
final class LoginFlowController: UIViewController {
private let dependencyContainer: DependencyContainer
private var embeddedNavigationController: UINavigationController!
weak var delegate: LoginFlowControllerDelegate?
init(dependencyContainer: DependencyContainer) {
self.dependencyContainer = dependencyContainer
super.init(nibName: nil, bundle: nil)
embeddedNavigationController = UINavigationController()
add(childController: embeddedNavigationController)
}
func start() {
let loginController = LoginController(dependencyContainer: dependencyContainer)
loginController.delegate = self
embeddedNavigationController.viewControllers = [loginController]
}
}7. FlowController and responder chain
Coordinator
Sometimes we want a quick way to bubble up message to parent Coordinator, one way to do that is to replicate UIResponder chain using associated object and protocol extensions, like Inter-connect with Coordinator
extension UIViewController {
private struct AssociatedKeys {
static var ParentCoordinator = "ParentCoordinator"
}
public var parentCoordinator: Any? {
get {
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &AssociatedKeys.ParentCoordinator)
}
set {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &AssociatedKeys.ParentCoordinator, newValue, .OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN)
}
}
}
open class Coordinator<T: UIViewController>: UIResponder, Coordinating {
open var parent: Coordinating?
override open var coordinatingResponder: UIResponder? {
return parent as? UIResponder
}
}FlowController
Since FlowController is UIViewController, which inherits from UIResponder, responder chain happens out of the box
Responder objects—that is, instances of UIResponder—constitute the event-handling backbone of a UIKit app. Many key objects are also responders, including the UIApplication object, UIViewController objects, and all UIView objects (which includes UIWindow). As events occur, UIKit dispatches them to your app's responder objects for handling.
8. FlowController and trait collection
FlowController
I very much like how Kickstarter uses trait collection in testing. Well, since FlowController is a parent view controller, we can just override its trait collection, and that will affect the size classes of all view controllers inside that flow.
As in A Better MVC, Part 2: Fixing Encapsulation
The huge advantage of this approach is that system features come free. Trait collection propagation is free. View lifecycle callbacks are free. Safe area layout margins are generally free. The responder chain and preferred UI state callbacks are free. And future additions to UIViewController are also free.
From setOverrideTraitCollection
When implementing a custom container view controller, you can use this method to change the traits of any embedded child view controllers to something more appropriate for your layout. Making such a change alters other view controller behaviors associated with that child
let trait = UITraitCollection(traitsFrom: [
.init(horizontalSizeClass: .compact),
.init(verticalSizeClass: .regular),
.init(userInterfaceIdiom: .phone)
])
appFlowController.setOverrideTraitCollection(trait, forChildViewController: loginFlowController)9. FlowController and back button
Coordinator
One problem with UINavigationController is that clicking on the default back button pops the view controller out of the navigation stack, so Coordinator is not aware of that. With Coordinator you needs to keep Coordinator and UIViewController in sync, add try to hook up UINavigationControllerDelegate in order to clean up. Like in Back Buttons and Coordinators
extension Coordinator: UINavigationControllerDelegate {
func navigationController(navigationController: UINavigationController,
didShowViewController viewController: UIViewController, animated: Bool) {
// ensure the view controller is popping
guard
let fromViewController = navigationController.transitionCoordinator?.viewController(forKey: .from),
!navigationController.viewControllers.contains(fromViewController) else {
return
}
// and it's the right type
if fromViewController is FirstViewControllerInCoordinator) {
//deallocate the relevant coordinator
}
}
}Or creating a class called NavigationController that inside manages a list of child coordinators. Like in Navigation coordinators
final class NavigationController: UIViewController {
// MARK: - Inputs
private let rootViewController: UIViewController
// MARK: - Mutable state
private var viewControllersToChildCoordinators: [UIViewController: Coordinator] = [:]
// MARK: - Lazy views
private lazy var childNavigationController: UINavigationController =
UINavigationController(rootViewController: self.rootViewController)
// MARK: - Initialization
init(rootViewController: UIViewController) {
self.rootViewController = rootViewController
super.init(nibName: nil, bundle: nil)
}
}FlowController
Since FlowController is just plain UIViewController, you don't need to manually manage child FlowController. The child FlowController is gone when you pop or dismiss. If we want to listen to UINavigationController events, we can just handle that inside the FlowController
final class LoginFlowController: UIViewController {
private let dependencyContainer: DependencyContainer
private var embeddedNavigationController: UINavigationController!
weak var delegate: LoginFlowControllerDelegate?
init(dependencyContainer: DependencyContainer) {
self.dependencyContainer = dependencyContainer
super.init(nibName: nil, bundle: nil)
embeddedNavigationController = UINavigationController()
embeddedNavigationController.delegate = self
add(childController: embeddedNavigationController)
}
}
extension LoginFlowController: UINavigationControllerDelegate {
func navigationController(_ navigationController: UINavigationController, willShow viewController: UIViewController, animated: Bool) {
}
}10. FlowController and callback
We can use delegate pattern to notify FlowController to show another view controller in the flow
extension ProductFlowController: ProductListControllerDelegate {
func productListController(_ controller: ProductListController, didSelect product: Product) {
let productDetailController = ProductDetailController(
productNetworkingService: dependencyContainer.productNetworkingService,
productEditService: dependencyContainer.productEditService,
imageDownloaderService: dependencyContainer.imageDownloaderService
)
productDetailController.delegate = self
embeddedNavigationController.pushViewController(productDetailController, animated: true)
}
}Another approach is to use closure as callback, as proposed by @merowing_, and also in his post Improve your iOS Architecture with FlowControllers
Using closures as triggers rather than delegate allows for more readable and specialized implementation, and multiple contexts
final class ProductFlowController {
func start() {
let productListController = ProductListController(
productNetworkingService: dependencyContainer.productNetworkingService
)
productListController.didSelectProduct = { [weak self] product in
self?.showDetail(for: product)
}
embeddedNavigationController.viewControllers = [productListController]
}
}11. FlowController and deep linking
TBD. In the mean while, here are some readings about the UX
Nice post! I think it would make a little more sense if you explain how it integrates with the AppDelegate before explaining how the AppCoordinator works.
I wrote a Coordinator-based framework with a demo project which also explains some of the concepts in it's README, including how it integrates with the AppDelegate. Feel free to check it out: https://github.com/Flinesoft/Imperio
We are already successfully using it in our projects, thank you @khanlou for your great blog posts which pointed us into the right direction. 👍
Awesome article, and hit me right while I was researching Coordinators.
BUT... I still have a similar issue I have with other coordinator approaches. Suppose I present a flow controller (which contains a navigation controller, and some VC doing stuff), and suddenly one of its child VCs calls dismiss without notifying the flow controller or any other collaborator. Then the flow controller will be removed too (which is fine), but it's parent flow controller does not notice it. But I need it to notice in order to do some cleanup work. Any ideas on how to solve this?
I could implement deinit in the presented flow controller and there send a distress signal to its parent flow controller. I hope there are better alternatives.
I have asked the question on SO as well, but leaving away the coordinator part:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/47350720/how-can-a-presentingviewcontroller-get-notified-that-its-presentedviewcontroller
@fabb Hi, the recommended way is that the presented FlowController should call back (delegate, closure) to the original FlowController so that it can decide what to clean up and to dismiss this presented FlowController.
The other workaround I think, is to listen to willMove(toParentViewController:) inside the presented FlowController, if it was dismissed/removed, then the parentViewController will be nil
@onmyway133 Yeah, unfortunately my presented FlowController doesn't know about the dismiss call (as in my case it stems from an kind-of-ill-behaved VC in a library I cannot easily modify).
willMove(toParentViewController:) will not be called for presented VCs, similarly as the childViewControllers array does not include any presented VCs.
I have some other questions. Let's say I have a tab bar based UI with navigation controllers in each tab. Let's visualize it with some sprinkled flow controllers:
AppFlowController -> TabBarController -> [Tab1FlowController, Tab2FlowController, ...]
Tab1FlowController -> NavigationController -> [ViewController1, ViewController2, SpecialFlowController -> ViewController3, ViewController2]
ViewController3 -> ModalFlowController -> NavigationController -> ...
Tab2FlowController -> NavigationController -> [ViewController1, ViewController4, ViewController5, ViewController6]
Some notes to this:
- Not all ViewControllers will be directly contained in a flow controller, as they don't do anything special, and just push other things which they can delegate to the next parent flow controller,
TabXFlowController ViewController3does get an own flow controller, as it might present something, and the next parent flow controllerTab1FlowControllerdoesn't really need to know about this
Question 1: Does this make sense until now, would you structure your app similarly?
So now for the more contrived question. Let's say ViewController4, ViewController5 and ViewController6 form an own process (checkout or anything else that belongs together) while the first on the stack, ViewController1 is not part of that process. Now at ViewController6, when I click a button, I want to pop back to ViewController1. As ViewControllers should be encapsulated, they should not need to know how to navigate somewhere else, but rather delegate it to someone who knows.
Question 2: Whom would you delegate the popping back to ViewController1 and in what way?
I have several ideas for doing it in a clean encapsulated fashion, but I'm not sure which one to choose or if there is an even better one.
- Approach 1: When
ViewController1initiates the process, it delegates it toTab2FlowControllerwhich knows that it needs to pushViewController4.Tab2FlowControlleralso sets either a dismissal delegate or closure onViewController4that the latter can use to pop back toViewController1later. It will be passed fromViewController4toViewController5andViewController6which will use it in the end.
The downside of this approach is thatTab2FlowControllerneeds to know that it might contain the processViewController4-ViewController6and pass/be a delegate or pass a closure. On the upside there is compiletime-safety due to the delegate protocol, or initializers taking the closure, and a clear way what to do on dismissal. - Approach 2: Use something similar to what unwind segues do. Just like in approach 1, when
ViewController1initiates the process, it delegates it toTab2FlowControllerwhich knows that it needs to pushViewController4. Unlike approach 1 though,Tab2FlowControllercan be agnostic toViewController4needing a way to dismiss itself later, and does not need to pass any delegate or closure. In the end,ViewController6sends out a dismiss message in a similar way to how unwind segues do, i.e. a traversal mechanism needs to pass the"ViewController6 tells that the process is finished"message in this way:ViewController6 -> NavigationController -> ViewController5 -> ViewController4 -> ViewController1, andViewController1needs to react to this message.ViewController1then needs to tellTab2FlowControllerthat it wants to be shown which can pop back to it.
The downside is that there is less compiletime-safety, asViewController6shoots a dismissal message into the blue. Also it's more elaborate due to the messaging system that needs to follow a similar path as unwind segues, instead of just calling a delegate method / closure. On the upside,Tab2FlowControllercan have less knowledge andViewController1can handle both theshow processandfinish processsteps (yes, it still delegates both toTab2FlowController, but in a more generic way not depending on the process at hand).
Which way would you choose? Maybe something completely different?
And on it goes with the questions/findings, sorry for spamming guys ;-)
startmethods unnecessary?
I have found that instead of dedicated start methods it's much more natural to just use overwrite viewDidLoad for that.
E.g. makeKeyAndVisible will add the view of the AppFlowCoordinator to the UIWindow anyways, which will implicitly call viewDidLoad on the AppFlowCoordinator where it can start doing its thing.
Further down the hierarchy it might even be desirable to use viewDidLoad instead, as it will keep the lazy loading of the view property intact. There are some pitfalls though:
- Lazy loading of the
viewproperty vs.add(childController:)
The method add(childController:) as described in the article also adds the childVC view as a subview to the parentVC view. This implicitly triggers lazy loading of the child view, and viewDidLoad on the childVC. This might not always be wanted.
E.g. in my example in the previous comment, I have flow controllers contained in a UITabBarController. The UITabBarController by default initially only loads the view of the first tab, the other tabs' view properties will only be lazy loaded when the tab becomes active later. To keep that functionality, it's necessary to not add the childVC of the TabXFlowController until its viewDidLoad method is called, like this:
class Tab1FlowController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let vc1 = NamedViewController(name: "1-1")
let navC = UINavigationController(rootViewController: vc1)
navC.delegate = self
add(childController: navC)
}
}
I also like to sprinkle asserts everywhere, so I do this:
extension UIViewController {
func add(childController: UIViewController) {
assert(self.isViewLoaded)
addChildViewController(childController)
...
}
}
- FlowControllers need to forward some stuff though
When I added flow controllers as children of the UITabBarController, I noticed that my tabbar items did not appear, as I previously have only set them on the UINavigationController. Now they need to be set on the flow controller instead. Unfortunately this has to be done before viewDidLoad is called, as UITabBarController will call it before it adds the views - makes sense, as you need to show tabbar items for all tabs, even those which still have not been lazily loaded.
So something like this is needed:
class Tab1FlowController: UIViewController {
init() {
super.init(nibName: nil, bundle: nil)
// need to set tabBarItem in init, as it will be accessed before viewDidLoad is called
self.tabBarItem = UITabBarItem(title: "1", image: nil, tag: 0)
}
}
Or alternatively, If you like delegation:
class Tab2FlowController: UIViewController {
private let navC: UINavigationController = {
let c = UINavigationController()
c.tabBarItem = UITabBarItem(title: "2", image: nil, tag: 0)
return c
}()
override var tabBarItem: UITabBarItem! {
get {
return navC.tabBarItem
}
set {
navC.tabBarItem = newValue
}
}
}
I'm sure there will be a few more methods that need forwarding in flow controllers.
- Remember autoresizing masks?
You know, the ones deemed "uncool" after autolayout appeared? The one you know all too well from translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints?
There is still a place for it. Rather than overriding viewDidLayoutSubviews, just use autoresizing masks when adding the subVC:
extension UIViewController {
func add(childController: UIViewController) {
assert(self.isViewLoaded)
addChildViewController(childController)
view.addSubview(childController.view)
childController.view.frame = self.view.bounds
childController.view.autoresizingMask = [.flexibleWidth, .flexibleHeight]
childController.didMove(toParentViewController: self)
}
}
- Prefix extension methods to ObjC objects
As Peter Steinberger pointed out, when we create Swift extensions to an ObjC object, we should still prefix them, as we might run into strange issues. Also I don't like how add(childController:) conflicts with the name of the UIKit method addChildViewController(_:), where the one adds the child view, and the other doesn't. I think we can do better naming this properly. How about this (better ideas welcome)?
extension UIViewController {
@objc(coord_addChildViewControllerAndView:)
func addChildViewControllerAndView(_ childViewController: UIViewController) {
...
}
}
Or just make it unavailable in ObjC, should do the trick too if your app project is not convoluted by too much ObjC cruft:
@nonobjc extension UIViewController {
...
}
- Beware of broken magic
UIKit does a little automagic here and there. The problem with that is that it might break due to small changes and not be immediately possible but introduce hard to find bugs.
For example when I put a Tab1FlowController inbetween UITabBarController and UINavigationController, I broke a little piece of magic: Before doing this, clicking the tabbar item of an already active tab would pop a navigation controller back to its root view. Users are used to this from iOS system apps, and many other apps due to this automagic.
This is how UIKit does it (taken from disassembly of UITabBarController._tabBarItemClicked:):

Naughty naughty...
In this case it is necessary to do it manually:
extension AppFlowController: UITabBarControllerDelegate {
func tabBarController(_ tabBarController: UITabBarController, shouldSelect viewController: UIViewController) -> Bool {
let didSelectCurrentlyActiveTab = viewController == tabBarController.selectedViewController
if didSelectCurrentlyActiveTab, let toRootPoppable = viewController as? ToRootPoppable {
assert(!(viewController is UINavigationController))
toRootPoppable.popToRoot(animated: true)
}
return true
}
}
There might be more issues hidden like this in UIKit.
And a nice way to return the next parent flow controller without having to explicitly set it. I think both the explicit and implicit ways have their perks.
@nonobjc extension UIResponder {
func nextConformingToProtocol<Protocol>() -> Protocol? {
return nextSequence().first { responder in
return responder is Protocol
} as? Protocol
}
func nextSequence() -> AnySequence<UIResponder> {
return AnySequence({ [weak self] () -> AnyIterator<UIResponder> in
var nextResponder: UIResponder? = self
return AnyIterator({
// self is not included in sequence
nextResponder = nextResponder?.next
return nextResponder
})
})
}
}
protocol MyViewControllerFlowDelegate: AnyObject {
func doSomething()
}
class MyViewController: UIViewController {
private var delegate: MyViewControllerFlowDelegate? {
let delegate = nextConformingToProtocol() as MyViewControllerFlowDelegate?
assert(delegate != nil)
return delegate
}
private func someButtonPressed() {
delegate?.doSomething()
}
}
This searches through the responder chain until it finds an object that conforms to the needed protocol. This even works when starting at a UIView.
WARNING: When you call this from a VC that has been presented, it might not work as expected. The responder chain, starting from the presented VC, will contain all VCs up to the presented VC, then as next responder return the root parent VC of the VC that presented (and if that was presented itself, it's next responder will in turn return the root parent VC that presented that VC) and continue normally from there. It's caused due to the strange nature what presentingViewController returns - which contradicts what documentation says. It will not return the same VC that present was called on, but rather its root parent. Consider that when using the responder chain.
If I have main flow like this :
MainFlowController has an embedded tab bar controller. And it has three sub flow controllers, each of them has an embedded navigation controller.
I set the viewControllers of the tab bar controller with sub flow controllers, in MainFlowController class:
self.tabBarController.viewControllers = [feedFlowController, profileFlowController, settingsFlowController]I expect to hide tab bar when feedViewController pushed, but it not works.
extension FeedFlowController: FeedViewControllerDelegate {
func showDetail(_ detail: String) {
let feedDetail = FeedDetailViewController(detail, dependencyContainer: self.dependencyContainer)
feedDetail.hidesBottomBarWhenPushed = true
embeddedNavigationController.pushViewController(feedDetail, animated: true)
}
}So, do I have to give the embedded navigation controller of sub flow controller to the viewControllers of tab bar controller in MainFlowController?If that, I feel confused with the point of view in this blog.
@onmyway133 Can you help me to understand? Or a better way to solve this?
Seems like hidesBottomBarWhenPushed does not work for the tab bar when the UITabBarController is not the direct parent of the UINavigationController: John-Lluch/SWRevealViewController#13 (comment)
@fabb Yes, we have to be careful about the magic hidden in UIViewController when using FlowController as container view controller.
@calvingit I stepped a bit through the disassembly. I think we cannot really fix hidesBottomBarWhenPushed. As far as I found out it works the following way:
pushis called on aUINavigationController- This internally calls
-[UINavigationController _hideOrShowBottomBarIfNeededWithTransition:] - In this method,
hidesBottomBarWhenPushedfrom the pushed VC is read - Then, the
UINavigationControllergets itstabBarControllerand calls_selectedViewControllerInTabBaron it - Then the
UINavigationControllercompares ifselfis equal to that_selectedViewControllerInTabBar, and only if this istrue, the tabbar is hidden.
Unfortunately when we use a flow controller as container around that UINavigationController, the last check is false, and the tabbar will not be hidden.
The only ugly hack I could think of would be to use a custom subclass of UINavigationController, overwrite the tabBarController property and return an NSProxy object there that delegates everything to the real tabBarController, except for calls to _selectedViewControllerInTabBar where we could return self. Could break a lot of other things though.
I like this idea and have been playing around with it. The issue I ran into was with animated transitions between child view controllers. If you transition to a UINavigationController the navigation bar size is wrong at the start and animates to the correct size together with the transition.

addChildViewController(targetFlowController)
transition(from: startingFlowController, to: targetFlowController, duration: 2.5, options: [], animations: {
// empty to showcase the issue more clearly
}) { (completed) in
self.remove(childController: startingFlowController)
}To save some time for everybody else, here are the workarounds I found:
Workaround 1:
Use UIView animations instead of transition(from:to:duration:options:animations:completion:).
add(childController: targetFlowController) // call the extension function instead of `addChildViewController`
UIView.animate(withDuration: 2.5, animations: {
// again empty to showcase that the issue is resovled
}) { (completed) in
self.remove(childController: startingFlowController)
}Caveat: ViewDidAppear is called immediately, at the same time as ViewWillAppear, instead of waiting for the transition animation to finish. This may cause issues if you are starting animations in ViewDidAppear of other view controllers.
Workaround 2:
Remove animations from the navigationBar in the presented navigation controller's viewWillAppear method.
override func viewWillAppear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewWillAppear(animated)
// it is important to wait for a bit as animations have not yet been added
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.navigationBar.layer.removeAllAnimations()
}
}or the slightly more complex way that ensures animations from all sublayers of the navigationBar are removed. I'm not sure if this is necessary.
override func viewWillAppear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewWillAppear(animated)
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.removeSubLayerAnimations(layer: self.navigationBar.layer)
}
}
func removeSubLayerAnimations(layer: CALayer) {
layer.removeAllAnimations()
guard let sublayers = layer.sublayers else { return }
for sublayer in sublayers {
sublayer.removeAllAnimations()
removeSubLayerAnimations(layer: sublayer)
}
}Caveat: this is a hack, we are messing with system animations which could have unforeseen consequences and could stop potentially working after an iOS update.
If anyone has a better way to solve this issue I would like to hear it :)
The „sequence vs. UI“ categorization of VCs reminds me of this React article which differentiates between „Presentational“ and „Container“ components:
https://medium.com/@dan_abramov/smart-and-dumb-components-7ca2f9a7c7d0
I think using the responder chain is a more elegant approach :
https://augmentedcode.io/2018/11/18/navigating-using-flow-controllers-and-responder-chain-on-ios/
Are there any updates on solving the hideBottomBarWhen pushed using FlowControllers?