A tool for saving and visualising IPython parallel cluster usage.
For a one time dump, given an IPython client or view, simply call ipy_client_usage.dump:
import ipy_client_usage
with open('cluster_dump.json', 'w') as fh:
ipy_client_usage.dump(fh, ipy_client)
Instead of keying dump infomation by uuid, it is possible to preserve human readable names with the uuid_to_name keyword. A full IPython parallel job might look like:
import ipy_client_usage
from IPython.parallel import Client
import time
view = Client().load_balanced_view()
tasks = [('a', 1), ('c', 3), ('d', 5), ('e', 2), ('f', 5), ('g', 2),
('h', 4), ('i', 2)]
names, lengths = zip(*tasks)
result = view.map_async(time.sleep, lengths)
# Map the UUID (from the result), to the name that we care about.
uuid_to_name = dict(zip(result.msg_ids, names))
view.wait()
with open('cluster_dump.json', 'w') as fh:
ipy_client_usage.dump(fh, view, uuid_to_name)
From the command line, ipy_client_usage.view can be invoked:
python -m ipy_client_usage.view --help
usage: view.py [-h] dump_file
View an IPython client dump.
positional arguments:
dump_file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
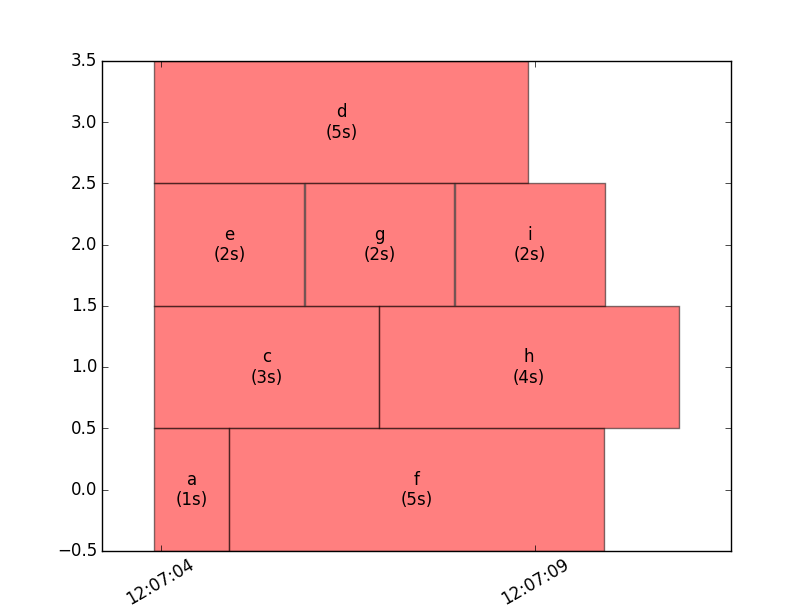
Passing the filename of the dump file will result in a matplotlib figure displaying usage:
python -m ipy_client_usage.view cluster_dump.json
It is often interesting to watch the cluster working in real time. ipy_client_usage.wait_and_dump is a
drop-in replacement for client.wait which repeatedly updates the dump file with the latest information.
In the earlier example:
view.wait()
with open('cluster_dump.json', 'w') as fh:
ipy_client_usage.dump(fh, view, uuid_to_name)
Could be replaced with:
ipy_client_usage.wait_and_dump('cluster_dump.json', view, uuid_to_name)
This can be watched with:
python -m ipy_client_usage.watch cluster_dump.json