Use this library to declare move, assign and submap instructions which, when executed, transform an input javascript object into an output javascript object.
Optional parameters and transform functions make these instructions flexible enough to handle most data mapping requirements.
npm install js-object-mappercd js-object-mapper
node docs/sample.jsYou should see:
================== mapper ===================
var Mapper = require('../src/mapper');
var mapper = new Mapper('sampleMap')
.move('Title', 'subject') // move value from property 'subject' to property 'Title'
.assign('Version', 1) // assign 1 to property 'Version'
.submap('Names', 'list', {}, new Mapper() // map property 'list' to property 'Names' using submap
.move('LastName','surname', {}, function(v){return v.toUpperCase();}) // transform using function
)
.log('Title')
;
module.exports = mapper;
================== input ===================
{ subject: 'Duty Roster',
list: [ { surname: 'Smith' }, { surname: 'Jones' } ] }
================== output ===================
{ Title: 'Duty Roster',
Version: 1,
Names: [ { LastName: 'SMITH' }, { LastName: 'JONES' } ] }npm test
npm run cov // writes code coverage to .coverageConstruct a named mapper using the Mapper constructor and configure with a cascade of move, assign and submap instructions.
var Mapper = require('mapper');
var mapper = new Mapper('myMapper')
.move(..)
.assign(..)
.submap(..)
;Detailed description of the instructions can be found in the Instruction reference below.
var context = {config:config, data:data}; // for example
var output = mapper.execute(input, context);When mapper is executed instructions are carried out in the order in which they are defined.
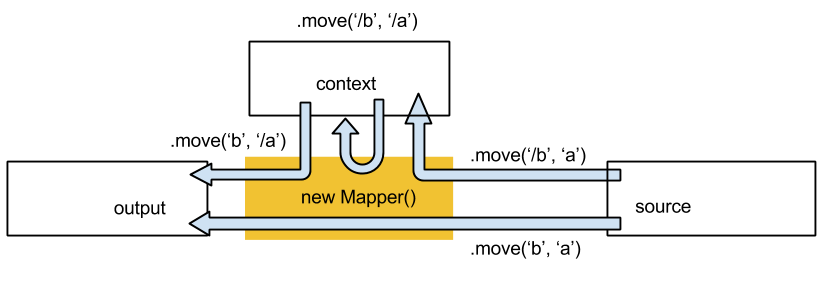
Execution context may be used to pass external variables into and out of the mapper (e.g configuration parameters or reference data). It may also be used to store intermediate results during mapper execution. (e.g a currency code may be defined at the highest level in the input but embedded within several sub-maps in the output. We can move it from source into the context in the top level map, and move it from the context to the output in an embedded sub-map.)
Context is indicated by a leading / in the field label of a move instruction, as the following diagram illustrates:
Instructions take up to four parameters:
- to specifies the property in the output object for the instruction to update.
* Can be a property name e.g.
'lastName'* or a dot-separated list of nested property names e.g.'name.last'* A'/'prefix is used to indicate that the target is a property of the execution context rather than the output. * Mandatory. - from specifies the properties in the input object used by the instruction.
* Can be property name e.g.
'lastName'* or a dot-separated list of nested property names e.g.'name.last'* or a JSONPath expression e.g.'$..last'*' 'indicates the entire input object. * Multiple inputs may be specified in an array e.g.['last','first']* or an object e.g.{last:'last', first:'first'}* A'/'prefix is used to indicate that the source is a property of the execution context rather than the input object. * Optional. If not specified then it is assumed to be the same as 'to'. - options - an object with properties (e.g. condition, filter, default) which modify the instruction's behaviour.
- Varies by instruction (see below)
- Optional.
- transform - function or mapper instance used to transform ''from' value to 'to' value'. * Varies by function (see below) * Optional.
sets target property from values of source properties.
options
- condition
function(v,i,c){return boolean}- v is input value, i is index of containing iterated submap, c is execution context
- returns true or false to indicate whether on not the move takes place
- multiple
- false (default) - set target value
- true - push value to target array
- default - set target to this value if otherwise unset
transform
function(v,i,c){return output;}- v is value of source property (or array or object of values)
- i is index of enclosing iterated submap (or undefined if not iterated)
- c is execution context
- target property set to output (unless transform returns undefined)
Sets target property from static value.
options
- condition
function(v,i,c){return boolean}- v is input value, i is index of containing iterated submap, c is execution context
- returns true or false to indicate whether on not the move takes place
transform
function(v,i,c){return output;}- v is value of source property (or array or object of values)
- i is index of enclosing iterated submap (or undefined if not iterated)
- c is execution context
- target property set to output (unless transform returns undefined)
A submap is an instance of Mapper which is applied to the value of the source object property to generate a value to push or set to target object property.
If the source object is an array then, by default, sub-map will be applied to each element of the array, generating an output array.
If the source object is not an array then, by default, sub-map generates an output object.
options
- filter
function(v,i,c){return boolean}- v is value of current element, i is index of current element, c is execution context
- returns true to apply submit to this element, false to skip.
- condition
function(v,i,c){return boolean}- v is full input value, i is index of containing iterated submap, c is execution context
- returns true or false to indicate whether on not the submap is executed
- multiple
- false (default) - set target value
- true - push value to target array
- default - set target to this value if otherwise unset
transform
new Mapper()
The log instruction takes the to parameter only, and displays debug information about the value of the output or context property specified. For example:
DEBUG=js-object-mapper node sample.jsOutput will include:
js-object-mapper ==============start mapping log: sampleMap Title=============== +0ms
js-object-mapper 'Duty Roster' +0ms
js-object-mapper ================end mapping log: Title=============== +0msThis can be particularly useful for examining intermediate results.
To safely get nested property values from the input or context use the Mapper.get function. Takes a dot separated string and returns data or undefined.
- Complicated mappings can always be implemented in raw javascript, however it is often more readable/maintainable to split the mapping into a number of intermediate stages, storing results in the execution context
- For example some output formats use variable property names (dependant on data). To handle this with a mapper you can firstly map to an equivalent form with static property names in the context, then use a javascript function (in a move instruction) to convert to the final form.
- It is a common requirement to take multiple arrays from the source and merge them together in some way. Sometimes the arrays match one for one and can be merged element by element, in other cases data from one array is looked up to enhance the elements of another. Arrays with a similar structure can also be merged by concatenation.
- No specific instructions are included in js-object-mapper for merging arrays, but most requirements can be met by iterating over a single array with a submap, using the index parameter passed to contained transform functions to fetch data from elsewhere. Concatenation will occur automatically if two different arrays are submapped to the same target.
movecopies values by reference.This does not usually cause a problem, but beware of making updates to properties in the execution context which are referenced by more than one target.- Be careful when using an array in the execution context; this is the main source of hard-to-find mapping bugs. Arrays are not reset automatically so be sure to reset as necessary during submap iterations. Use
.assign(‘/array’, null)( not.assign(‘/array’, []))
For good unit test coverage, transform, condition and filter functions should be referenced and tested individually. This can be done with to and paramTo properties of the map as in the following snippet:
var mapper = new Mapper()
.submap('A', 'a', {}, new Mapper()
.move( 'B',
'b',
{condition: function(v,i,c){ return v > 0;}},
function(v,i,c){return Math.sqrt(v);}
)
)
;
var transform = mapper.to.A.to.B;
var condition = mapper.to.A.paramTo.B.condition;If a mapper instance is exported from a node module ( using module.exports = new Mapper()....) the tools/unitTestGenerator can be used to generate a mocha test skeleton for unit testing the map. For example:
node tools/unitTestGenerator.js ./docs/sampleMap.jswill write a sample unit map test skeleton for sampleMap to stdout:
/* global describe, it, before, after */
/* jslint node: true */
'use strict';
var should = require('should');
var sampleMap = require('./docs/sampleMap.js');
var context = {}; // TODO
describe('sampleMap', function(){
describe('Title', function(){
it('should .....', function(){ // TODO
var input = {}; // TODO
var output = {}; // TODO
sampleMap.to.Title(input, 0, context).should.eql(output);
});
});
describe('Version', function(){
it('should .....', function(){ // TODO
var input = {}; // TODO
var output = {}; // TODO
sampleMap.to.Version(input, 0, context).should.eql(output);
});
});
describe('Names', function(){
describe('LastName', function(){
it('should .....', function(){ // TODO
var input = {}; // TODO
var output = {}; // TODO
sampleMap.to.Names.to.LastName(input, 0, context).should.eql(output);
});
});
});
});Unit tests are good for test coverage of embedded javascript functions but don't test map output for given input. To create a map test execute the map with the environment variable MAPPER_TEST_GEN set to true.
MAPPER_TEST_GEN=true node docs/sample.jsexecutes the sampleMap mapper, causing sampleMap.spec.js to be written to the test directory:
/* global describe, it, before, after */
/* jslint node: true */
'use strict';
var should = require('should');
var sampleMap = require('../docs/sampleMap.js');
var context = {} ;
describe("Test for mapper sampleMap", function () {
var input = { subject: 'Duty Roster',
list: [ { surname: 'Smith' }, { surname: 'Jones' } ] };
it("Test for mapper sampleMap", function () {
var output = sampleMap.execute(input, Object.create(context));
output.should.eql({ Title: 'Duty Roster',
Version: 1,
Names: [ { LastName: 'SMITH' }, { LastName: 'JONES' } ] });
});
});To run this test:
npm test