Sleep Prediction
Create example screen on/off dataset
The following code generates some example screen on/off data for ndays=10 days of follow up, with average time to bed at 1:00AM (mu_s=1) with std. dev. sd_s=1 hour. Average time to wake up is 8:30AM (mu_w=8.5) with std. dev. sd_w=0.5. Time between screen on events is generated according to an exponential distribution with rate lambda_s=0.3 when the person is asleep and rate lambda_w=2 when the person is awake. Smaller rates imply longer waiting times between phone use, as we might expect when a person is asleep. The anchor_t parameter should represent an hour of the day that is unlikely to occur during sleep. In this example anchor_t=14 corresponds to 2:00PM. The starting hour on the first day when data is first collected is init_t=15 (3:00PM).
The generated data is stored in the outmat matrix. This matrix has three columns, column 1 is the starting time (in hours) of the screen off interval, column 2 is the ending time (in hours) of the screen off interval, with column 3 corresponding to the day of follow-up. Note that starting times (Column 1) are on the interval [anchor_t,anchor_t+24] rather than [0,24]. To see the screen off intervals (outmat_mod) in time-date format where d0 is the variable representing the first day of followup, see the outmat_orig matrix. The Mod2Orig() and Orig2Mod() functions convert back and forth between these two data formats (the formats represented by outmat_mod and outmat_orig).
ndays=10
lambda_s = 1.5
lambda_w = 5
mu_s = 1
mu_w = 8.5
sd_s = .5
sd_w = .25
init_t = 15
anchor_t=14
d0="3/2/2019" ## d0 is the first day of follow-up. If you have your own data, set d0 equal to the date of first data.
#2pm = origin
A2B_ts = function(xx,anchor_hr=14){
if(length(xx)>1){
for(i in 1:length(xx)){
if(xx[i]<=anchor_hr){
xx[i]=(24-anchor_hr)+xx[i]
}else{
xx[i]=xx[i]-anchor_hr
}
}
return(xx)
}else{
if(xx<=anchor_hr){
return(24-anchor_hr+xx)
}else{
return(xx-anchor_hr)
}
}
}
## generate time to bed/wake for each day
t_s = rnorm(ndays,mu_s,sd_s)
t_w = rnorm(ndays,mu_w,sd_w)
## generate waiting times
curt = init_t
curday=1
outmat_mod=c()
while(TRUE){
if(curt>init_t+24){
curt = curt-24
curday=curday+1
if(curday>ndays){
break
}
}
if(A2B_ts(curt)<A2B_ts(t_s[curday])){
tnex = curt+rexp(1,lambda_w)
if(A2B_ts(tnex)>=A2B_ts(t_s[curday])){
tnex = curt+A2B_ts(t_s[curday])-A2B_ts(curt)+rexp(1,lambda_s)
}
outmat_mod=rbind(outmat_mod,c(curt,tnex,curday))
}else if(A2B_ts(curt)<A2B_ts(t_w[curday])){
tnex = curt+rexp(1,lambda_s)
if(A2B_ts(tnex)>=A2B_ts(t_w[curday])){
tnex = curt+A2B_ts(t_w[curday])-A2B_ts(curt)+rexp(1,lambda_w)
}
outmat_mod=rbind(outmat_mod,c(curt,tnex,curday))
}else{
tnex = curt+rexp(1,lambda_w)
outmat_mod=rbind(outmat_mod,c(curt,tnex,curday))
}
curt=tnex
}
Mod2Orig = function(tmat,d0,format="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S",tz="EST"){
tmat_out = matrix(NA,nrow=nrow(tmat),ncol=2)
t0=as.POSIXct(paste(d0,"00:00:00",sep=" "),tz=tz,format)
for(i in 1:nrow(tmat)){
tmat_out[i,1]=strftime(as.POSIXct(as.numeric(t0)+60*60*(tmat[i,1]+24*tmat[i,3]),tz=tz,origin="1970-01-01"),tz="EST",format)
tmat_out[i,2]=strftime(as.POSIXct(as.numeric(t0)+60*60*(tmat[i,2]+24*tmat[i,3]),tz=tz,origin="1970-01-01"),tz="EST",format)
}
return(data.frame(t0=tmat_out[,1],t1=tmat_out[,2],stringsAsFactors=F))
}
Orig2Mod = function(tmat,anchor_hr,format="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S",tz="EST"){
tmat_out = matrix(NA,nrow=nrow(tmat),ncol=3)
for(i in 1:nrow(tmat)){
anchor_cur=anchor_hr*60*60+as.numeric(as.POSIXct(strftime(as.POSIXct(tmat[i,1],tz=tz,format=format,origin="1970-01-01"),tz=tz,format="%m/%d/%Y"),tz=tz,format="%m/%d/%Y"))
if(as.numeric(as.POSIXct(tmat[i,1],tz=tz,format=format,origin="1970-01-01"))<anchor_cur){
anchor_cur=anchor_hr*60*60+as.numeric(as.POSIXct(strftime(as.POSIXct(as.numeric(as.POSIXct(tmat[i,1],tz=tz,format=format,origin="1970-01-01"))-24*60*60,tz=tz,origin="1970-01-01"),tz=tz,format="%m/%d/%Y"),tz=tz,format="%m/%d/%Y"))
}
if(i==1){anchor0=anchor_cur}
tmat_out[i,1]=anchor_hr+(as.numeric(as.POSIXct(tmat[i,1],tz=tz,format=format,origin="1970-01-01"))-anchor_cur)/(60*60)
tmat_out[i,2]=anchor_hr+(as.numeric(as.POSIXct(tmat[i,2],tz=tz,format=format,origin="1970-01-01"))-anchor_cur)/(60*60)
tmat_out[i,3]=round((anchor_cur-anchor0)/(24*60*60))+1
}
return(tmat_out)
}
outmat_orig=Mod2Orig(outmat_mod,d0,format="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S") #d0 tells Mod2Orig when the first day of follow-up is.
compare_to_outmat_mod=Orig2Mod(outmat_orig,anchor_hr=anchor_t)
head(outmat_orig)## t0 t1
## 1 03/03/2019 15:00:00 03/03/2019 15:02:10
## 2 03/03/2019 15:02:10 03/03/2019 15:16:43
## 3 03/03/2019 15:16:43 03/03/2019 15:28:40
## 4 03/03/2019 15:28:40 03/03/2019 15:32:49
## 5 03/03/2019 15:32:49 03/03/2019 15:44:52
## 6 03/03/2019 15:44:52 03/03/2019 16:15:06
head(outmat_mod)## [,1] [,2] [,3]
## [1,] 15.00000 15.03625 1
## [2,] 15.03625 15.27870 1
## [3,] 15.27870 15.47803 1
## [4,] 15.47803 15.54704 1
## [5,] 15.54704 15.74790 1
## [6,] 15.74790 16.25183 1
head(compare_to_outmat_mod)## [,1] [,2] [,3]
## [1,] 15.00000 15.03611 1
## [2,] 15.03611 15.27861 1
## [3,] 15.27861 15.47778 1
## [4,] 15.47778 15.54694 1
## [5,] 15.54694 15.74778 1
## [6,] 15.74778 16.25167 1
To see what the resulting data looks like:
hist(outmat_mod[,1] %% 24,breaks=24,xlim=c(0,24),xlab="Hour of day",main="Frequency of screen on events")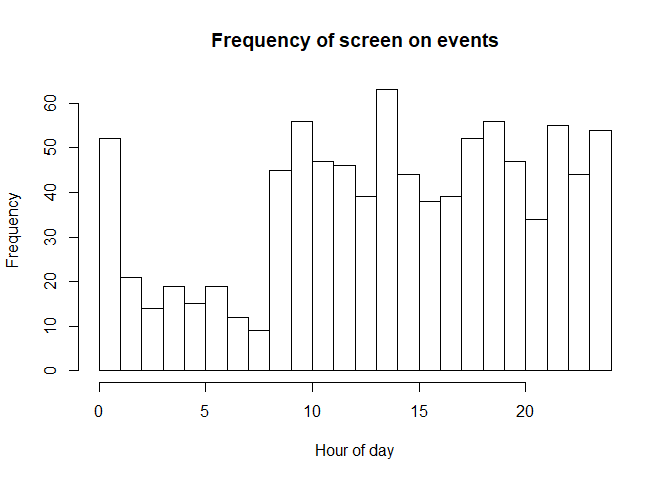 Notice how there are fewer screen on events During the nighttime hours, as expected.
Notice how there are fewer screen on events During the nighttime hours, as expected.
Gaussian quadrature for bivariate integration
The time to bed x_s and time to wake x_w is unknown for each night of follow-up. In this approach, we treat (x_s,x_w) as a bivariate normal random variable with mean (mu_s,mu_w) with cor(x_s,x_w)=rho and marginal variances (sigma_s2,sigma_w2). To calculate the marginal likelihood we integrate over the conditional likelihood with respect to (x_s,x_w) for each night in follow up. Because this is a Gaussian integral it can be done efficiently using Guassian quadrature, more specifically Gauss-Hermite quadrature. The code for this is here:
## perform quadrature of multivariate normal
## compute Gauss-Hermite quadrature points and weights
## for a one-dimensional integral.
## points -- number of points
## interlim -- maximum number of Newton-Raphson iterations
library(mvtnorm)
hermite <- function (points, z) {
p1 <- 1/pi^0.4
p2 <- 0
for (j in 1:points) {
p3 <- p2
p2 <- p1
p1 <- z * sqrt(2/j) * p2 - sqrt((j - 1)/j) * p3
}
pp <- sqrt(2 * points) * p2
c(p1, pp)
}
gauss.hermite <- function (points, iterlim = 50) {
x <- w <- rep(0, points)
m <- (points + 1)/2
for (i in 1:m) {
z <- if (i == 1)
sqrt(2 * points + 1) - 2 * (2 * points + 1)^(-1/6)
else if (i == 2)
z - sqrt(points)/z
else if (i == 3 || i == 4)
1.9 * z - 0.9 * x[i - 2]
else 2 * z - x[i - 2]
for (j in 1:iterlim) {
z1 <- z
p <- hermite(points, z)
z <- z1 - p[1]/p[2]
if (abs(z - z1) <= 1e-15)
break
}
if (j == iterlim)
warning("iteration limit exceeded")
x[points + 1 - i] <- -(x[i] <- z)
w[i] <- w[points + 1 - i] <- 2/p[2]^2
}
r <- cbind(x * sqrt(2), w/sum(w))
colnames(r) <- c("Points", "Weights")
r
}
## compute multivariate Gaussian quadrature points
## n - number of points each dimension before pruning
## mu - mean vector
## sigma - covariance matrix
## prune - NULL - no pruning; [0-1] - fraction to prune
mgauss.hermite <- function(n, mu, sigma, prune=NULL) {
if(!all(dim(sigma) == length(mu)))
stop("mu and sigma have nonconformable dimensions")
dm <- length(mu)
gh <- gauss.hermite(n)
#idx grows exponentially in n and dm
idx <- as.matrix(expand.grid(rep(list(1:n),dm)))
pts <- matrix(gh[idx,1],nrow(idx),dm)
wts <- apply(matrix(gh[idx,2],nrow(idx),dm), 1, prod)
## prune
if(!is.null(prune)) {
qwt <- quantile(wts, probs=prune)
pts <- pts[wts > qwt,]
wts <- wts[wts > qwt]
}
## rotate, scale, translate points
eig <- eigen(sigma)
rot <- eig$vectors %*% diag(sqrt(eig$values))
pts <- t(rot %*% t(pts) + mu)
return(list(points=pts, weights=wts))
}Estimating model parameters
Next, we write the likelihood function and use Hermite-Gauss quadrature to perform numerical integration over the unknown bedtimes and wake-up times (x_s and x_w). We do a grid search over some of the parameter space (rho, sigma_s, and sigma_w) to pick an initial value for the numerical optimization of the likelihood, but we make smarter data-based guesses as initial values for the remaing parameters (mu_s, mu_w, lambda_s, and lambda_w).
IndLik = function(t_init,wt,xs,xw,lambda_s,lambda_w){
if(t_init< xs){
numer = lambda_w*exp(-lambda_w*wt)
denom = 1-exp(-lambda_w*(xs-t_init))+exp(-lambda_s*(xs-t_init))-exp(-lambda_s*(xw-t_init))+exp(-lambda_w*(xw-t_init))
}else if(t_init < xw){
numer = lambda_s*exp(-lambda_s*wt)
denom = 1-exp(-lambda_s*(xw-t_init))+exp(-lambda_w*(xw-t_init))
}else{
numer = lambda_w*exp(-lambda_w*wt)
denom = 1
}
return(numer/denom)
}
JointLik = function(mat,mu_s,mu_w,sigma_s,sigma_w,rho,lambda_s,lambda_w,x_s,x_w,INCL_DENSITY=FALSE){
if(x_s>x_w){return(0)}
if(!is.null(nrow(mat)) && nrow(mat)>0){
t1=1
for(i in 1:nrow(mat)){
t1=t1*IndLik(mat[i,1],mat[i,2]-mat[i,1],x_s,x_w,lambda_s,lambda_w)
}
}else{
t1=1
}
if(INCL_DENSITY){
t2=dmvnorm(c(x_s,x_w),mean = c(mu_s,mu_w), sigma= matrix(c(sigma_s^2,rho*sigma_s*sigma_w,rho*sigma_s*sigma_w,sigma_w^2),nrow=2,byrow=T))
}else{
t2=1
}
return(t1*t2)
}
MargLik = function(mat,mu_s,mu_w,sigma_s,sigma_w,rho,lambda_s,lambda_w){
if( mu_s> mu_w || sigma_s<0 || sigma_w<0 || abs(rho)>1 || lambda_s<0 || lambda_w <0 || lambda_s > lambda_w){return(0)}
if(is.null(nrow(mat)) || nrow(mat)==0){return(1)}
Sigma=matrix(c(sigma_s^2,rho*sigma_s*sigma_w,rho*sigma_s*sigma_w,sigma_w^2),nrow=2,byrow=T)
ghout=mgauss.hermite(10,c(mu_s,mu_w),Sigma)
return(sum(ghout$weights*unlist(lapply(1:nrow(ghout$points),function(xx) JointLik(mat,mu_s,mu_w,sigma_s,sigma_w,rho,lambda_s,lambda_w,ghout$points[xx,1],ghout$points[xx,2])))))
}
InitialParameters = function(mat_mod,anchor_t){
itrvl_len_v = seq(6,9,.5)
out_ls=list()
ratio_v = rep(NA,length(itrvl_len_v))
# find mu_s0, mu_w0
for(j in 1:length(itrvl_len_v)){
itrvl_len=itrvl_len_v[j]
start_vals=seq(0,24-itrvl_len,.25)
frac_vals = rep(NA,length(start_vals))
for(i in 1:length(start_vals)){
frac_vals[i]=length(intersect(which(mat_mod[,1]>anchor_t+start_vals[i]),which(mat_mod[,1]<anchor_t+start_vals[i]+itrvl_len)))/nrow(mat_mod)
}
mu_s0=start_vals[order(frac_vals)[1]]+anchor_t
mu_w0=mu_s0+itrvl_len
# find rate during average sleep and average waking interval
ndays= length(unique(mat_mod[,3]))
lambda_s0=(min(frac_vals)*nrow(mat_mod)/ndays)/itrvl_len
lambda_w0=((1-min(frac_vals))*nrow(mat_mod)/ndays)/(24-itrvl_len)
out_ls[[j]]=list(mu_s0,mu_w0,lambda_s0,lambda_w0)
ratio_v[j]=lambda_s0/lambda_w0
}
return(unlist(out_ls[[order(ratio_v)[1]]]))
}
GridSearchInitPars = function(mat_mod,anchor_t,labels,ls_ids,mu_s0,mu_w0,lambda_s0,lambda_w0){
sd_s_v = c(.25,.5,1)
sd_w_v = c(.25,.5,1)
rho_v= c(0,.25,.5,.75)
g=function(par_v){
liktot=0
for(i in 1:length(labels)){
mat=mat_mod[ls_ids[[i]],1:2]
liktot=liktot-log(MargLik(mat,par_v[1],par_v[2],par_v[3],par_v[4],par_v[5],par_v[6],par_v[7]))
}
return(liktot)
}
minval=Inf
for(sd_s in sd_s_v){
for(sd_w in sd_w_v){
for(rho in rho_v){
par_v=c(mu_s0,mu_w0,sd_s,sd_w,rho,lambda_s0,lambda_w0)
curval=g(par_v)
if(curval<minval){
cur_par=par_v
minval=curval
}
}
}
}
return(par_v)
}
FindParamMLEs = function(dat,anchor_t,maxiter=20,init_par=NULL,tol=.0001){
labels=unique(dat[,3])
ls_ids = list()
for(i in 1:length(labels)){
ls_ids[[i]]=which(dat[,3]==i)
}
if(is.null(init_par)){
cat("Identifying good initial model parameters...\n")
init_pars4=InitialParameters(dat,anchor_t)
mu_s0=init_pars4[1]
mu_w0=init_pars4[2]
lambda_s0=init_pars4[3]
lambda_w0=init_pars4[4]
init_par = GridSearchInitPars(dat,anchor_t,labels,ls_ids,mu_s0,mu_w0,lambda_s0,lambda_w0)
}
cur_par=init_par
prev_par=cur_par
cat("Numerical optimization (using optim) until convergence (maxiter=",maxiter,"):\n")
for(i in 1:maxiter){
g1=function(par_v){
liktot=0
for(i in 1:length(labels)){
mat=dat[ls_ids[[i]],1:2]
liktot=liktot-log(MargLik(mat,par_v[1],par_v[2],cur_par[3],cur_par[4],cur_par[5],par_v[3],par_v[4]))
}
return(liktot)
}
optim.out1=optim(par=cur_par[c(1,2,6,7)],g1,control=list(maxit=1000))
cur_par[c(1,2,6,7)]=optim.out1$par
g2=function(par_v){
liktot=0
for(i in 1:length(labels)){
mat=dat[ls_ids[[i]],1:2]
liktot=liktot-log(MargLik(mat,cur_par[1],cur_par[2],par_v[1],par_v[2],par_v[3],cur_par[6],cur_par[7]))
}
return(liktot)
}
optim.out2=optim(par=cur_par[c(3,4,5)],g2,control=list(maxit=1000))
cur_par[c(3,4,5)]=optim.out2$par
cat("Iter ",i,": mu_s =",cur_par[1],"; mu_w =",cur_par[2],"; sd_s =",cur_par[3],"; sd_w =",cur_par[4],"; rho =",cur_par[5],"; lambda_s =",cur_par[6],"; lambda_w =",cur_par[7],"\n")
if(sum((prev_par-cur_par)^2)<tol){
break
}else{
prev_par=cur_par
}
}
return(cur_par)
}
mle.out=FindParamMLEs(outmat_mod,anchor_t)## Identifying good initial model parameters...
## Numerical optimization (using optim) until convergence (maxiter= 20 ):
## Iter 1 : mu_s = 25.19385 ; mu_w = 32.14444 ; sd_s = 1.092032 ; sd_w = 0.9572812 ; rho = 0.7782903 ; lambda_s = 1.751777 ; lambda_w = 4.77403
## Iter 2 : mu_s = 25.19036 ; mu_w = 32.11145 ; sd_s = 1.092591 ; sd_w = 0.9572735 ; rho = 0.7775206 ; lambda_s = 1.731941 ; lambda_w = 4.756752
## Iter 3 : mu_s = 25.19036 ; mu_w = 32.11145 ; sd_s = 1.092593 ; sd_w = 0.9573155 ; rho = 0.777545 ; lambda_s = 1.731947 ; lambda_w = 4.756758
The maximum likelihood estimates and the interpretations of the model parameters are:
sleep_t_h=floor(mle.out[1]%%24)
sleep_t_m=floor((mle.out[1]%%24-floor(mle.out[1]%%24))*60)
if(sleep_t_m<10){
sleep_t=paste(sleep_t_h,":0",sleep_t_m,sep="")
}else{
sleep_t=paste(sleep_t_h,":",sleep_t_m,sep="")
}
wake_t_h=floor(mle.out[2]%%24)
wake_t_m=floor((mle.out[2]%%24-floor(mle.out[2]%%24))*60)
if(wake_t_m<10){
wake_t=paste(wake_t_h,":0",wake_t_m,sep="")
}else{
wake_t=paste(wake_t_h,":",wake_t_m,sep="")
}
cat(paste(" Avg. time to sleep = ",sleep_t," (+/- ",round(mle.out[3],1)," hour)\n",sep="")
,(paste("Avg. time to wake = ",wake_t," (+/- ",round(mle.out[4],1)," hour)\n",sep=""))
,(paste("Correlation between time to sleep and time to wake = ",round(mle.out[5],2),"\n",sep=""))
,(paste("Rate (per hour) of frequency of phone use while asleep = ", round(mle.out[6],5),"\n",sep=""))
,(paste("Rate (per hour) of frequency of phone use while awake = ", round(mle.out[7],5),"\n",sep="")))## Avg. time to sleep = 1:11 (+/- 1.1 hour)
## Avg. time to wake = 8:06 (+/- 1 hour)
## Correlation between time to sleep and time to wake = 0.78
## Rate (per hour) of frequency of phone use while asleep = 1.73195
## Rate (per hour) of frequency of phone use while awake = 4.75676
Estimating bed times and wake up times for each day
Now that the model parameters have been estimated, we can maximize the joint density function of a) the bed times (x_s), b) the wake-up times (x_w), and c) the screen on/off data, with respect to the x_s and x_w. These will be our bed time and wake-up time estimates for each individual night. The rationale for maximizing the joint likelihood is that the distribution of the x_s and x_w will pull estimates towards mu_s and mu_w, respectively, while the distribution of the screen on/off data will pull bedtime and wake-up estimates towards the data fit. This way if there is very little data, then bedtime and wake-up estimates will be close to mu_s and mu_w, while more data will allow us to trust the data more and estimates will reflect that. This balance is ideal for situations where sparse data may be present.
The R function to find these estimates are here:
GetIndSleepEstimates =function(mat_mod,mle.out){
labels=unique(mat_mod[,3])
ls_ids = list()
for(i in 1:length(labels)){
ls_ids[[i]]=which(mat_mod[,3]==i)
}
xmat = matrix(NA,nrow=length(labels),ncol=3)
for(i in 1:length(labels)){
mat=mat_mod[ls_ids[[i]],1:2]
g3=function(par_v){
return(-log(JointLik(mat,mle.out[1],mle.out[2],mle.out[3],mle.out[4],mle.out[5],mle.out[6],mle.out[7],par_v[1],par_v[2],INCL_DENSITY=TRUE)))
}
optim.out3=optim(par=mle.out[1:2],g3,control=list(maxit=1000))
xmat[i,]=c(optim.out3$par,labels[i])
}
return(xmat)
}Let's run this function on our simulated data (outmat_mod) using the parameter MLEs (mle.out) we just estimated as input.
xest=GetIndSleepEstimates(outmat_mod,mle.out)xest contains each day's estimated bedtimes and wake-up times. Let's convert back to the original time scale using the Mod2Orig() function we defined before.
xest_orig=Mod2Orig(xest,d0,format="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S")
names(xest_orig)=c("bedtime","wake-up time")
xest_orig## bedtime wake-up time
## 1 03/04/2019 01:49:58 03/04/2019 08:27:47
## 2 03/05/2019 00:50:51 03/05/2019 07:48:57
## 3 03/06/2019 01:54:51 03/06/2019 08:19:00
## 4 03/07/2019 00:55:23 03/07/2019 08:21:11
## 5 03/08/2019 02:13:17 03/08/2019 08:40:13
## 6 03/09/2019 01:07:53 03/09/2019 08:01:17
## 7 03/10/2019 00:48:15 03/10/2019 07:18:14
## 8 03/11/2019 02:04:52 03/11/2019 08:53:14
## 9 03/12/2019 01:14:14 03/12/2019 08:02:56
## 10 03/13/2019 00:50:47 03/13/2019 07:35:17