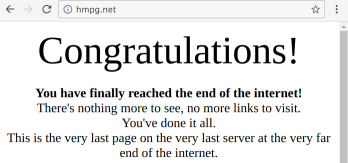
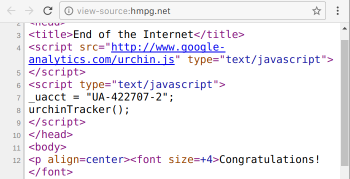
This module provides a grunt multi-task for taking "snapshots" of the HTML markup on web pages - of their immediate DOM content - and saving them to HTML files. It can be used to obtain content of web pages, which are built dynamically by JavaScript, and check it for validity and accessibility. It uses webdriverio to control the selected web browser.
In addition, recent versions can save "screenshots" of browser viewport at the same time to support visual testing by comparing the look of the page with the baseline picture. Actually, this task is quickly evolving to offer end-to-end test capabilities too.
See the migration documentation about compatibility of older versions with the latest v6.
Recent versions of this documentation show how to use WebDrivers directly fror controlling the web browser (grunt-chromedriver, grunt-geckodriver and grunt-safaridriver). It needs neither Java not [Selenum] installed. See the version 6.0.1 or older for examples how to use the full Selenium.
Additional Grunt tasks, which are usually used to support test automation:
- grunt-accessibility - checks accessibility of HTML markup according to the WCAG standard
- grunt-accessibility-html-report-converter - converts JSON report of
grunt-accessibilityto HTML - grunt-contrib-connect - starts a static web server to server testing pages for the web browser
- grunt-html - validates HTML markup according to the W3C HTML standard
- grunt-html-html-report-converter - converts JSON report of
grunt-htmlto HTML - grunt-reg-viz - compares images and generates report with differences
- grunt-chromedriver - runs a standalone chromedriver - no need for Selenium
- grunt-geckodriver - runs a standalone geckodriver - no need for Selenium
- grunt-safaridriver - runs a standalone safaridriver - no need for Selenium
- @prantlf/grunt-selenium-standalone - runs a standalone Selenium server
You need node >= 10, npm and grunt >= 1.0.0 installed and your project build managed by a Gruntfile with the necessary modules listed in package.json. If you have not used Grunt before, be sure to check out the [Getting Started] guide, as it explains how to create a Gruntfile as well as install and use Grunt plugins. Once you are familiar with that process, you may install this plugin with this command:
$ npm install grunt-html-dom-snapshot --save-devAdd the html-dom-snapshot entry with the task configuration to the options of the grunt.initConfig method:
grunt.initConfig({
'html-dom-snapshot': {
'google': {
url: 'https://www.google.com'
}
}
});Default options support the most usual usage scenario:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
options: {
webdriver: {
logLevel: 'warn',
capabilities: {
browserName: 'chrome',
'goog:chromeOptions': {
args: ['--headless']
}
}
},
viewport: {
width: 1024,
height: 768
},
selectorTimeout: 10000,
instructionDelay: 0,
doctype: '<!DOCTYPE html>',
snapshots: 'snapshots',
screenshots: null,
fileNumbering: false,
fileNumberDigits: 3,
fileNumberSeparator: '.',
hangOnError: false,
snapshotOnError: '_last-error',
singleElementSelections: false,
force: false
},
'google': {
url: 'https://www.google.com'
}
}Make sure, that you have the stable version of Chrome installed, if you leave the defaults intact.
Type: Object
Default value: see above
Chooses the web browser to take snapshots with, and other parameters supported by WebdriverIO as input for the webdriverio.remote method. This object has to contain the property capabilities with browserName and optionally other properties depending on the web browser driver. The following browser names are the most usually used: chrome, firefox, safari. Depending on what browser you specify, you will need to load the corresponding WebDdriver. These are the tasks to load the drivers:
chromedriver: {
default: { port: 4445 }
},
geckodriver: {
default: { port: 4446 }
},
safaridriver: {
default: { port: 4447 }
},The other often used property is logLevel, set to "warn" by default. Valid values are "trace", "debug", "info", "warn", "error" and "silent".
Type: Object
Default value: {width: 1024, height: 768}
Resizes the web browser viewport to the specified width and height values (in pixels) before taking snapshots.
Type: Number
Default value: 10000
Maximum waiting time (in milliseconds), until a DOM node with the selector specified by the wait property appears or disappears. Taking the snapshot fails, if this time is exceeded.
Type: Number
Default value: 0
Waiting time after executing an instruction. If the test is not run in the headless browser, but debugged in the browser window, it is sometimes helpful to watch outcome of every operation. If introducing waiting instructions all over is too cumbersome, this configuration will add the delay (in milliseconds) after every instruction automatically.
Type: String
Default value: ''
Sets the HTML doctype to be written to the file with the snapshot. WebdriverIO API does not support getting its value. HTML validators require the doctype and to make the integration with other tasks easier it can be written to the snapshot file using this option.
Type: String
Default value: 'snapshots'
Destination directory to write the page snapshots to. It will be created if it does not exist. If set to null, snapshots will not be saved. It can be used to have only screenshots saved.
Type: String
Default value: null
Destination directory to write the viewport screenshots to. It will be created if it does not exist. Default value is null, which means, that no screenshots will be written out.
Type: Booolean|String
Default value: false
If set to true, enables prefixing names of snapshot and screenshot files with their index number, for example: "002.google-input.html". Every occurrence of the file instruction increases the file count.
If set to "per-directory", the index number will be increased separately per sub-directory with snapshots. If the value of the file instruction contains a slash, it will put the snapshot to a sub-directory, which may be useful to organize many snapshots created by multiple tasks.
Type: Number
Default value: 3
Ensures, that file numbers will have always at least the specified count of digits. If the number is smaller, than its power of 10, the number will be padded by zeros (0) from the left.
Type: String
Default value: '.'
The character to put between the file number and the file name.
Type: Boolean
Default value: false
If set to true, it will not abort the process in case of a failure. It is useful, if you want to investigate the situation on the screen right after an error occurred. If you encounter an error flip this flag and re-run the failing scenario. Once you are finished terminate the process or interrupt it by Ctrl+C.
Type: String
Default value: '_last-error'
If set to a non-empty string, if will be used as a file name for an automatically taken snapshot and screenshot (if those are enabled), if the task execution fails.
Type: Boolean
Default value: false
If set to true, it will enforce every selector match either one or none elements. If any selector matches multiple elements, the instruction will fail. Tests usually address just one element. This setting helps to uncover errors like checking isFocus for multiple elements, which has unpredictable results.
This option can be set for the whole task or within a single command object.
Type: Boolean
Default value: false
If set to true, it suppresses failures, which happened during taking snapshots. Instead of making the Grunt fail, the errors will be written only to the console.
This option can be set for the whole task or within a single command object.
File names for snapshots can be used as sub-task names. Separate sub-tasks initialize separate instance of the webdriver:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
'google': {
url: 'https://google.com'
},
'github': {
url: 'https://github.com'
}
}If the sub-task contains a property commands, this property is supposed to point to an array of command objects - navigations and other browser interactions, waiting for browser states and making snapshots. They share the same instance of the webdriver, which improves the performance:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
all: {
commands: [
{
url: 'https://google.com',
file: 'google'
},
{
url: 'https://github.com',
file: 'github'
}
]
}
}If the sub-task contains a property scenarios, this property is supposed to point to a JavaScript module path or to an array of JavaScript module paths, which would export the array of commands. Relative paths will be resolved to the current (process) directory. It allows to keep the Gruntfile legible and supply the test instructions from other files:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
all: {
scenarios: 'scenarios/*.js'
}
}You can use sub-tasks, commands and scenarios to structure your code and execute the tests separately, or all of them in one browser window.
One of the instructions has to be present in every command, otherwise its execution will fail. If you include a key in your command object, which is not recognised as an instruction or other known key (file, options), the execution will fail too. The following instructions are recognised (and their effect is executed) in the order, in which they are listed below:
- if-then-else
- while-do
- do-until
- repeat-do
- setViewport
- url
- go
- scroll
- focus
- clearValue
- setValue
- addValue
- selectOptionByIndex
- selectOptionByValue
- moveCursor
- click
- clickIfVisible
- keys
- elementSendKeys
- wait
- isExisting
- isVisible
- isVisibleWithinViewport
- isEnabled
- isSelected
- isFocused
- isNotExisting
- isNotVisible
- isNotVisibleWithinViewport
- isNotEnabled
- isNotSelected
- isNotFocused
- hasAttribute
- hasClass
- hasValue
- hasText
- hasInnerHtml
- hasOuterHtml
- break
- abort
- file
Type: Object (optional)
Options specific for the one particular command. They will be merged with the task options to specialize taking of the particular snapshot:
{
options: {
viewport: {
width: 1600,
height: 900
}
},
url: 'https://google.com',
file: 'google'
}The following array of commands within the commands property will change location, make a snapshot immediately to save the server-side pre-rendered content, then another one to see the progress after the first 500 milliseconds and yet another one, once the search form is ready. Then it submits the form by clicking on the "Search" button, waits until the search results are displayed and makes one final snapshot.
{
url: 'https://localhost/app'
file: 'initial.html'
},
{
wait: 500,
file: 'after-500ms'
},
{
wait: '#search',
file: 'form-ready'
},
{
wait: function (browser) {
return browser.$('#search')
.then(element => {
element.click();
return element;
})
.then(element => element.waitForExist({ timeout: 1000 }));
},
file: 'results-shown'
}The last command can be written in a declarative way too:
{
options: {
selectorTimeout: 1000
},
click: '#search',
wait: '#results',
file: 'results-shown'
}Other Grunt tasks can run later and validate, compare or otherwise process the page content in different stages of the "Search" scenario.
Navigating to other location, interacting with the page, waiting for some effect to show and saving a snapshot can be divided to different objects in the commands array. However, at least One of the file, url ans wait parameters has to be present in ever object.
When the commands become too many, you can divide them per page or per other criterion, which corresponds with a scenario and load them from separate modules:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
addressbook: require('./test/scenarios/addressbook'),
calendar: require('./test/scenarios/calendar'),
inbox: require('./test/scenarios/inbox'),
tasks: require('./test/scenarios/tasks')
}The module for the address book implementation would look like this:
module.exports = {
options: {...}, // optional task-specific options
commands: [
{
url: 'https://localhost/addressbook'
wait: '#addressbook.complete'
},
...
]
}The same tests will be run in a single browser window, if the Gruntfile contains just a single sub-task and the tests are specified by scenario files:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
all: {
scenarios: 'test/scenarios/*.js'
}
}The directory "test/scenarios" would contain files "addressbook.js", "calendar.js", "inbox.js" and "tasks.js", which would specify only the array of commands; not the entire sub-task objects. For example, the address book implementation:
module.exports = {
{
options: {...}, // optional command-specific options
url: 'https://localhost/addressbook'
wait: '#addressbook.complete'
},
...
]Load the plugin in Gruntfile.js:
grunt.loadNpmTasks('grunt-html-dom-snapshot');Call the html-dom-snapshot task:
$ grunt html-dom-snapshotor integrate it to your build sequence in Gruntfile.js:
grunt.registerTask('default', ['html-dom-snapshot', ...]);When webdriverio is called, it needs to connect to a WebDriver or to the Selenium server. The easiest way, how to get it running, is using grunt-chromedriver, grunt-geckodriver, grunt-safaridriver, or @prantlf/grunt-selenium-standalone Grunt tasks, which download, start and stop the browser. If the usage scenario is to validate static files or a mocked web application, a local web server like grunt-contrib-connect is usually added. And additional checking tasks like grunt-html pr grunt-accessibility. The complete Grunt initialisation could look like this:
grunt.initConfig({
connect: { // Serves static files in the current directory.
server: {
options: {port: 8881}
}
},
clean: { // Cleans the previously taken snapshots.
snapshots: ['snapshots/*']
},
'html-dom-snapshot': { // Takes new snapshots.
all: {
...
}
},
htmllint: { // Checks if the HTML markup is valid.
all: {
src: ['snapshots/*.html']
}
},
accessibility: { // Checks if the page complies to the WCAG AA standard.
all: {
src: ['snapshots/*.html']
}
},
chromedriver: { // Launches the Chrome executable
default: {}
}
});
grunt.loadNpmTasks('grunt-accessibility');
grunt.loadNpmTasks('grunt-chromedriver');
grunt.loadNpmTasks('grunt-contrib-clean');
grunt.loadNpmTasks('grunt-contrib-connect');
grunt.loadNpmTasks('grunt-html');
grunt.loadNpmTasks('grunt-html-dom-snapshot');
grunt.registerTask('default', [
'chromedriver:default:start',
'connect', 'clean', 'html-dom-snapshot',
'chromedriver:default:stop',
'htmllint', 'accessibility']);The installation of the necessary Grunt tasks:
npm install grunt-html-dom-snapshot grunt-chromedriver \
grunt-contrib-clean grunt-contrib-connect \
grunt-accessibility grunt-html --save-devChrome, Chromium and Firefox support a headless mode. It simplifies automated testing, because you need no graphic subsystem like X.Org installed.
The default configuration of this task will choose Chrome in the headless mode:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
options: {
webdriver: {
capabilities: {
browserName: 'chrome',
'goog:chromeOptions': { args: ['--headless'] }
}
}
}
},
chromedriver: {
default: {}
}If you want to run Chrome in the windowed mode, override the chromeOptions object with yours, even an empty one, which is missing the --headless argument, for example:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
options: {
webdriver: {
capabilities: {
browserName: 'chrome',
'goog:chromeOptions': {}
}
}
}
},
chromedriver: {
default: {}
}If you want to run Chrome in Travis CI, override the goog:chromeOptions object with yours and disable the sandbox with --no-sandbox:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
options: {
webdriver: {
capabilities: {
browserName: 'chrome',
'goog:chromeOptions': { args: ['--headless', '--no-sandbox'] }
}
}
}
},
chromedriver: {
default: {}
}The following configuration will choose Firefox in the headless mode:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
options: {
webdriver: {
capabilities: {
browserName: 'firefox',
'moz:firefoxOptions': { args: ['-headless'] }
}
}
}
},
geckodriver: {
default: {}
}The following configuration will choose Safari in the windowed mode:
'html-dom-snapshot': {
options: {
webdriver: {
capabilities: { browserName: 'safari' }
}
}
},
safaridriver: {
default: {}
}In lieu of a formal styleguide, take care to maintain the existing coding style. Add unit tests for any new or changed functionality. Lint and test your code using Grunt.
- 2020-04-25 v6.0.0 Upgrade to WebDriverIO 6
- 2019-09-21 v5.1.0 Reorder checking instructions, enforce single-element matching
- 2019-09-21 v4.0.0 Upgrade to WebDriverIO 5, add the instruction "elementSendKeys"
- 2019-07-21 v3.0.0 Report unrecognised instructions as errors, introduce new instructions (focus, while-do, do-until, repeat-do, break)
- 2019-07-08 v2.2.0 Optionally hang the browser in case of failure to be able to inspect the web page in developer tools
- 2018-11-26 v2.0.0 Use headless Chrome instead of PhantomJS by default, introduce conditional if-then-else instructions
- 2018-05-14 v1.3.0 Allow saving snapshots to sub-directories, file numbering per-directory, add
scrollinstruction - 2018-05-11 v1.2.0 Introduce delay after every instruction to be able to visually follow the actions when debugging
- 2018-03-29 v1.1.0 Allow specifying all initialization parameters supported by WebdriverIO
- 2018-03-28 v1.0.2 Stop Selenium and Chromedriver processes on unexpected Grunt process abortion
- 2018-03-28 v1.0.1 Workaround for hanging chromedriver after finishing the task
- 2018-03-11 v1.0.0 Require Node.js >= 6
- 2018-03-11 v0.8.0 Add a new instruction - "abort"
- 2018-03-01 v0.7.0 Add optional automatic file numbering
- 2018-02-28 v0.6.0 Add the allRequired option to the hasClass instruction
- 2018-02-26 v0.5.0 Allow checking and setting various properties
- 2018-02-22 v0.4.0 Allow sending key strokes to the browser
- 2018-01-30 v0.3.0 Allow specifying test commands in separate modules
- 2018-01-27 v0.2.0 Allow saving screenshots in addition to snapshots
- 2017-11-18 v0.1.0 Allow separate navigation, page interaction and saving snapshots
- 2017-11-12 v0.0.1 Initial release
Copyright (c) 2017-2020 Ferdinand Prantl
Licensed under the MIT license.