ultraheatmap facilitates the production of deepTools heatmaps. The heatmaps typically show signal at genomic regions, which can be appended by orthogonal data, like associated gene expression. ultraheatmap facilitates adding orthogonal data to a deepTools matrix and allows to cluster a genomic heatmap by selected samples in just one single command-line call.
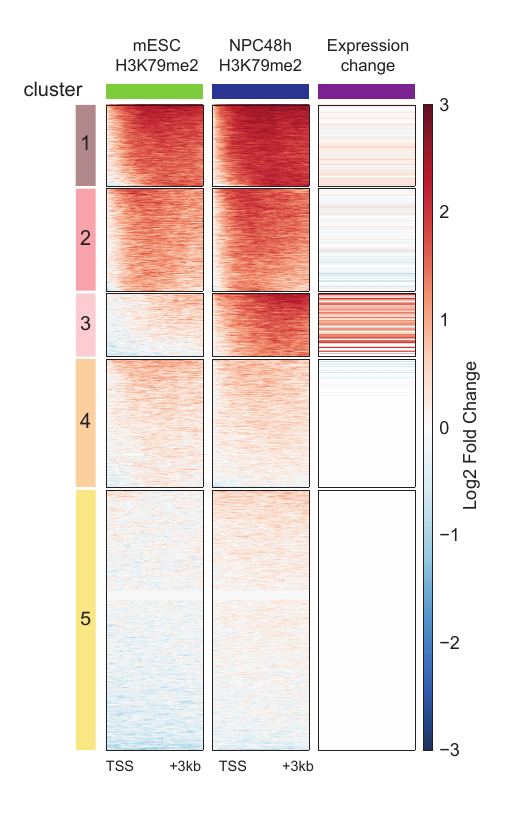
This figure has been generated by the ultraheatmap on real data. The first two columns show the ChIPs signal while the last column shows the gene expression of the closest gene to each region of any cluster.
These instructions will get you a copy of ultraheatmap up and running on your local machine.
The Prerequisites can be found in requirements.yaml
First, get the source code:
$ git clone https://github.com/maxplanck-ie/ultraheatmap.git
Afterwards, create a new conda environment with all the Prerequisites by running the following command line:
$ conda env create -f requirements.yaml
Then activate the environment:
$ conda activate ultraheatmap
To install the program in this environment:
$ python setup.py install
from the ultraheatmap directory.
Alternatively, pip or conda can be used to install the package. We highly
recommend you to create a new conda environment prior to the installation and
install it after activating this environment. This can be done as follows:
$ conda create -n ultraheatmap python=3.6
$ conda activate ultraheatmap
$ conda install -c bioconda -c conda-forge ultraheatmap
Now, you already have the program installed and can access each of the modules by calling them. Try
$ ultraheatmap -h ,
$ computeOrderedMatrix -h
or
$ addFeatureToMatrix -h
$ conda deactivate
$ computeOrderedMatrix -h
usage: computeOrderedMatrix [-h] -S BIGWIGS [BIGWIGS ...] -R REGIONOFINTEREST
[REGIONOFINTEREST ...] -o MATRIXOUTPUT
[-g REFINDICES [REFINDICES ...]]
[-p NUMBEROFPROCESSORS [NUMBEROFPROCESSORS ...]]
[--outFileSortedRegions OUTFILESORTEDREGIONS]
[--outputReferenceMatrix OUTPUTREFERENCEMATRIX]
[--kmeans INT] [--hclust INT]
[-b BEFOREREGIONSTARTLENGTH [BEFOREREGIONSTARTLENGTH ...]]
[-a AFTERREGIONSTARTLENGTH [AFTERREGIONSTARTLENGTH ...]]
[-op PLOTOUTPUT] [--config USERCONFIG]
The program sorts/clusters regions considering the reference samples ( given
by --groupUsingSamples) and makes a matrix over all the samples using the
sorted/clustered regions.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
required arguments:
-S BIGWIGS [BIGWIGS ...], --scoreFileName BIGWIGS [BIGWIGS ...]
bigwig files, the ordered matrix is computedfrom.
(default: None)
-R REGIONOFINTEREST [REGIONOFINTEREST ...],
--regionsFileName REGIONOFINTEREST [REGIONOFINTEREST ...]
BED files definig the genomic regions of the
matrix.Multiple files can be provided, but the per
group information will be lost due to the clustering
(default: None)
-o MATRIXOUTPUT, --outFileName MATRIXOUTPUT
Matrix clustered by the given reference samples
(default: None)
optional arguments:
-g REFINDICES [REFINDICES ...],
--groupUsingSamples REFINDICES [REFINDICES ...]
sample indices (order of the bigwig files given via -S).
It is 1-based and is used to define the reference samples.
The reference samples will be used for sorting/clustering the
regions (given bed files), before all samples will be used to
generate the output matrix. Several indices can be added while
separated by space from each other. Default is None and will
take all the samples into account to sort/cluster the regions.
(default: None)
-p NUMBEROFPROCESSORS [NUMBEROFPROCESSORS ...],
--numberOfProcessors NUMBEROFPROCESSORS [NUMBEROFPROCESSORS ...]
From deepTools doc: Number of processors to use. Type
"max/2" to use half the maximum number of processors
or "max" to use all available processors. (default:
[1, 1])
--outFileSortedRegions OUTFILESORTEDREGIONS
From deepTools doc: File name in which the regions are
saved after skiping zeros or min/max threshold values.
The order of the regions in the file follows the
sorting order selected. This is useful, for example,
to generate other heatmaps keeping the sorting of the
first heatmap. (default: None)
--outputReferenceMatrix OUTPUTREFERENCEMATRIX
Matrix on the reference sampels only before clustering
(default: None)
--kmeans INT number of clusters in k-means clustering (default: None)
--hclust INT number of clusters to compute using
hierarchicalclustering as defined by deepTools
plotHeatmap (default: None)
-b BEFOREREGIONSTARTLENGTH [BEFOREREGIONSTARTLENGTH ...],
--upstream BEFOREREGIONSTARTLENGTH [BEFOREREGIONSTARTLENGTH ...],
--beforeRegionStartLength BEFOREREGIONSTARTLENGTH [BEFOREREGIONSTARTLENGTH ...]
From deepTools doc: Distance upstream of the start
site of the regions defined in the region file. If the
regions are genes, this would be the distance upstream
of the transcription start site. (default: [0, 0])
-a AFTERREGIONSTARTLENGTH [AFTERREGIONSTARTLENGTH ...],
--downstream AFTERREGIONSTARTLENGTH [AFTERREGIONSTARTLENGTH ...],
--afterRegionStartLength AFTERREGIONSTARTLENGTH [AFTERREGIONSTARTLENGTH ...]
From deepTools doc: Distance downstream of the end
site of the given regions. If the regions are genes,
this would be the distance downstream of the
transcription end site. (default: [0, 0])
-op PLOTOUTPUT, --plotOutput PLOTOUTPUT
File name to save the intermediate heatmap. The file
ending will be used to determine the format of the
image . Available formats are: "png", "eps", "pdf" and
"svg" (From deeptools doc) (default: None)
--config USERCONFIG Added to the default configuration, overwrites if
example
$ computeOrderedMatrix -S signal1.bw signal2.bw -R regions.bed \
-o final_matrix.gz -p 20 -a 100 -b 100 --outputReferenceMatrix intermediate_matrix.gz \
-op intermediate_matrix_heatmap.png -g 1 --kmeans 2
the above command line produces a deeptools matrix on both given .bw files while
the regions are the clusters obtained from the given .bed file after using kmeans
clustering algorithm with 2 clusters (--kmeans 2) based on the signal of first bigwig file (-g 1).
$ addFeatureToMatrix -h
usage: addFeatureToMatrix [-h] --matrix STR --output STR
--feature.tables TABLES [TABLES ...]
[--annotationFeature ANNOTATIONFEATURE]
[--filteredGenomeGtfOutputFile ANNOTATIONOUTPUT]
[--genomeGtf STR]
[--featureNames FEATURES [FEATURES ...]]
[--featureIdColumn IDCOLUMN]
[--referencePoint REFERENCEPOINT]
[--closestGenesOutput CLOSESTGENESOUTPUT]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
required arguments:
--matrix STR, -m STR deeptools matrix (default: None)
--output STR, -o STR output matrix (default: None)
--feature.tables TABLES [TABLES ...], -t TABLES [TABLES ...]
gene id tables or name based tables, tables should be
space-separated. (default: None)
optional arguments:
--annotationFeature ANNOTATIONFEATURE, -F ANNOTATIONFEATURE
annotation file can be filtered by a feature such as
gene, exon or transcript (default: None)
--filteredGenomeGtfOutputFile ANNOTATIONOUTPUT, -oa ANNOTATIONOUTPUT
saving filtered annotation file if --annotationFeature
(default: None)
--genomeGtf STR, -g STR
genome annotation (gtf) to map peaks to closest gene.
Will be filtered through '--annotationFeature'
(default: None)
--featureNames FEATURES [FEATURES ...], -f FEATURES [FEATURES ...]
A list of features of interest from gene id tables or
name based tables (default: ['log2(FC)'])
--featureIdColumn IDCOLUMN
name of the column includes ids/names (default:
GeneID)
--referencePoint REFERENCEPOINT
If closest TSS or TES is needed, otherwise closest
gene body will be found (default: None)
--closestGenesOutput CLOSESTGENESOUTPUT, -og CLOSESTGENESOUTPUT
A bed file to save the closest genes (default: None)
example
$ addFeatureToMatrix -m deeptools_matrix.gz -o appended_matrix.gz \
-t feature_table.tsv -g annotaion.gtf -f column_of_interest_header \
--featureIdColumn id_col_header
The above command adds extra columns to the input matrix. The output will be a matrix with
deeptools format which can be visualized by deeptools plotHeatmap. The extra columns could be gene expression. If annotation file is provided, program finds the closest gene for each region of the input matrix and looks for the gene expression of that gene from the given feature tables.
If no annotation file is given, program checks for the exact match between regions name from the input matrix and finds the same name on the given feature tables. The above image presents a matrix which has been generated by this module after mapping genes to peaks on real data.