Stacks and queues are two commonly used data structures. You can read about them below or watch this video. If you watch the video, note that all the operations mentioned take O(1) time. What does that mean? No matter how big your stack or queue gets (that's n), the operations in the video, and the operations we'll focus on below, take the same amount of time. The time needed DOES NOT depend on the number of things in the stack, so it's constant, O(1) time.
##Stacks
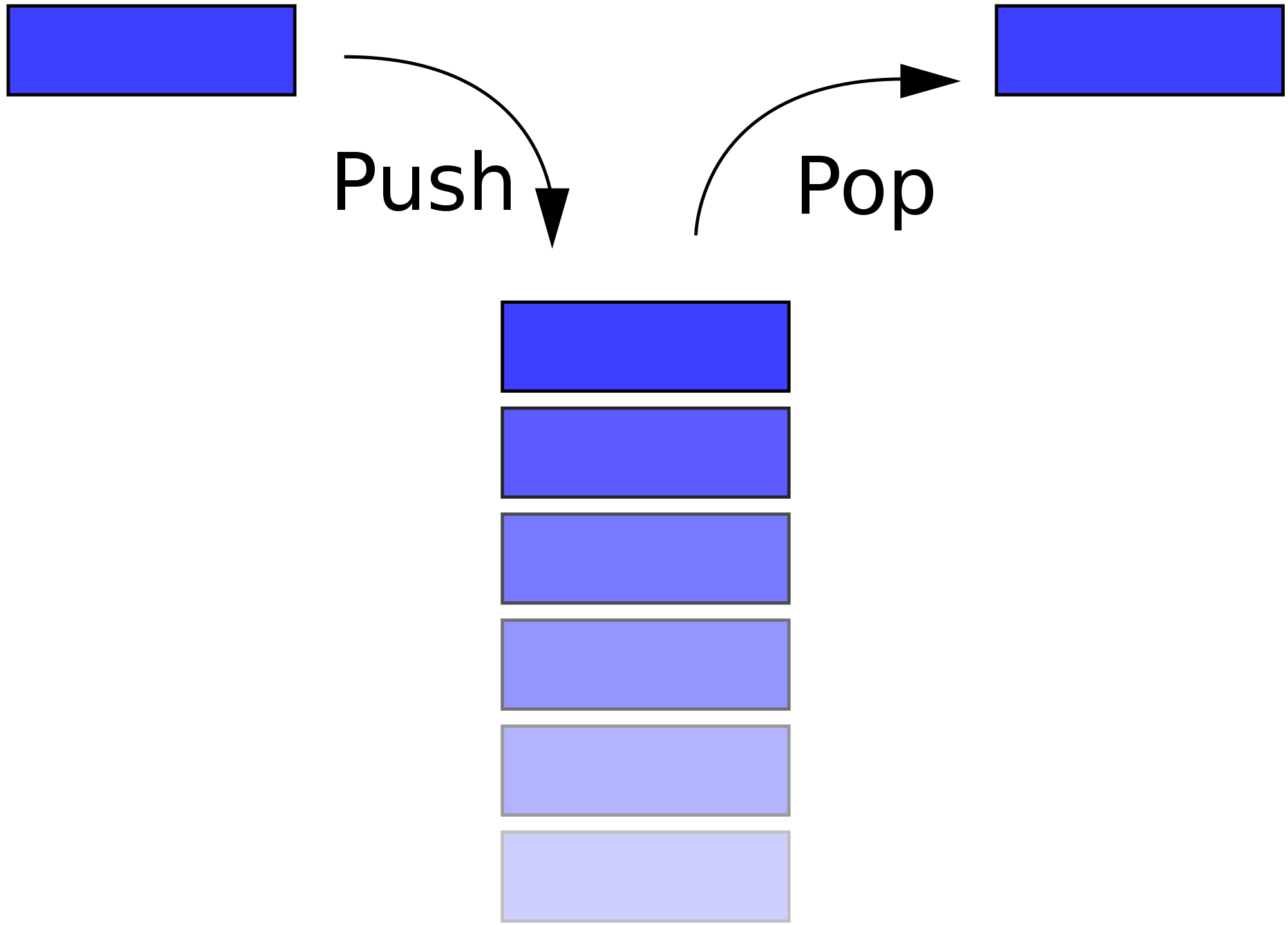
Stacks as a data structure are a lot like stacks as a physical structure. Think of stacks of dishes or books. We can remove an item from the top of the stack (by poping), or add an item to the top of the stack (by pushing it). While we may be able to carefully pull from within stacks of real world objects, the data structure only allows us to manipulate the top item of the stack. These main operations for a stack - push and pop - are both O(1) constant time. Some stack implementations also allow us to peek at the value of the top item without actually poping it off of the stack.
Stacks are "Last In, First Out" -- the last item pushed on top of a stack will be the first thing popped off of the stack.
Don't pop from Jimmy's stack of pancakes.
- Draw a stack after each of the following operations:
- PUSH 0
- POP
- PUSH 2
- PUSH 4
- PUSH 6
- POP
- PUSH 8
click for answer
```
* start []
* PUSH 0 [0]
* POP []
* PUSH 2 [2]
* PUSH 4 [2, 4]
* PUSH 6 [2, 4, 6]
* POP [2, 4]
* PUSH 8 [2, 4, 8]
```
- Stacks are often implemented with arrays, given the built-in methods we have access to in JavaScript and Ruby. So, let's think of arrays. Where would you put the "top" of the stack? How would you add something to the top the stack? How would you take something off?
super stuck? click for an answer...
> The "top" could be the end of the array, and you could use array methods `push` and `pop`. Thanks, high level programming languages!##Queues
Queues as a data structure are a lot like queues as a physical structure. This makes more sense with British English, where queue means "a line" or "to line up". Think of an orderly line of people waiting to do something. We can remove an item from the front of the queue when its turn comes (by dequeueing), or add an item to the back of the queue when it joins the line (by enqueueing it). Again, while we may be able to "cut" in line in the real world, the queue data structure only allows us to add to the end of the stack or remove from the beginning. The enqueue and dequeue operations for a queue are both O(1) - constant time. Like with stacks, some implementations of queues also allow us to peek at the value of the first item without dequeueing it.
Queues are "First In, First Out" -- the first item enqueued will be the first to move all the way through the line and get dequeued.
- Draw a queue after each of the following operations:
- ENQUEUE 0
- DEQUEUE
- ENQUEUE 2
- ENQUEUE 4
- ENQUEUE 6
- DEQUEUE
- ENQUEUE 8
click for answer...
``` * start [] * ENQUEUE 0 [0] * DEQUEUE [] * ENQUEUE 2 [2] * ENQUEUE 4 [2, 4] * ENQUEUE 6 [2, 4, 6] * DEQUEUE [4, 6] * ENQUEUE 8 [4, 6, 8] ```- How would you implement a queue with an array? Where would you decide the front of the queue would be? How would you
enqueuesomething to the end of the queue? How would youdequeuesomething from the front of the queue?
super stuck? click for an answer...
> The "front" could be the beginning of the array. To enqueue, you'd use JavaScript or Ruby's handy `push` array method. To dequeue, you could use JavaScript or Ruby's `shift` method, which removes and returns the first element from an array.Would you use a stack or a queue to...
-
... let users create playlists and play back the songs?
-
... allow a user to undo changes to a document, one by one?
-
... display only the 10 most recent messages a user posted, in the order they were posted?
Many processors and programming languages rely on something called the "call stack," especially for recursion. The call stack keeps track of function calls that are in the process of executing and where each function should "return" to. When a function is called, it's pushed onto the call stack. When the function returns, it's poped off of the stack. Actual call stacks are a little more complex, but you can think of the call stack as just storing function calls.
Here's a recursive factorial function:
function factorial(num){
if (num > 1){
return num * factorial(num-1);
} else if (num === 1 || num === 0){
return 1;
} else {
console.log("can't do factorial of this number!");
return undefined;
}
}
factorial(3);
// => 6Draw the full call stack for factorial(3) at each step in the function's execution.
click for an answer...
* [factorial(3)]
* [factorial(3), factorial(2)]
* [factorial(3), factorial(2), factorial(1)]
* [factorial(3), factorial(2)]
* [factorial(3)]
* []
Queues are often used to create "buffers" that temporarily store data from one part of a program until another part of a program can process the data. This is common with asynchronous data transfer and with mismatches between how often data is sent and how often it can be processed.
We'll think of a scenario where restaurant diners order food faster than the chefs can cook it.
-
Describe how you would use a queue help the chef keep track of meals to make.
-
What should the chef do when the queue is empty?
-
How would you distribute orders if there are 3 chefs?