[TOC]
- Region-Hierarchical is a baseline deep learning method for image paragraph captioning task.
- Image paragraph captioning aims to generate a diverse and coherent paragraph to describe the given image. It is much more challenge than classic image captioning.
- This implementation is not the official one.
- python 3.7
- pytorch 1.3.1
- torchvision 0.4.2
- tensorboard 2.0.1
- h5py
- tqdm
- spacy (We use it to pre-process original data)
- Prefetch version of DataLoader: IgorSusmelj/pytorch-styleguide#5
-
Download Stanford Paragraph Dataset Here
- paragraph annotation file:
paragraphs_v1.json - dataset splitting file:
train_split.json/test_split.json/val_split.json
- paragraph annotation file:
-
Download images by
urlinparagraphs_v1.json. Here is an example.{ "url": "https://cs.stanford.edu/people/rak248/VG_100K_2/2388350.jpg", "image_id": 2388350, "paragraph": "On a white plastic cutting board is a bunch of chopped vegetables. On one side are chopped mushrooms they are a white color. On the other side are some bright green chopped broccoli. In the middle are bright orange chopped carrots." } -
Create a new folder
./data/stanfordParagraphto store all unprocessed original datadata └──stanfordParagraph ├── images └── paragraphs
There are two widely adopted image encoders for paragraph captioning: DenseCap and BottomUp. They are responsible for detecting region of interests and encode them into dense vectors.
- For DenseCap features we refer you to jcjohnson/densecap,for more detailed instructions please follow chenxinpeng/im2p.
- For BottomUp features we refer you to peteanderson80/bottom-up-attention,also recommend to follow airsplay/lxmert who provides a docker solution.
For convenience, we share the extracted features and its correspond bounding boxes at OneDrive:
- DenseCap features are wrapped in
densecap.zipim2p_xxx_output.h5contains bounding box feature and coordinates.imgs_xxx_path.txtare the mappings between images and.h5file.
- BottomUP features have two versions:
bu.zip: 10 to 100 features per image (adaptive)bu36.zip:36 features per image (fixed)- We adopt the
scripts/make_bu_data.pyprovided by ruotianluo/ ImageCaptioning.pytorch to transformtsvintonpy. Specifically, change theinfilesat line 27 will work fine.
All pre-process functions are provided in preprocess.py. Note that the annotations in Stanford Paragraph Dataset are not as clean as the ones in MSCOCO. Please follow the orders below to generate processed files (See preprocess.py for more details):
- Create a new folder
cleanedunder./data - Create preprocessed paragraph file
- Create mappings
- Create vocab file
- Encode paragraphs
- Map densecap features
Also for convenience, we share the generated files except step 6 at OneDrive.
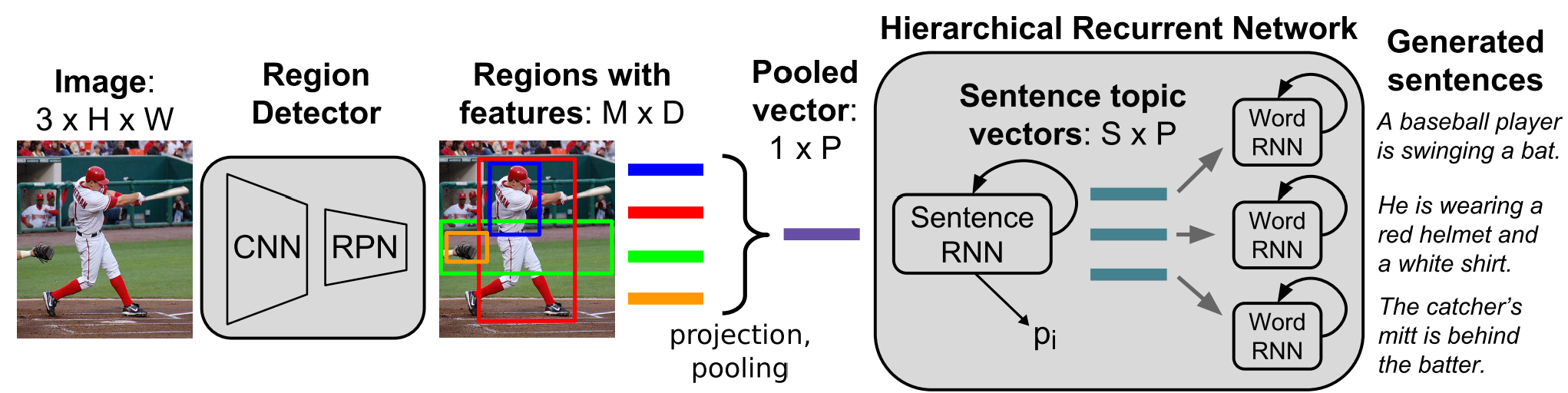
A Hierarchical Approach for Generating Descriptive Image Paragraphs
The model contains three parts:
-
A region detector (we have done this by pre-extracting features)
-
An encoder to project and pooling regional features:
./model/encoder.py. -
A hierarchical decoder with a Sentence-level RNN and a Word-level RNN:
./model/decoder.py
Difference between our implementation and the original paper:
We observe gradient vanishing problem during training the hierarchical RNN, we introduced the following techniques to mitigate it:
- Use Highway Network to replace simple
MLP + ReLU. - Adopt Merge strategy in Word-level RNN suggested in this paper.
Steps:
mkdir model_paramspython train.py
Note that
- Change settings by
set_args()and global variables. - Suppose the
MODEL_NAME = 'debug'.model_params ├── debug.pth.tar └── debug └── config.json - If you adopt BottomUp features, please manually switch
CaptionDatasetto the correspond one in the./utils/data_loader.py.
-
We wrap all inference code in
./captioner.py. -
There are three decoding strategies: greedy decoding, greedy with trigram repetition penalty, beam search.
- Trigram repetition penalty is copied from lukemelas/image-paragraph-captioning
- Beam search is based on sgrvinod/a-PyTorch-Tutorial-to-Image-Captioning
-
We utilize Illuminati91/pycocoevalcap to evaluate the model. It is a python 3.x version of the widely used coco-eval. Corresponding code is organized in folder
./pycocoevalcapand./utils/coco.py. -
To obtain COCO format ground truth file, we adopt the script
./utils/prepro_captions.pyfrom lukemelas/image-paragraph-captioning. And put files into folder./data/coco_gt. -
To evaluate a trained paragraph model
python evaluate.py --model_name debug --model_check_point debug.pth.tar -
Generated paragraphs will be store in a coco format json file under the folder
./model_params/debug.
Here we report a baseline we trained from scratch on DenseCap features with our implementation.
input_size 4096
output_size 1024
f_max 50
feat_size 1024
emb_size 512
srnn_hidden_size 1024
srnn_num_layers 1
wrnn_hidden_size 512
wrnn_num_layers 2
emb_dropout 0.5
fc_dropout 0.5
s_min 3
s_max 6
w_min 2
w_max 33
visual_features_path ./data/cleaned/densecap_image_features_f_max_50_f_size_4096.h5
encoded_paragraphs_path ./data/cleaned/encoded_paragraphs_s_3_6_w_2_33.h5
mapping_file_path ./data/cleaned/mappings.pkl
word2idx_path ./data/cleaned/word2idx_s_min_3_w_min_2.pkl
vocab_size 6730
sent_weight 5.0
word_weight 1.0
lr 0.0005
batch_size 16
is_grad_clip True
grad_clip 5.0
modified_after_epochs 5
modified_lr_ratio 0.8
- On test set,
[6 sents]denotes we force the model to generate 6 sentences.
| decode | Bleu-1 | Bleu-2 | Bleu-3 | Bleu-4 | METEOR | CIDEr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Paper | 41.90 | 24.11 | 14.23 | 8.69 | 15.95 | 13.52 | |
| Ours | greedy | 36.78 | 20.65 | 11.67 | 6.50 | 14.28 | 15.00 |
| greedy + RP | 37.15 | 21.02 | 11.95 | 6.66 | 14.47 | 15.16 | |
| beam 2 | 35.81 | 20.46 | 11.80 | 6.75 | 14.08 | 14.84 | |
Ours [6 sents] |
greedy | 40.34 | 22.70 | 12.85 | 7.17 | 15.24 | 15.57 |
| greedy + RP | 40.80 | 23.14 | 13.19 | 7.37 | 15.46 | 16.26 | |
| beam 2 | 39.54 | 22.66 | 13.10 | 7.51 | 15.06 | 15.13 |
# greedy or beam_size=1
{"image_id": 2357356, "caption": "a bus is parked outside . the bus is parked on the side of the road . the bus is parked in the rear of the road . the bus is white with a yellow line . the bus is a light brown color . the sky is blue with white clouds .", "id": 2317}
# greedy + trigram repetition penalty
{"image_id": 2357356, "caption": "a bus is parked outside . the bus is large and black . the bus has the sun shining through the windows . the bus is white with a yellow line . the bus has a large white door and a black roof . the sky is blue with white clouds .", "id": 2317}
# beam_size = 2
{"image_id": 2357356, "caption": "a large bus is parked on the road . the bus is parked on the side of the road . the bus is parked in the rear of the road . the bus has two large windows on the side of it . the bus is a light brown color . the sky is a bright blue .", "id": 2317}# greedy or beam_size=1
{"image_id": 2383807, "caption": "there is a city street . there are several cars parked on the street in a city . there is a white car parked on the street . there is a black car driving down the street . there is a street light on the left side of the street . there is a street light on a pole next to the street .", "id": 1118}
# greedy + trigram repetition penalty
{"image_id": 2383807, "caption": "there is a city street . there are several cars parked on the street in a city . there is a white car parked on the street . there is a black car driving down the street . there is an empty street light on the left side of the street . there is a street light on a pole next to the street .", "id": 1118}
# beam_size = 2
{"image_id": 2383807, "caption": "there is a city street . there is a street light in the corner of a street . there is a white car on the street . there is a black car driving down the street . there are cars parked on the street in front of the person . there is a street light on a pole next to the street .", "id": 1118}Q: Why there is a performance gap between this implementation and the original paper?
A: Here are some possible reasons: (1) In the original paper, the authors use a pre-trained word-level language decoder initiated from dense captioning. However, we train our model from scratch. (2) In the original paper, you can observe that more than 6 sentences are generated in a paragraph. However we set our model to generate at most 6 sentences in a paragraph. As shown in the table above, more sentences could lead to better metrics. Note that, smaller sentence loss weight (eg. 1.0 instead of 5.0) and dropout rate (around 0.3 instead of 0.5) might lead to higher metrics. Moreover, switch to ButtomUp features can also boost performance. If you can achieve better result, please let me know!
Q: Why beam search is not working?
A: If no bug left unfounded (I have tried my best), this could because beam search may generate better single sentence caption but can be more likely to generate redundant phrases.
Special thanks to all the papers and code that mentioned above.