VLSI design open source RTL2GDSII
Physical design
Physical design means netlist (.v ) converted into GDSII form(layout form) logical connectivity of cells converted into physical connectivity. During physical design, all design components are instantiated with their geometric representations. In other words, all macros, cells, gates, transistors, etc., with fixed shapes and sizes per fabrication layer, are assigned spatial locations (placement) and have appropriate routing connections (routing) completed in metal layers.
Physical design directly impacts circuit performance, area, reliability, power, and manufacturing yield. Examples of these impacts are discussed below. Performance: long routes have significantly longer signal delays.
- Area: placing connected modules far apart results in larger and slower chips.
- Reliability: A large number of vias can significantly reduce the reliability of the circuit.
- Power: transistors with smaller gate lengths achieve greater switching speeds at the cost of higher leakage current and manufacturing variability; larger transistors and longer wires result in greater dynamic power dissipation.
- Yield: wires routed too close together may decrease yield due to electrical shorts occurring during manufacturing, but spreading gates too far apart may also undermine yield due to longer wires and a higher probability of opens
OpenLANE (open source automated flow):
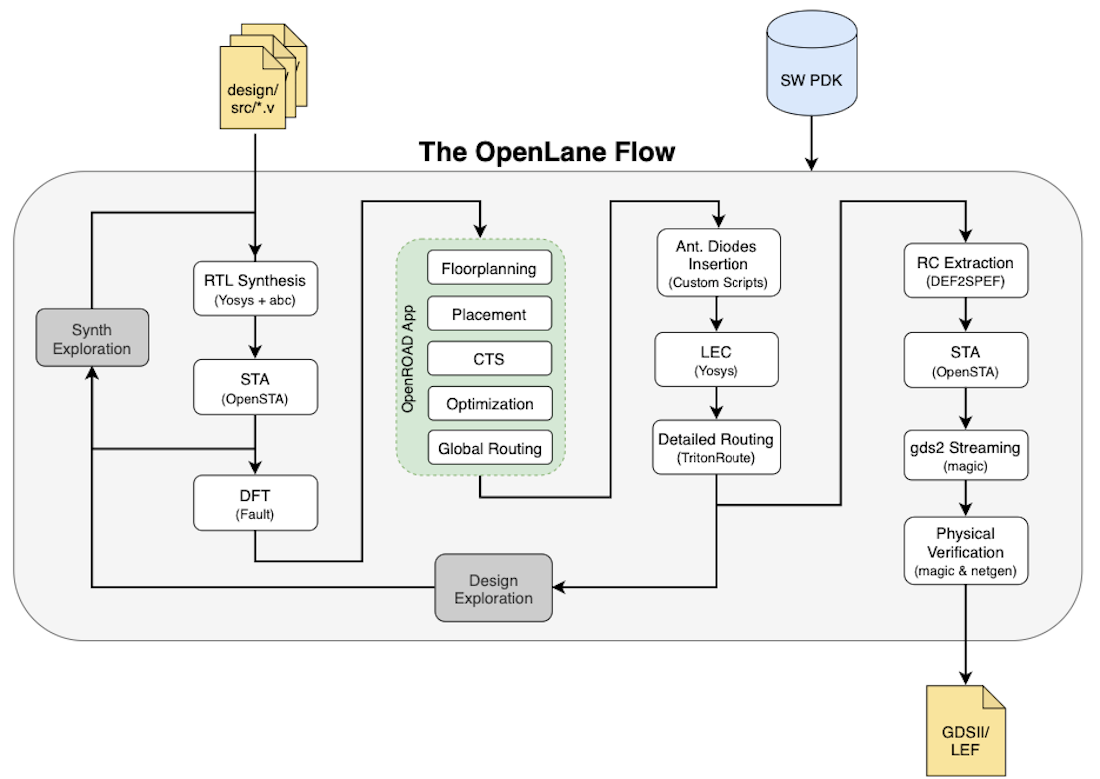
OpenLANE is an automated RTL to GDSII flow based on several components including OpenROAD, Yosys, Magic, Netgen, Fault, OpenPhySyn, SPEF-Extractor and custom methodology scripts for design exploration and optimization.
Below is the openLANE flow (RTL2GDSII):
Each flow run based on TCL scripts available in the vsdflow
Working directory and available folders:
Note that PDK is the process design kit, this is very important in the open source design environment. The PDK folder contains delay,minimum length and foundry capabilities of process across PVT corners.In this workshop, the directory is:
Before start the OpenLANE, important to make sure the file ./designs/[design]/config.tcl available and updated as per need.
Config file:
Below is the command to start openLANE:
Adding Package openLANE 0.9:
It is important to prepare the design after invoke the package. The current design is picorv32a.so we need to issue prep -design picorv32a which will merge all the LEF and also complete padding:
After preparing, we need to perform synthesis. The Mapping and static timing analysis also performed in the Synthesis stage.below are the open source tools used for each tasks:
SYNTHESIS
Synthesis transforms the simple RTL design into a gate-level netlist with all the constraints as specified by the designer. In simple language, Synthesis is a process that converts the abstract form of design to a properly implemented chip in terms of logic gates.
Synthesis takes place in multiple steps:
Synthesis is a very important process for the designers as it enables them to see how the design will actually look like after fabrication. All parameters including area, timing, power can be reported and checked by the designer beforehand. He/She can make the necessary changes(if required) before the actual fabrication process, thus saving both time and cost. Also,Mapping those gates to actual technology-dependent logic gates available in the technology libraries and optimizing the mapped netlist keeping the constraints set by the designer intact.
Tools:
- yosys - Performs RTL synthesis
- abc - Performs technology mapping
- OpenSTA - Performs static timing analysis on the resulting net-list to generate timing reports
run_synthesis is the command for start synthesis. Synthesis takes a few minutes(according to the depth of design), below is the result summary:
Important is flop ratio. the flop ratio = Total number of flip-flops / Total number of Cells
Here,the total number of D flip-flop = 1634 and total number of Cells = 17323 and the ratio = 0.094
All the runs available in working_dir/openLANE/design/picorv32a/runs directory names as date.
FLOORPLAN AND PDN:
This is the first major step in getting your layout done, and this is the most important one.Your floorplan determines your chip quality. Floorplanning includes
- Define the size of your chip/block and Aspect ratio
- Defining the core area and IO core spacing
- Defining ports specified by top level engineer.
- Design a Floor Plan and Power Network with horizontal metal layer such that the total IR Drop must be less than 5% (VDD+VSS) of VDD to operate within the power budget.
- IO Placement/Pin placement
- Allocates power routing resources
- Place the hard macros (fly-line analysis) and reserve space for standard cells.
- Defining Placement and Routing blockages blockages
- If we have multi height cells in the reference library separate placement rows have to be provided for two different unit tiles.
- Creating I/O Rings
- Creating the Pad Ring for the Chip
- Creating I/O Pin Rings for Blocks
Tools:
- init_fp - Defines the core area for the macro as well as the rows (used for placement) and the tracks (used for routing)
- ioplacer - Places the macro input and output ports
- pdn - Generates the power distribution network
- tapcell - Inserts welltap and decap cells in the floorplan
In this workshop, we are going to run floorplan first. The PDN (Power distribution network) will run later part in the flow.
Floorplan config:
run_floorplan is the command for start floorplan.Below are a few snapshots after completing floorplan:
Below snapshot contains the die area with the UNIT DISTANCE MICRONS 1000; this means the die area [(Lower left(ll) X,Lower left(ll) Y),(Upper Right(ur) X,Upper Right(ur) Y)] are calculated with 1 um = 1000 Database unit.
Command to open the floorplan /work_dir/openLANE/design/picorv32a/runs/[Tag]/floorplan/*.def file using magic:
Floorplan in Magic (more details available in http://opencircuitdesign.com/magic/):
Use "z" and "Shift+z" for zoom-in and zoom-out and use the command "what" in the "tkcon 2.3 main" xterm for viewing detials of any selected (use "s" once mouse point over the pin) pins:
PLACEMENT
Placement is the process of finding a suitable physical location for each cell in the block. Tool only determine the location of each standard cell on the die. Placement does not just place the standard cell available in the synthesized netlist, it also optimized the design.
The tool determines the location of each of the standard cell on the core. Various factors come into play like the timing requirement of the system, the interconnect length and hence the connections between cells, power dissipation, etc. the interconnect length depends on the placement solution used, and it is very important in determining the performance of the system as the geometries shrink. Placement will be driven based on different criteria like timing driven, congestion driven, power optimization.
Tools:
- RePLace - Performs global placement
- Resizer - Performs optional optimizations on the design
- OpenPhySyn - Performs timing optimizations on the design
- OpenDP - Perfroms detailed placement to legalize the globally placed components
run_placement is the command for start placement.Below are a few snapshots after completing placement using magic:
Terminal :
Magic "expand" command to view the layout of a cell after placement:
STANDARD CELLS
There are multiple standard cells available in github or skywater. In this workshop let's cloning from github as below:
Goto cloned vsdstdcelldesign and copy the technology from PDK folder available in work directory because technology file needed for MAGIC tool to open the cell layout.
As we can see the sky130_inv.mag in the vsdstdcelldesign , we can open sky130_inv.mag using magic with the copied technology file. Below is the command to open the .mag file in magic:
The standard cell inverter layout looks as below:
In the inverter layout, select a mask as below to know the MOSFET type with the magic command "what" :
An inverter layout consists of multiple layers, below snapshot shows the layers used in inverter layout:
Next step is to characterise the inverter using ngspice. The command " extraxt all,ext2spice chresh 0 rthresh 0 followed by ext2spice" create spice netlist.
THe spice netlist can be observed with the nodes available in the layout:
The spice netlist is not completed without the VDD,VSS and input pulse. Below update spice netlist consist of all the necessary input and power:
Now, we are ready for ngspice simualtion.Below is the terminal result after issuing the ngspice command ngspice sky130_inv.spice :
As we need to observe the waveform we can use the command plot.
To reduce the spike in the rising edge, we will update the spice netlist C3 capacitance (output (Y) Load capacitance ) as below:
The inverter waveform can observe as below after re-run the ngspice sky130_inv.spice and plot command:
As the part of characterisation, we can get the propogation delay from the ngspice as below:
Using the waveform in ngspice tool, we are mesuring the propogation delay. there are 8 different timing threshold characterisation need to perform which are listed below:
- slew_low_rise_thr - considering 20% of rise time
- slew_high_rise_thr - considering 80% of rise time
- slew_low_fall_thr - considering 20% of fall time
- slew_high_fall_thr - considering 80% of fall time
- in_rise_thr - considering 50% of input rise time
- in_fall_thr - considering 50% of input fall time
- out_rise_thr - considering 50% of output rise time
- out_fall_thr - considering 50% of out fall time
propogation delay = time(out_thr) - time(in_thr)
DRC CHECK IN DRC TESTS LAYERS
The DRC (Design Rule Check) is one of the very important in the layout.In this workshop, we are trying to download all the metal layers. Below is command and respective website for download the list of drc_tests.
wget http://opencircuitdesign.com/open_pdks/archive/drc_tests.tgz
Untar the downloaded folder with tar -xvz and goto the drc_test folder to open in magic (using command magix -d XR)
Here, opened metal3 layout as below:
Now that create a box and add metal2 init and see via using cif see VIA2 :
There are a few more commands for DRC as below:
- ;drc why - to check the drc error from layout
- tech load[tech file] & command drc check - to load the updated tech file and check the drc
some other commands as below :
Feed clear (to clear the via2):
Load command to load any .mag file (here poly layer) :
To clear the DRC rules, need to follow the Skywater PDK website (https://skywater-pdk--136.org.readthedocs.build/en/136/rules/periphery.html#poly) for right measurements.
LEF FILE EXTRACTION FROM STD CELL LAYOUT
Next is to get the grid in magic. The grid details available in pdk/TRACE.info file as below:
Include grid in magic with grid:
Define port (using options -> texts) :
Define port class and port use in magic:
Create LEF from STD CELL inverter using write lef:
INCLUDE STD CELL TO PICORV32A
Copy the library and new created inverter .lef file to the /design/picorv32a/src directory:
Next step to update the config file with std cell inverter .lef file as below:
Add .lef after prep :
The inverter cell can be observed after placement in magic as below:
Create/copy the my_base.sdc file for timing analysis and pre_sta.conf file as below:
SYNTHESIS variables need to set for reduce the slack violations as below:

Reducing slack after using the sta pre_sta.conf and replace a few buffers:
We can reduce the slack and use write_verilog command to write to the synthesis verilog in the result/synthesis/synthesis.v
CLOCK TREE ANALYSIS
Use run_cts command to start CTS and we can see the result in terminal as below:
Next is to start openroad in openlane to start timing analysis with just issue the command openroad. Once the openroad ready for next command, use load_lef and load_def followed bt write_db to create a database. below are a few snapshots:
Below are a few debug steps to reduce the slack in timing analysis:
Slack violation for Hold time:
Slack violation for Setuptime time:
Command to remove the first buf from the list:
Need to use set to get reflected in the openlane:
Setting current def as placement for further steps in the openlane flow:
Another command to insert the buf back to the list:
PDN SETTING This is another important requirement for generate power routing. in openLANE we use gen_pdn command:
ROUTING
The last step in the openLANE is routing using run_routing :
Summary of routing available in terminal as below:
After the routing we can see the DRC violations as below:
After the routing, SPEF(standard paracitic extraction form) file need to generate from DEF and LEF in outside of openlane flow as below:
FULL DESIGN WITH INVERTER STD CELL
We can observe our routing layout including inverter with magic as below:
GDSII file can be obtained with run_magic command.
Note: more snapshots available in snapshot directory in github.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Kunal Ghosh, Co-Founder (VSD Corp. Pvt. Ltd)
- Nickson P Jose, Teaching Assistant (VSD Corp. Pvt. Ltd)