This project is aiming to classify images of flowers from the Oxford Flowers dataset using deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The project involves multiple phases, including dataset preparation, network training, and evaluation.
The project is divided into two main phases:
-
Phase 1: Train a CNN on the first 80 classes of the Oxford Flowers dataset (
A dataset), then evaluate the model on the same dataset.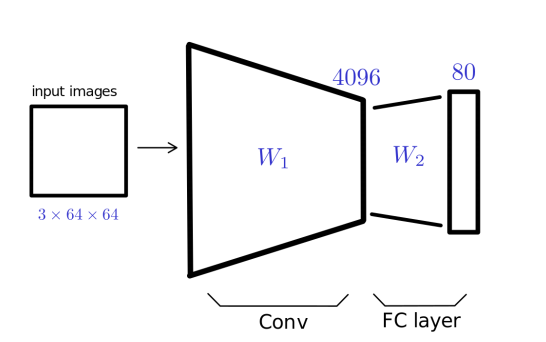
-
Phase 2: Use the trained network to classify the additional 20 classes (
B dataset). This phase includes several strategies to handle the limited data available for the new classes.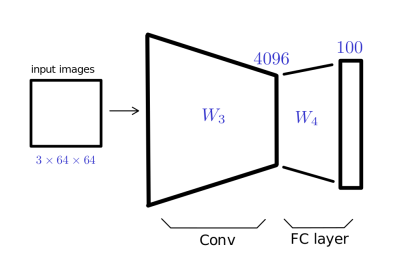
The Oxford Flowers dataset contains images of 102 flower categories. The data will be downloaded while the notebook is running. For this project, we divide the dataset as follows:
- A dataset: First 80 classes.
- B dataset: Remaining 20 classes.
The dataset is split into training and testing sets for both A and B datasets.
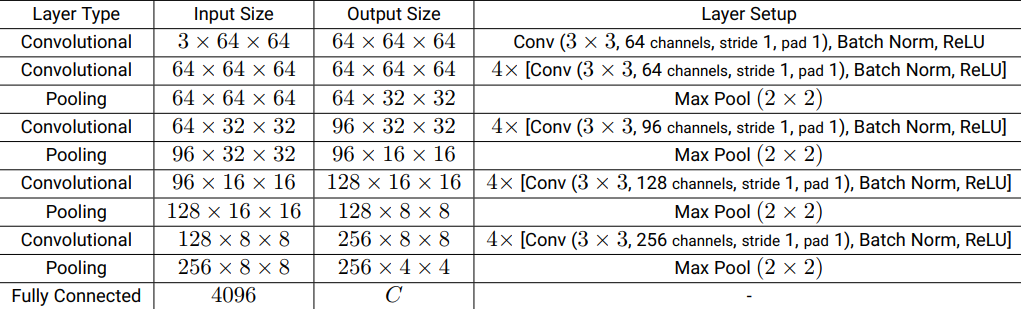
The CNN architecture consists of several convolutional layers followed by pooling layers and fully connected layers. Here are the details:
- Convolutional layers: Use 3x3 kernels, stride of 1, and padding of 1. Each convolutional layer is followed by batch normalization and ReLU activation.
- Pooling layers: Max pooling layers are used to reduce the spatial dimensions.
- Fully connected layer: The final layer flattens the input and maps it to the output classes.
- Training: Train the CNN on the
A datasetusing cross-entropy loss. - Evaluation: Evaluate the trained model on the test set of the
A dataset.
The second phase involves three methods for fine-tuning the network to classify the B dataset:
-
Method 1: Train the new network normally using the
B dataset. -
Method 2: Freeze all layers except the last fully connected layer and train using the
B dataset.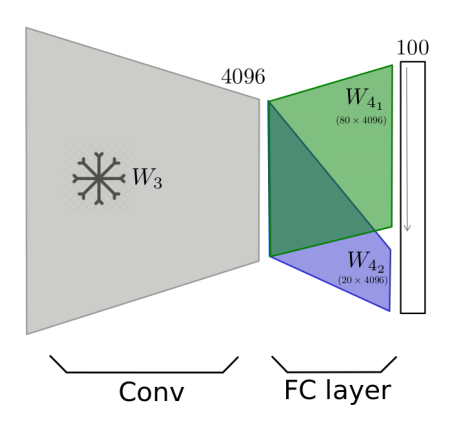
-
Method 3: Freeze all layers except the last 20 neurons of the fully connected layer and train using the
B dataset.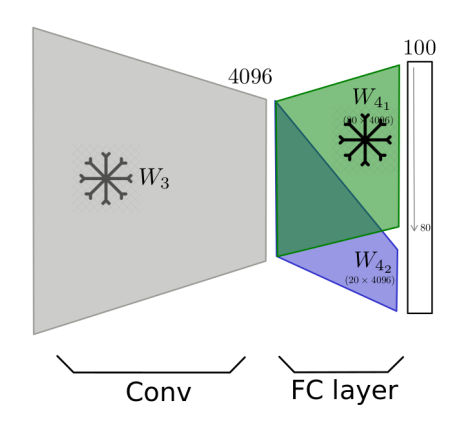
The CNN_classification.ipynb notebook contains the following:
- Data loading and preprocessing.
- Network architecture definition.
- Training and evaluation functions.
- Visualization of training progress and evaluation metrics.
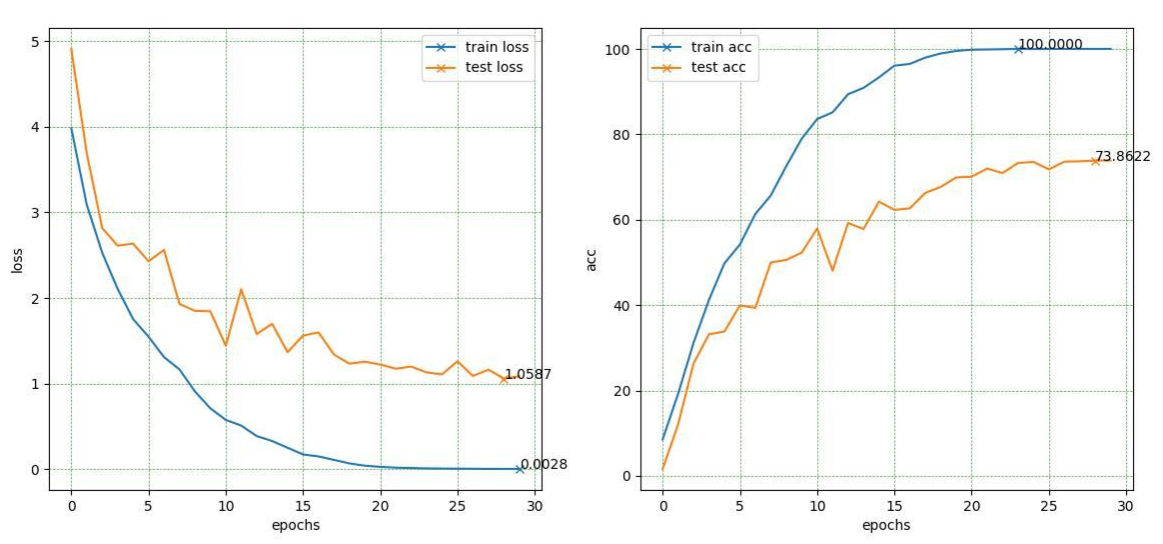
The performance of the model is evaluated based on accuracy and loss for both the A and B datasets. Detailed results and comparisons between different methods are included in document.txt file.
Below is a summary of the optimal parameters and the corresponding achieved accuracy for each phase of the project:
-
Optimal Parameters:
- Batch Size: 250
- Learning Rate: 0.0005
- Number of Epochs: 30
-
Accuracy: Achieved 71% test accuracy with the optimal parameters.
- Optimal Parameters:
- Batch Size: 250
- Learning Rate: 0.0003
- Number of Epochs: 60
- Momentum: 0.9
- Optimizer: SGD
- Accuracy: Best test accuracy achieved with these parameters.
- Optimal Parameters:
- Batch Size: 250
- Learning Rate: 0.0003
- Number of Epochs: 60
- Momentum: 0.9
- Optimizer: SGD
- Accuracy: Similar to Section 1, best test accuracy with SGD outperforming Adam.
- Optimal Parameters:
- Batch Size: 250
- Learning Rate: 0.0002
- Number of Epochs: 60
- Momentum: 0.9
- Optimizer: SGD
- Accuracy: Learning rate of 0.0002 provided the best performance for partially frozen layers.
- Python 3.10
- PyTorch
- Jupyter Notebook
- Other dependencies as listed in
requirements.txt
To run the project, ensure you have Python installed along with the necessary libraries. You can install the required packages using:
pip install -r requirements.txtThis project demonstrates the effectiveness of different strategies for training deep neural networks on a limited dataset. By leveraging transfer learning and fine-tuning techniques, the model achieves good performance on the additional classes in the B dataset.