Parse Dashboard is a standalone dashboard for managing your Parse apps. You can use it to manage your Parse Server apps and your apps that are running on Parse.com.
- Getting Started
- Local Installation
- Running as Express Middleware
- Deploying Parse Dashboard
- Contributing
Node.js version >= 4.3 is required to run the dashboard. You also need to be using Parse Server version 2.1.4 or higher.
Install the dashboard from npm.
npm install -g parse-dashboard
You can launch the dashboard for an app with a single command by supplying an app ID, master key, URL, and name like this:
parse-dashboard --appId yourAppId --masterKey yourMasterKey --serverURL "https://example.com/parse" --appName optionalName
You may set the host, port and mount path by supplying the --host, --port and --mountPath options to parse-dashboard. You can use anything you want as the app name, or leave it out in which case the app ID will be used.
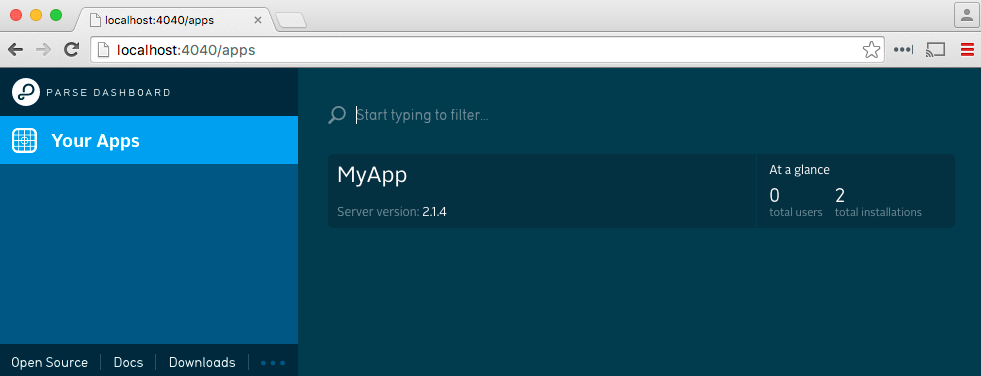
After starting the dashboard, you can visit http://localhost:4040 in your browser:
You can also start the dashboard from the command line with a config file. To do this, create a new file called parse-dashboard-config.json inside your local Parse Dashboard directory hierarchy. The file should match the following format:
{
"apps": [
{
"serverURL": "http://localhost:1337/parse",
"appId": "myAppId",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey",
"appName": "MyApp"
}
]
}You can then start the dashboard using parse-dashboard --config parse-dashboard-config.json.
This only works when starting the app using the
parse-dashboardcommand
There are also two methods you can use to configure the dashboard using environment variables.
Provide the entire JSON configuration in PARSE_DASHBOARD_CONFIG and it will be parsed just like the config file.
You can also define each configuration option individually.
HOST: "0.0.0.0"
PORT: "4040"
MOUNT_PATH: "/"
PARSE_DASHBOARD_TRUST_PROXY: undefined // Or "1" to trust connection info from a proxy's X-Forwarded-* headers
PARSE_DASHBOARD_SERVER_URL: "http://localhost:1337/parse"
PARSE_DASHBOARD_MASTER_KEY: "myMasterKey"
PARSE_DASHBOARD_APP_ID: "myAppId"
PARSE_DASHBOARD_APP_NAME: "MyApp"
PARSE_DASHBOARD_USER_ID: "user1"
PARSE_DASHBOARD_USER_PASSWORD: "pass"
PARSE_DASHBOARD_SSL_KEY: "sslKey"
PARSE_DASHBOARD_SSL_CERT: "sslCert"
PARSE_DASHBOARD_CONFIG: undefined // Only for reference, it must not exist
Managing multiple apps from the same dashboard is also possible. Simply add additional entries into the parse-dashboard-config.json file's "apps" array.
You can manage self-hosted Parse Server apps, and apps that are hosted on Parse.com from the same dashboard. In your config file, you will need to add the restKey and javascriptKey as well as the other paramaters, which you can find on dashboard.parse.com. Set the serverURL to http://api.parse.com/1:
{
"apps": [
{
"serverURL": "https://api.parse.com/1", // Hosted on Parse.com
"appId": "myAppId",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey",
"javascriptKey": "myJavascriptKey",
"restKey": "myRestKey",
"appName": "My Parse.Com App",
"production": true
},
{
"serverURL": "http://localhost:1337/parse", // Self-hosted Parse Server
"appId": "myAppId",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey",
"appName": "My Parse Server App"
}
]
}Parse Dashboard supports adding an optional icon for each app, so you can identify them easier in the list. To do so, you must use the configuration file, define an iconsFolder in it, and define the iconName parameter for each app (including the extension). The path of the iconsFolder is relative to the configuration file. If you have installed ParseDashboard globally you need to use the full path as value for the iconsFolder. To visualize what it means, in the following example icons is a directory located under the same directory as the configuration file:
{
"apps": [
{
"serverURL": "http://localhost:1337/parse",
"appId": "myAppId",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey",
"appName": "My Parse Server App",
"iconName": "MyAppIcon.png",
}
],
"iconsFolder": "icons"
}Parse Dashboard supports adding an optional background color for each app, so you can identify them easier in the list. To do so, you must use the configuration file, define an primaryBackgroundColor and secondaryBackgroundColor in it, parameter for each app. It is CSS style. To visualize what it means, in the following example backgroundColor is a configuration file:
{
"apps": [
{
"serverURL": "http://localhost:1337/parse",
"appId": "myAppId",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey",
"appName": "My Parse Server App",
"primaryBackgroundColor": "#FFA500", // Orange
"secondaryBackgroundColor": "#FF4500" // OrangeRed
},
{
"serverURL": "http://localhost:1337/parse",
"appId": "myAppId",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey",
"appName": "My Parse Server App [2]",
"primaryBackgroundColor": "rgb(255, 0, 0)", // Red
"secondaryBackgroundColor": "rgb(204, 0, 0)" // DarkRed
}
]
}You can set appNameForURL in the config file for each app to control the url of your app within the dashboard. This can make it easier to use bookmarks or share links on your dashboard.
To change the app to production, simply set production to true in your config file. The default value is false if not specified.
Instead of starting Parse Dashboard with the CLI, you can also run it as an express middleware.
var express = require('express');
var ParseDashboard = require('parse-dashboard');
var dashboard = new ParseDashboard({
"apps": [
{
"serverURL": "http://localhost:1337/parse",
"appId": "myAppId",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey",
"appName": "MyApp"
}
]
});
var app = express();
// make the Parse Dashboard available at /dashboard
app.use('/dashboard', dashboard);
var httpServer = require('http').createServer(app);
httpServer.listen(4040);If you want to run both Parse Server and Parse Dashboard on the same server/port, you can run them both as express middleware:
var express = require('express');
var ParseServer = require('parse-server').ParseServer;
var ParseDashboard = require('parse-dashboard');
var api = new ParseServer({
// Parse Server settings
});
var options = { allowInsecureHTTP: false };
var dashboard = new ParseDashboard({
// Parse Dashboard settings
}, options);
var app = express();
// make the Parse Server available at /parse
app.use('/parse', api);
// make the Parse Dashboard available at /dashboard
app.use('/dashboard', dashboard);
var httpServer = require('http').createServer(app);
httpServer.listen(4040);Make sure the server URLs for your apps can be accessed by your browser. If you are deploying the dashboard, then localhost urls will not work.
In order to securely deploy the dashboard without leaking your apps master key, you will need to use HTTPS and Basic Authentication.
The deployed dashboard detects if you are using a secure connection. If you are deploying the dashboard behind a load balancer or front-facing proxy, then the app won't be able to detect that the connection is secure. In this case, you can start the dashboard with the --trustProxy=1 option (or set the PARSE_DASHBOARD_TRUST_PROXY config var to 1) to rely on the X-Forwarded-* headers for the client's connection security. This is useful for hosting on services like Heroku, where you can trust the provided proxy headers to correctly determine whether you're using HTTP or HTTPS. You can also turn on this setting when using the dashboard as express middleware:
var trustProxy = true;
var dashboard = new ParseDashboard({
"apps": [
{
"serverURL": "http://localhost:1337/parse",
"appId": "myAppId",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey",
"appName": "MyApp"
}
],
"trustProxy": 1
});You can configure your dashboard for Basic Authentication by adding usernames and passwords your parse-dashboard-config.json configuration file:
{
"apps": [{"...": "..."}],
"users": [
{
"user":"user1",
"pass":"pass"
},
{
"user":"user2",
"pass":"pass"
}
],
"useEncryptedPasswords": true | false
}You can store the password in either plain text or bcrypt formats. To use the bcrypt format, you must set the config useEncryptedPasswords parameter to true.
You can encrypt the password using any online bcrypt tool e.g. https://www.bcrypt-generator.com.
If you have configured your dashboard to manage multiple applications, you can restrict the management of apps based on user identity.
To do so, update your parse-dashboard-config.json configuration file to match the following format:
{
"apps": [{"...": "..."}],
"users": [
{
"user":"user1",
"pass":"pass1",
"apps": [{"appId": "myAppId1"}, {"appId": "myAppId2"}]
},
{
"user":"user2",
"pass":"pass2",
"apps": [{"appId": "myAppId1"}]
} ]
}The effect of such a configuration is as follows:
When user1 logs in, he/she will be able to manage myAppId1 and myAppId2 from the dashboard.
When user2 logs in, he/she will only be able to manage myAppId1 from the dashboard.
Starting parse-server 2.6.5, it is possible to provide a readOnlyMasterKey to parse-server to prevent mutations on objects from a client.
If you want to protect your dashboard with this feature, just use the readOnlyMasterKey instead of the masterKey. All write calls will fail.
Start your parse-server with
{
"masterKey": "YOUR_MASTER_KEY_HERE",
"readOnlyMasterKey": "YOUR_READ_ONLY_MASTER_KEY",
}Then in your dashboard configuration:
var trustProxy = true;
var dashboard = new ParseDashboard({
"apps": [
{
"serverURL": "http://localhost:1337/parse",
"appId": "myAppId",
"masterKey": "YOUR_READ_ONLY_MASTER_KEY",
"appName": "MyApp"
}
],
"trustProxy": 1
});Make sure you specify the readOnlyMasterKey for the apps that you want to use read-only feature in "apps" configuration.
You can mark a user as a read-only user:
{
"apps": [
{
"appId": "myAppId1",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey1",
"readOnlyMasterKey": "myReadOnlyMasterKey1",
"serverURL": "myURL1",
"port": 4040,
"production": true
},
{
"appId": "myAppId2",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey2",
"readOnlyMasterKey": "myReadOnlyMasterKey2",
"serverURL": "myURL2",
"port": 4041,
"production": true
}
],
"users": [
{
"user":"user1",
"pass":"pass1",
"readOnly": true,
"apps": [{"appId": "myAppId1"}, {"appId": "myAppId2"}]
},
{
"user":"user2",
"pass":"pass2",
"apps": [{"appId": "myAppId1"}]
}
]
}This way user1 will have a readOnly access to myAppId1 and myAppId2
Make sure you specify the readOnlyMasterKey for the apps that you want to use read-only feature in "apps" configuration.
You can give read only access to a user on a per-app basis:
{
"apps": [
{
"appId": "myAppId1",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey1",
"readOnlyMasterKey": "myReadOnlyMasterKey1",
"serverURL": "myURL",
"port": 4040,
"production": true
},
{"...": "..."}
],
"users": [
{
"user":"user",
"pass":"pass",
"apps": [{"appId": "myAppId", "readOnly": true}, {"appId": "myAppId2"}]
}
]
}With this configuration, user1 will have read only access to myAppId1 and read/write access to myAppId2.
With the latest version of the dashboard, it is possible to send localized messages for push notifications. You can provide a list of locales or languages you want to support for your dashboard users.
{
"apps": [
{
"serverURL": "http://localhost:1337/parse",
"appId": "myAppId",
"masterKey": "myMasterKey",
"appName": "My Parse Server App",
"iconName": "MyAppIcon.png",
"supportedPushLocales": ["en", "ru", "fr"]
}
],
"iconsFolder": "icons"
}It is easy to use it with Docker. First build the image:
docker build -t parse-dashboard .
Run the image with your config.json mounted as a volume
docker run -d -p 8080:4040 -v host/path/to/config.json:/src/Parse-Dashboard/parse-dashboard-config.json parse-dashboard
By default, the container will start the app at port 4040 inside the container. However, you can run custom command as well (see Deploying in production for custom setup).
In this example, we want to run the application in production mode at port 80 of the host machine.
docker run -d -p 80:8080 -v host/path/to/config.json:/src/Parse-Dashboard/parse-dashboard-config.json parse-dashboard --port 8080
If you are not familiar with Docker, --port 8080 will be passed in as argument to the entrypoint to form the full command npm start -- --port 8080. The application will start at port 8080 inside the container and port 8080 will be mounted to port 80 on your host machine.
We really want Parse to be yours, to see it grow and thrive in the open source community. Please see the Contributing to Parse Dashboard guide.
As of April 5, 2017, Parse, LLC has transferred this code to the parse-community organization, and will no longer be contributing to or distributing this code.