This is a sample LaunchDarkly implementation on Next.js using the App Router with Client and Server components and various rendering strategies. It demonstrates how to integrate LaunchDarkly feature flags into a Next.js application.
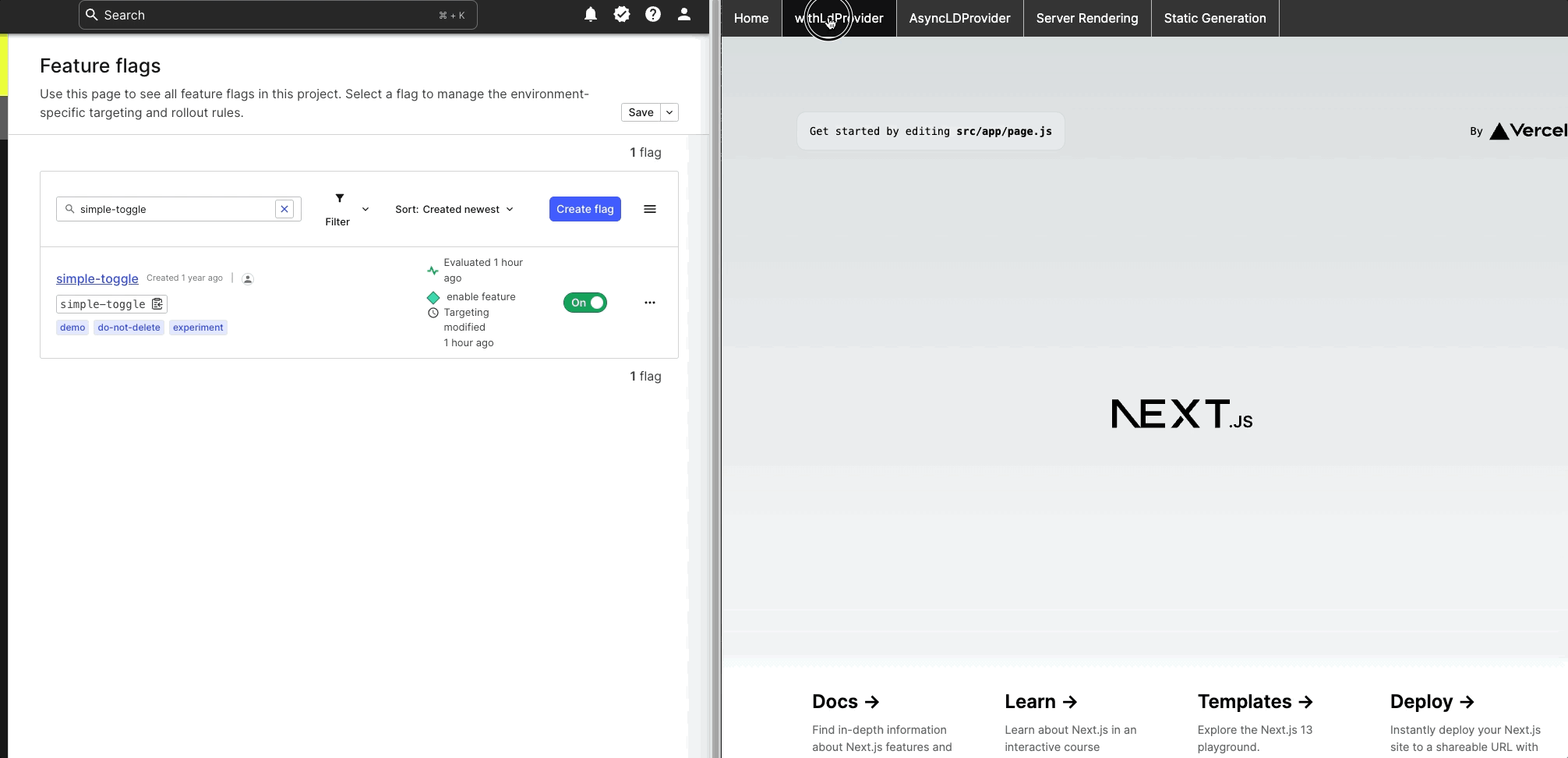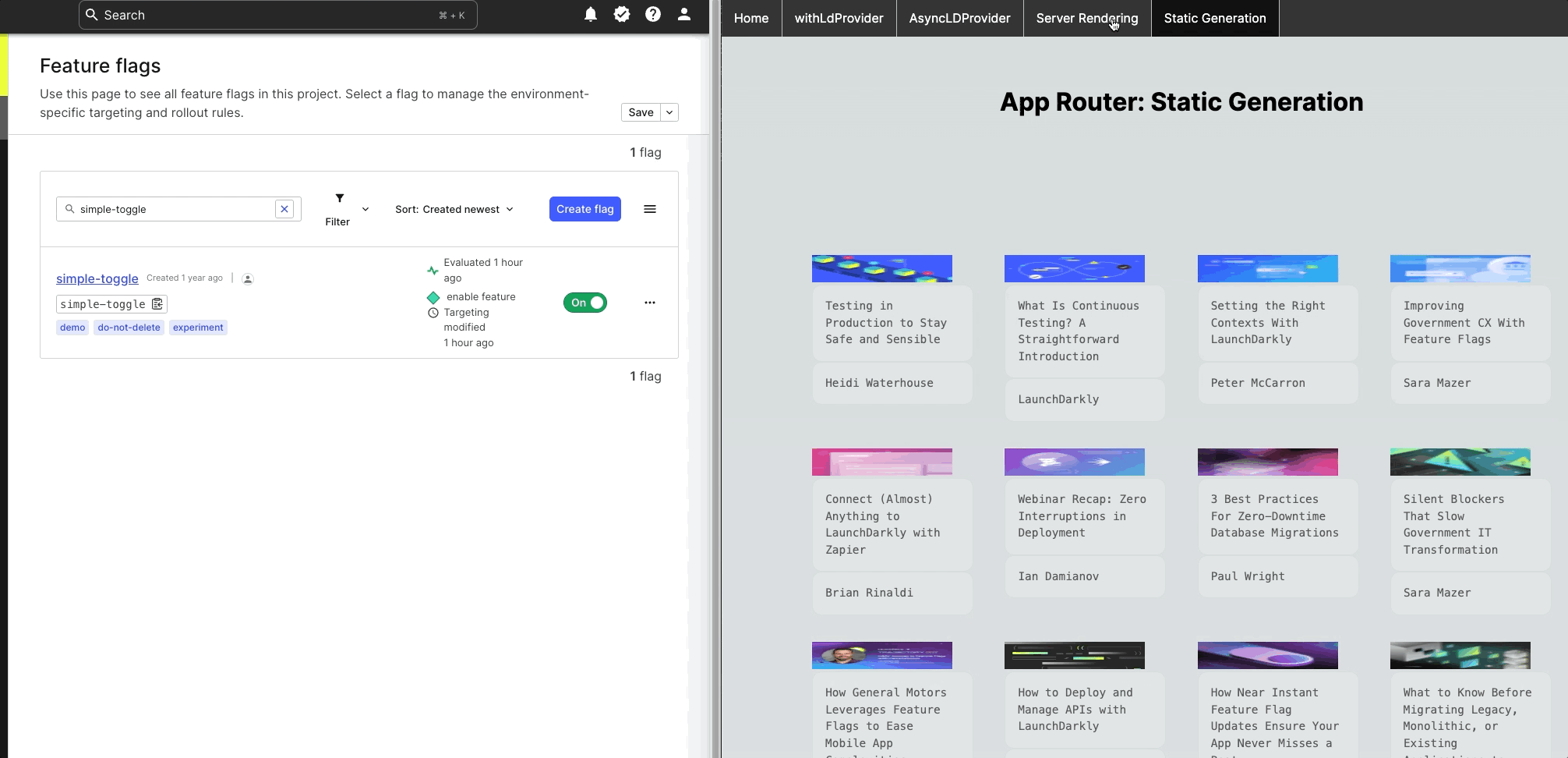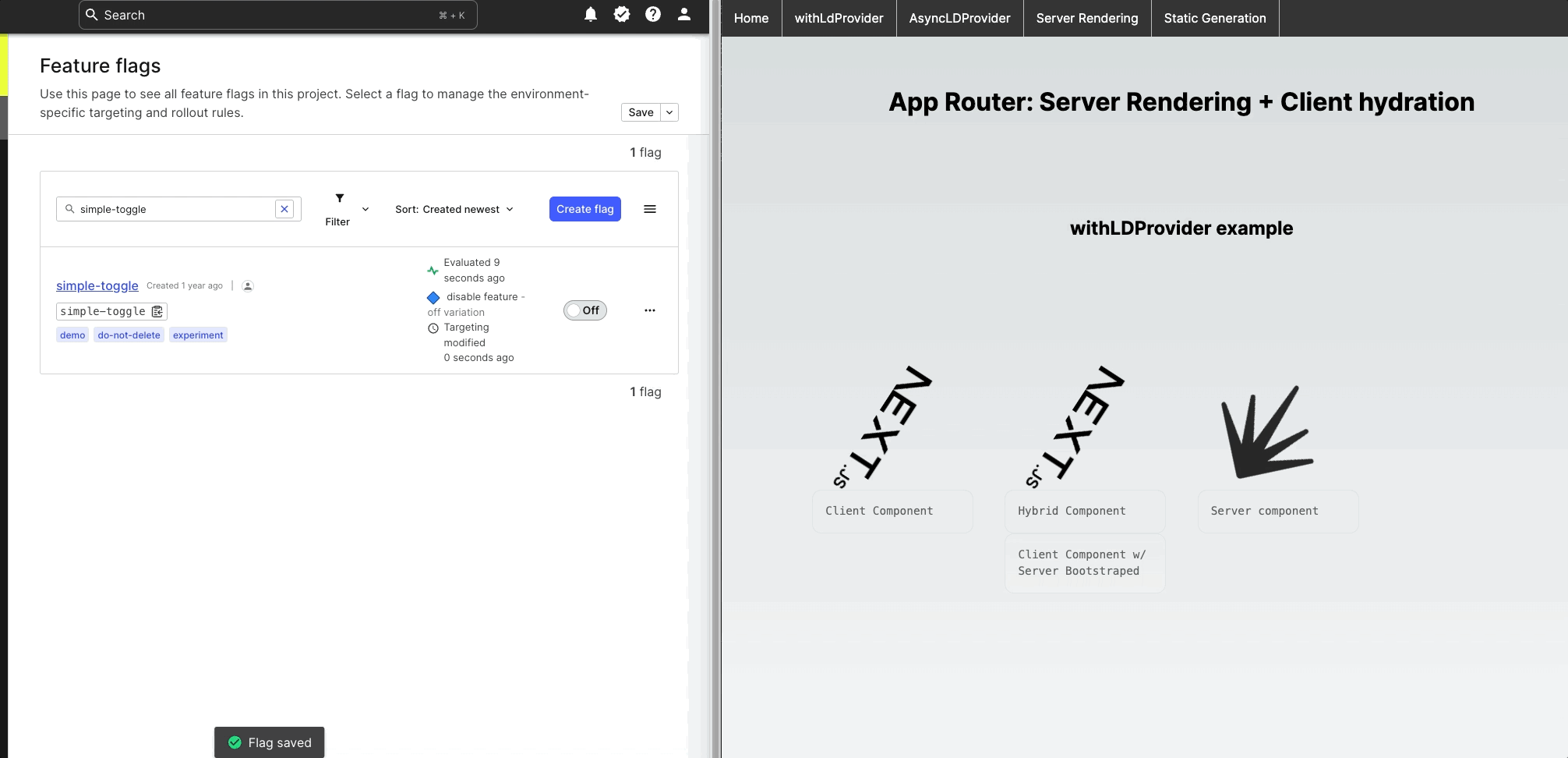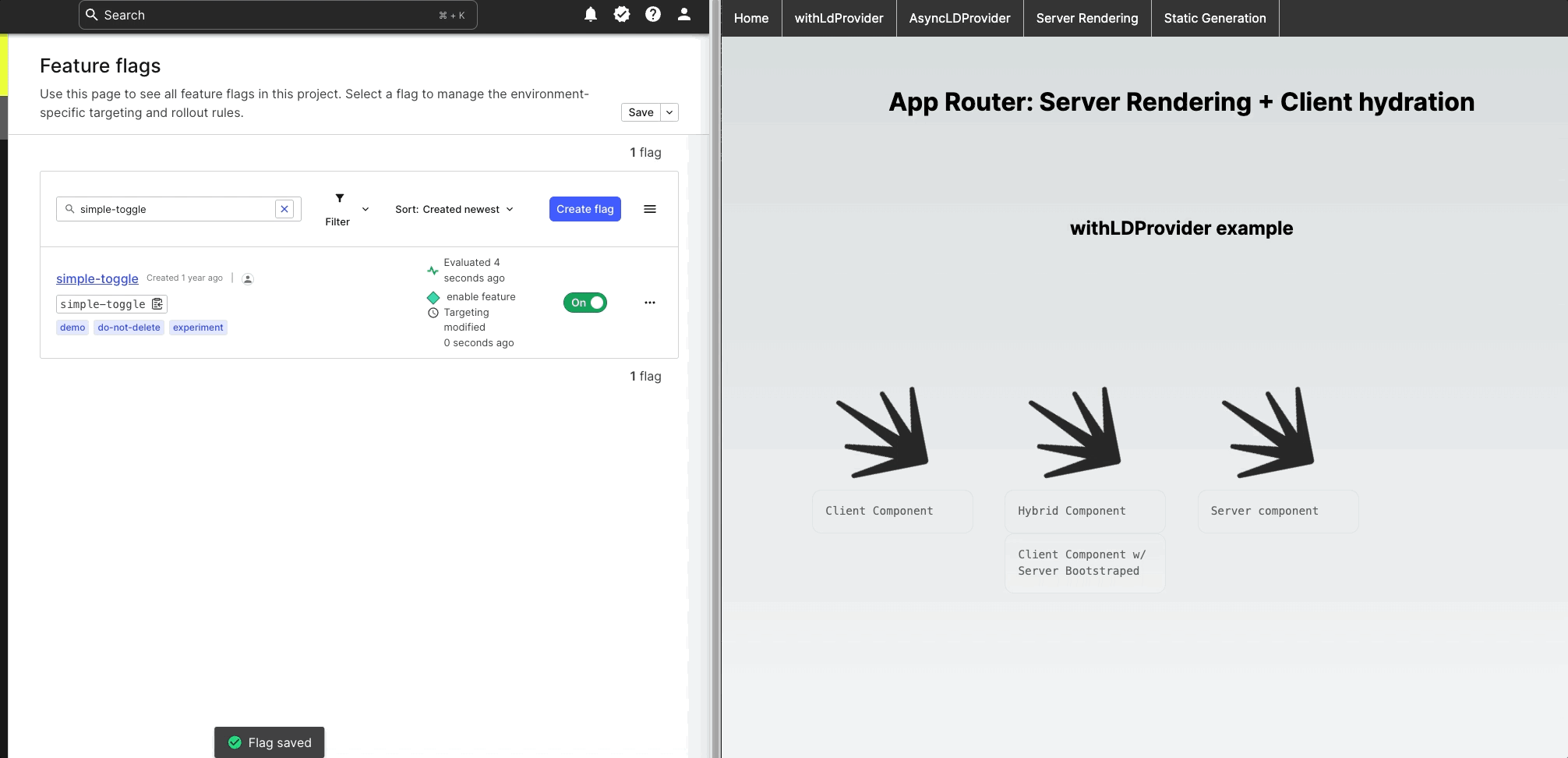 Rendering Performance: Server vs Client components
Rendering Performance: Server vs Client components
If you're developing with client components in Next.js, it's crucial to have a good grasp of how the platform manages client-side prerendering and the impact it may have on browser-specific libraries such as the LaunchDarkly React web SDK. For more information on this topic, I suggest checking out this article titled "Why do Client Components get SSR'd to HTML?".
Next.js improves page load times by prerendering both Client and Server components on the server and sending prerendered HTML to the browser. This makes page load times faster, especially for pages with lots of content and complex JavaScript.
During server-side prerendering, Client components do not involve hydration, which can cause runtime errors when browser-specific APIs are used such as when calling LaunchDarkly React SDK asyncWithLDProvider.
Important Changes in Next.js 15 & React 19:
- The
use()hook now requires stable/cached promises and cannot be used with promises created during render. - Server Components cannot use
ssr: falsewithnext/dynamic. Read Invalid Usage ofsuspenseOption ofnext/dynamicfor details. - New error: "A component was suspended by an uncached promise"
To avoid these issues, consider implementing the following updated approach:
- Initialize the LaunchDarkly React SDK in a Client component using traditional async patterns.
- Use code-splitting to defer the loading of the React web SDK until page hydration phase.
- Avoid using
use()hook with promises created in render - useuseEffectanduseStateinstead for compatibility. Read React v19 use() does not support promises created in render for details. - When using
dynamic()withssr: false, ensure the component calling it is a Client Component (has"use client"directive). Read Skipping SSR for details.
Here is an example of how to incorporate these modifications:
Client component: components/AsyncWithLDProvider.js
"use client";
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { asyncWithLDProvider, basicLogger } from "launchdarkly-react-client-sdk";
const defaultContext = {
kind: "user",
key: "user-key-123abc",
name: "Sandy Smith",
};
const createLDConfig = (clientSideID, context) => ({
clientSideID,
context,
timeout: 5,
options: {
logger: basicLogger({
destination: (line) => console.log(line),
level: "debug",
}),
},
reactOptions: {
useCamelCaseFlagKeys: true,
},
});
export default function AsyncLDProvider({
children,
context = defaultContext,
clientSideID,
}) {
const [LDProvider, setLDProvider] = useState(null);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
if (!clientSideID) {
setError(new Error("clientSideID is required"));
setLoading(false);
return;
}
let mounted = true;
const initializeLDProvider = async () => {
try {
const config = createLDConfig(clientSideID, context);
const provider = await asyncWithLDProvider(config);
if (mounted) {
setLDProvider(() => provider);
setLoading(false);
}
} catch (err) {
if (mounted) {
setError(err);
setLoading(false);
}
}
};
initializeLDProvider();
return () => {
mounted = false;
};
}, [clientSideID, context]);
if (error) {
return <div>Error: {error.message}</div>;
}
if (loading || !LDProvider) {
return <div>Loading LaunchDarkly...</div>;
}
return <LDProvider>{children}</LDProvider>;
}
create a client wrapper component : components/ClientAsyncLDProvider.js:
"use client";
import dynamic from "next/dynamic";
const LDAsyncPovider = dynamic(
() => import("@/components/AsyncWithLDProvider"),
{
ssr: false,
loading: () => <div>Loading LaunchDarkly...</div>
}
);
export default function ClientAsyncLDProvider({ children, clientSideID }) {
return (
<LDAsyncPovider clientSideID={clientSideID}>
{children}
</LDAsyncPovider>
);
}
Then use it in app/layout.js (Server Component):
import ClientAsyncLDProvider from "@/components/ClientAsyncLDProvider";
export default function Layout({ children }) {
return (
<ClientAsyncLDProvider clientSideID={process.env.CLIENT_SIDE_ID}>
{children}
</ClientAsyncLDProvider>
);
}
- LaunchDarkly account
- LaunchDarkly React Web client SDK >= 3.8.x
- LaunchDarkly Node.js server SDK >= 9.10.x
- Node.js version >= 18.17.x
- Next.js version 15.x
- React version 19.x
This Next.js project was bootstrapped with
create-next-app.
-
Create a feature flag in your LaunchDarkly account with the following details:
Flag Key Flag Type Description simple-toggle boolean Toggles flag status -
Clone this repository and navigate to the project directory.
-
Install the required packages by running:
npm install -
Create a
.envfile in the project root and add the following environment variables:LAUNCHDARKLY_SDK_KEY="<LaunchDarkly Server-side SDK Key" CLIENT_SIDE_ID="<LaunchDarkly Client Side ID>"Replace
<LaunchDarkly Server-side SDK Key>with your LaunchDarkly server-side SDK key and<LaunchDarkly Client-side ID>with your LaunchDarkly client-side ID.
-
Start the development server:
npm run devNote: If you encounter a Server 500 error while running the app, as discussed in vercel/next.js#49677, switch to Node.js version 16.8.
-
Open http://localhost:3000 with your browser to see the result.
For more information check out the following resources:
- LaunchDarkly React Web SDK - how to get started with the client-side React Web SDK, and links to reference information on all of the supported features.
- LaunchDarkly Quick Start Guide - describes how to get started with LaunchDarkly
- Next.js Documentation - learn about Next.js features and API.
- Learn Next.js - an interactive Next.js tutorial.
The easiest way to deploy your Next.js app is to use the Vercel Platform from the creators of Next.js.
Check out our Next.js deployment documentation for more details.