- Kubernetes
- Containers - Docker
- Container Orchestration?
- Setup Kubernetes
- k8 Concepts - PODs | ReplicaSets | Deployment | services
- Networking in kubernetes
- Kubernetes Management - Kubectl
- Kubernetes Definition Files - YAML
- Kubernetes on Cloud - AWS/GCP
- k8 -> Build by Google
- Google's Container Orchestration tools
- Open Source
- k8 --> Containers + Orchestration
- k8 -> open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- Ref: https://kubernetes.io/
- Why do we need containers ?
- Remeber about - Matrix from Hell !! (Each OS - Installing different s/w(redis,node) requires different configuration/setup which leads to ==> Compatibility/Dependency, Long setup time, Different dev/val/prod env makes it much complex, works in my system) <== Thus development, building and shipping take more time and not-smooth
- To solve this Matrix from Hell issue --> Birth of Docker
- Docker runs each component (s/w- Nodejs server, redis, mongodb) in its own Container
- Think Containers are separate environment for your component/images
- These Containers has its own libraries & Dependencies
- Thus we can quickly start running this image (without had to worry abt configur) just by running the docker image provided by DevOps team
- Thus Docker --> Containerize Application (Provides each appln/image its own environment)
- What are containers ?
- Containers are completely isolated Environments
- Containers has its own Processes, Network, Mounts
- Think Containers are like- VM except they share same OS-Kernel
- If your base/host OS Kernel is (Ubuntu)Linux then you can run container application of os like- fedora, suse, redhat (linux flavour) BUT YOU CANNOT RUN WINDOWS/MAC Conatiner Application on Linux based OS Kernel
- Docker is not meant to virtualize and run different Operating System (as done by VM) but main purpose of docker is to containerize the application (like- nodejs. redis, etc) and ship & run them
- H/w Infrastructure >> OS Kernel >> DOCKER >> {(lib + dependency) => Application} => Container
- VM : Heaver is Size (iso images in GB) thus use hig disk-space, take lot of RAM uses lot of resources, and Take more time to boot-up Containers: lower disk-space, less ram is utilized, fast boot-up
- Most popular containerizing techonlogy - docker
- Public Docker Registry --> Docker Hub (Where you can containerized ur custome application as images)
- Docker Hosts <-- (Think like VM HOST but for docker, Base Machine where docker was installed upon ur OS Kernel)
- When you run the docker image ->
docker run ansible(This will run the Instance of Ansible application on your docker host) - Docker images are run as instance is called containers
- Container v/s images
- Image is a package template (Think image as Class)
- When you run a particular image --> it create instance of this image/application is called containers (Think Container as Instance of a class)
- Containers are instance of a image which are isolated, each containers has its own environment,processes,network,mount
- Run you first docker image :
docker run hello-world - Secound image:
docker run docker/whalesay cowsay boo
- What is Orchestration:
- Orchestration is the automated configuration, management, and coordination of computer systems, applications, and services
- Orchestration helps IT to more easily manage complex tasks and workflows.
- Automation and orchestration are different, but related concepts.
- automation refers to automating a single task. This is different from orchestration, which is how you can automate a process or workflow that involves many steps across multiple disparate(different kind of) systems.
- Ref: https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/automation/what-is-orchestration
- How to run Docker host and all its container in Prod environment, how to scale-up or down different docker host based on traffic, Connect b/w docker Hosts, Managing containers etc --done_by--> Container Orchestration
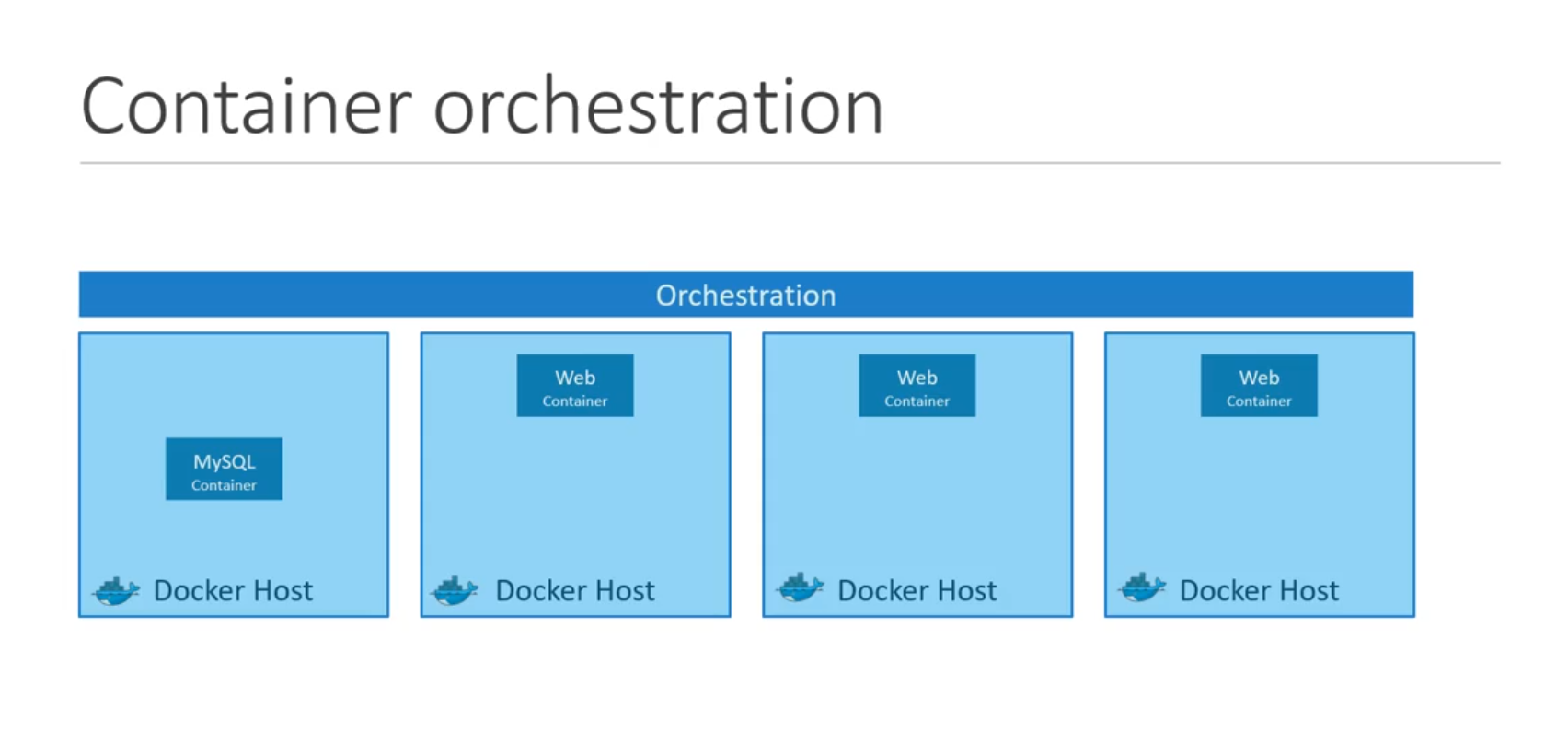
- Automatically deploying, Managing containers based on traffic, etc is know as Container Orchestration technology
- Kubernetes is Container Orchestration Technology ( Other technologies are - Docker Swarm, MESOS )
- Kubernetes is now avaliable in all Cloud Providers like- GCP, Amazon, Azure
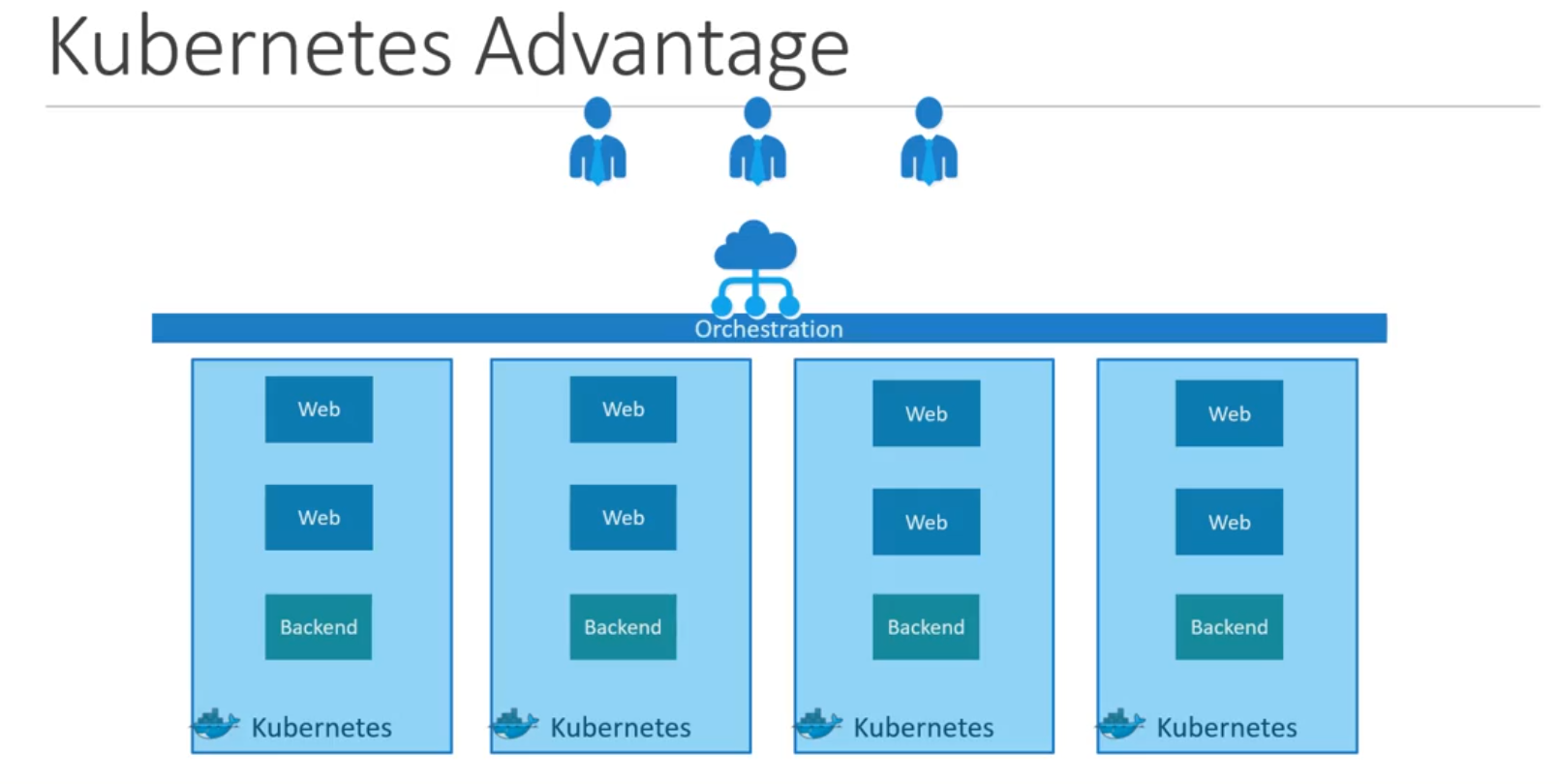
- Advantages
- Thus Kubernetes is Container Orchestration Technology which help to deploy and Manage containers in an clustered environment.
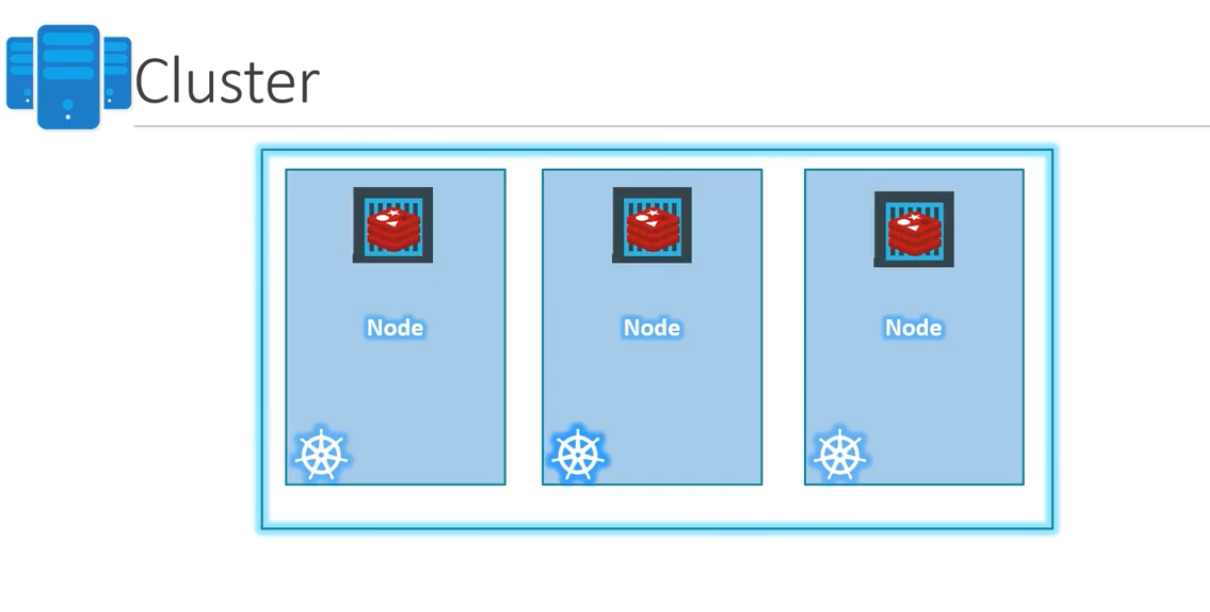
- Nodes
- Cluster
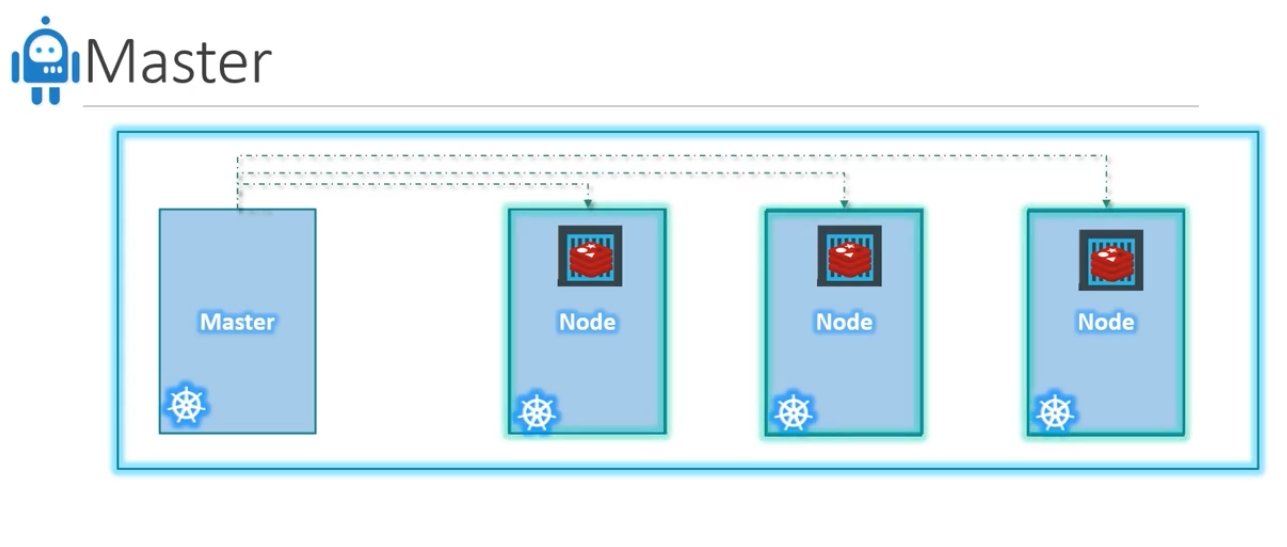
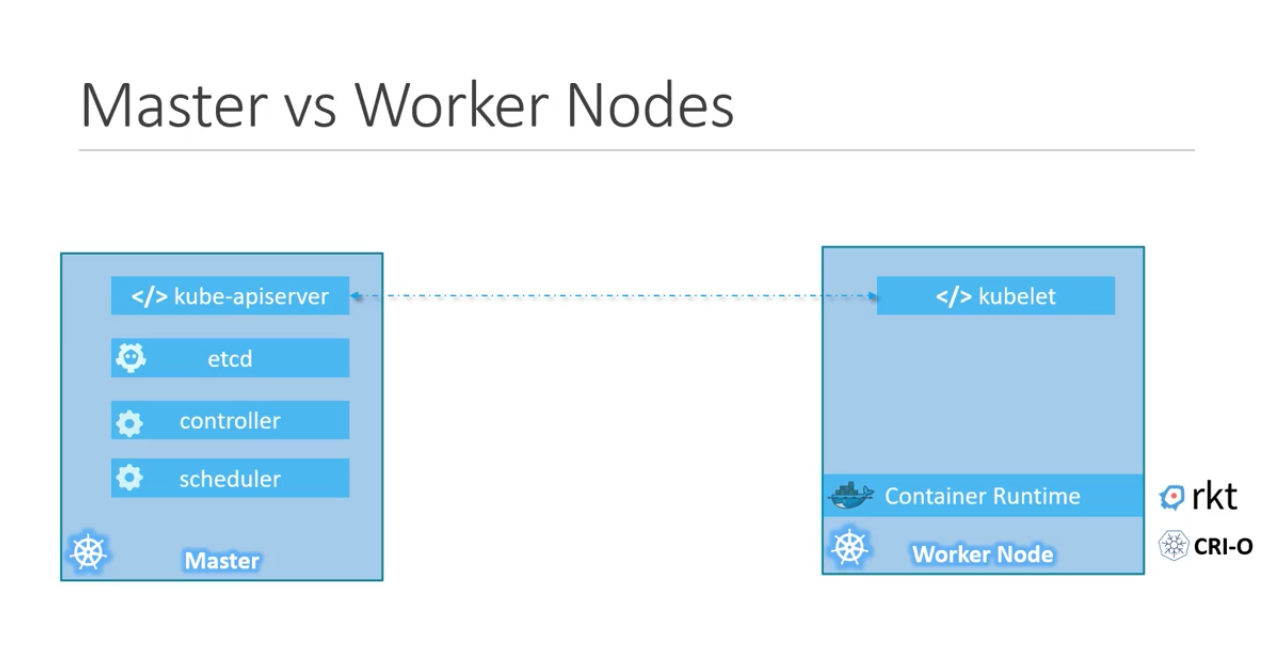
- Master
- Master is responsible for managing the cluster
- Other responsibility of Master node is - information of member of cluster stored, monitoring of all worker nodes, if a node fail then need to move the workload from fail node to another worker node
- Master is another node in which kubernetes installed in it (Configured it as Master Node).
- Master node is responsible for actual orchestration on worker nodes
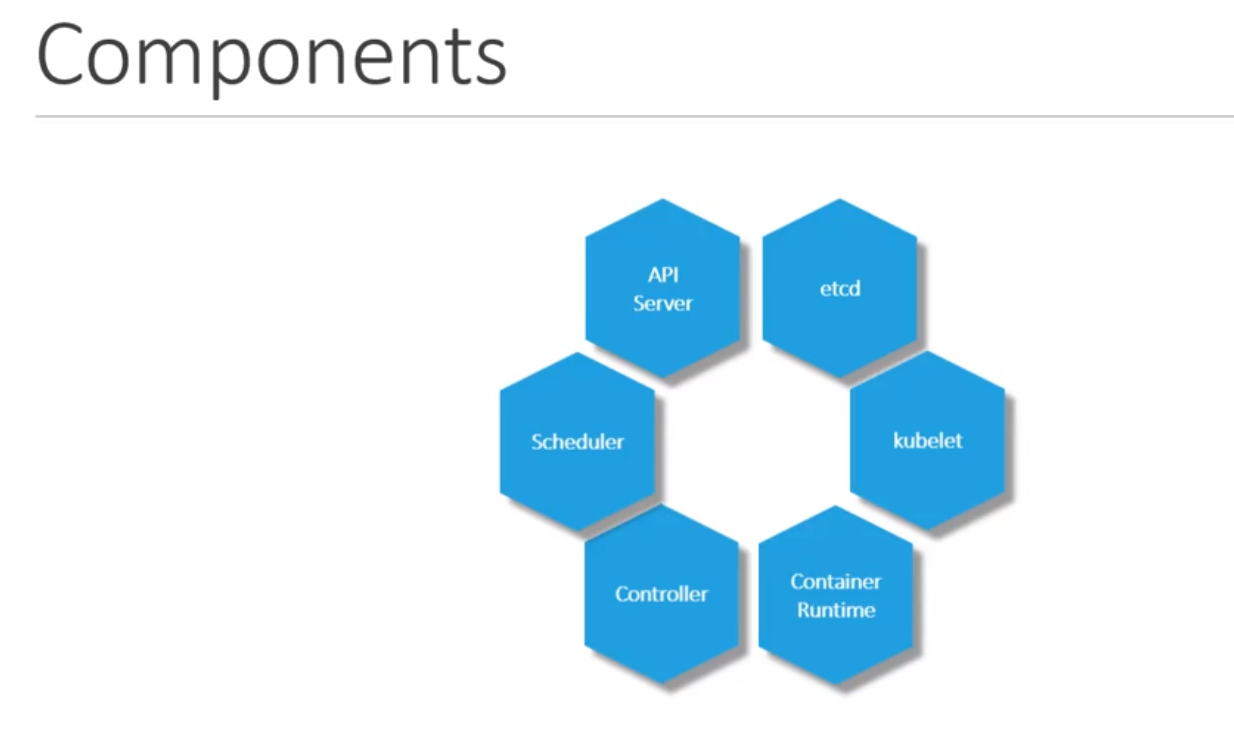
- K8 comes with following components:
- How can we distribute the kubernetes components among different servers (Consider you have different physical servers running fedora), How can we make one server Master Node and other Server Wokrer Nodes
- Worker Nodes or Minions <---where--- containers are hosted
- In order to run docker containers we require - Container Runtime Engine (ex- Docker, Rkt, CRI-O)
- Worker nodes has - kubelet agent
- Master Node has -> kube-apiserver (which make this server as Master node)
- Master component has etcd, controller, scheduler
- Kubernetes CLI - kube control tool (kubectl)
- Used to deploy and Manage application on kubernetes cluster- to get cluster information, get status of other nodes, etc
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl-macos/
- To deploy an application on cluster
\$ kubectl run hello-min
- To view cluster information
\$ kubectl cluster-info
- To list all nodes information
\$ kubectl get nodes
- Using kubectl we can run thousand instance of same application with single command.
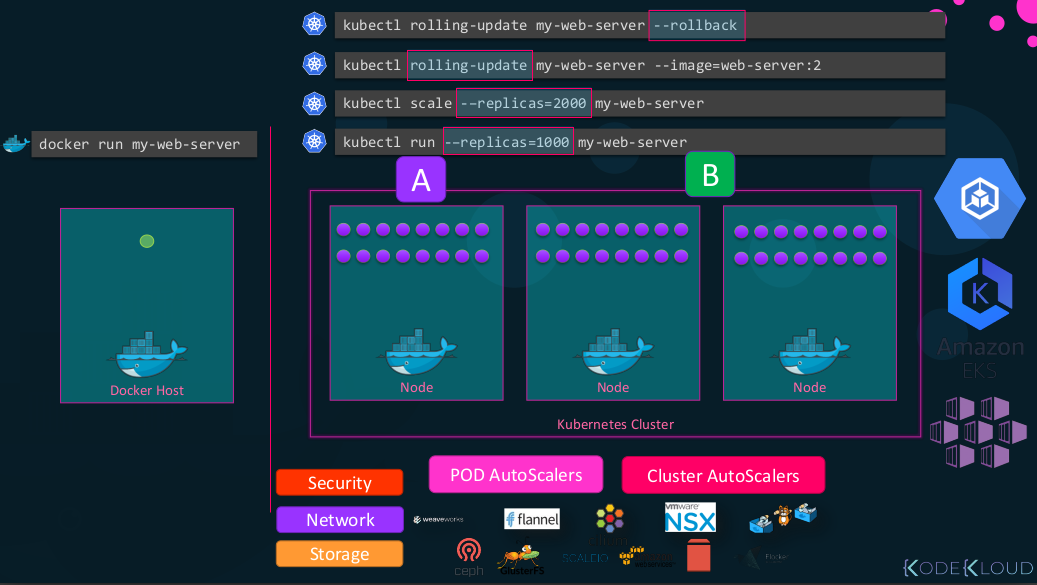
\$ kubectl run --replicas=1000 my-web-server
- We can confifure Kubernetes such that it can automatically handle traffic load and scale-up or down the instance depending on traffic, do load balancing, etc
\$ kubectl scale --replicas=2000 my-web-server
- with rolling-update command it can also upgrade these thousands of instances.
- k8 uses Docker Host inorder to host docker containers.
- K8 also provides alternative of docker -> Rocket
- Before Pods we assume that
- Our project appln is developed, build into docker images and these images are avaliable in docker repositry/hub (public registry) so that k8 can pull it down.
- Kubernetes Cluster is setup and its working (Single Node or Multi-Node cluster)
- K8 aim to deploy application in the form of Containers on set-of m/c which are configured as worker node in a cluster
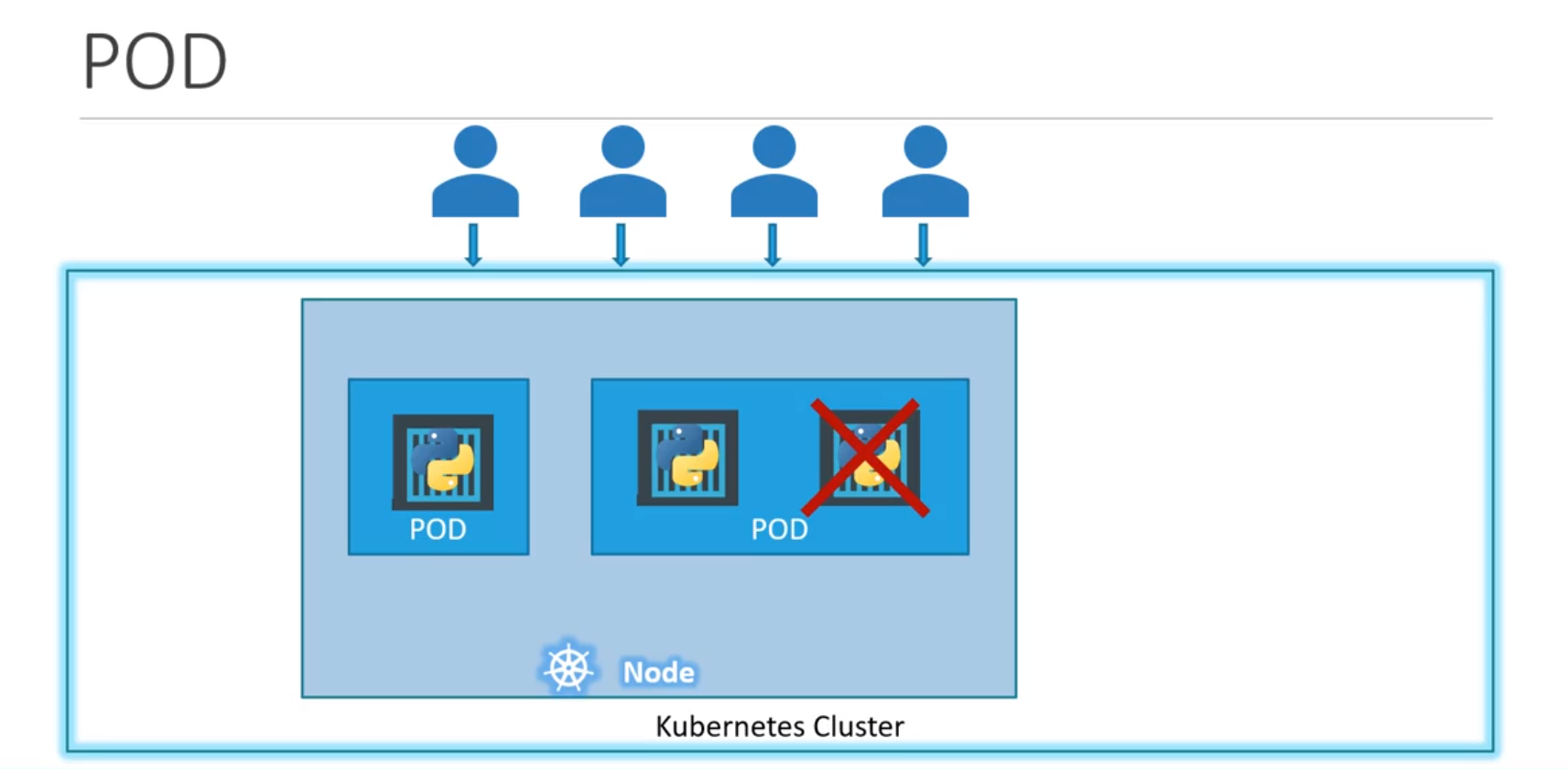
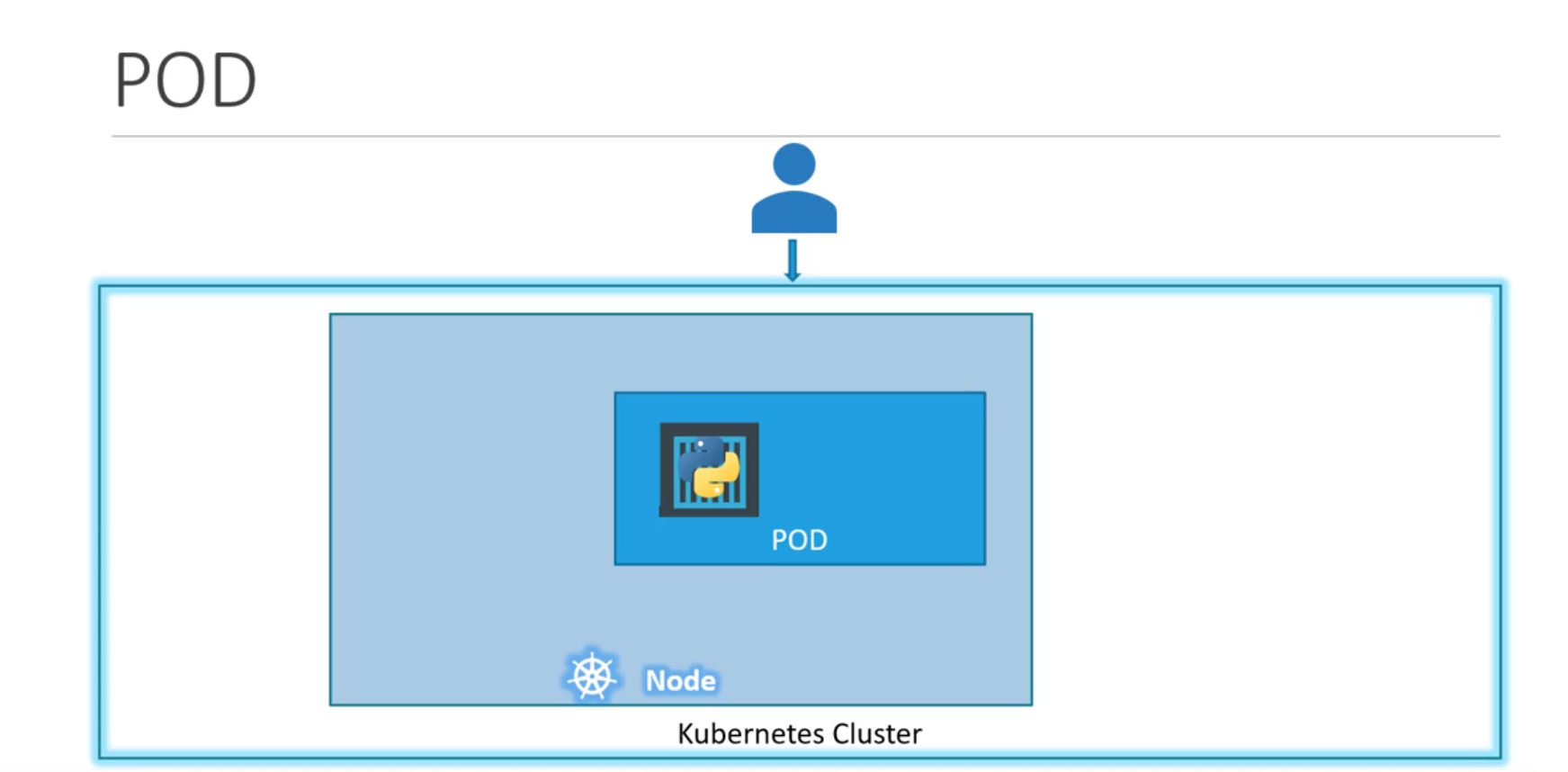
- k8 does not deploy containers directly onto worker Nodes, rather the containers are encapsulated into an k8-objects called --> PODs
- A Pod is a single instance of an application
- A Pod is smallest object which we can create in k8
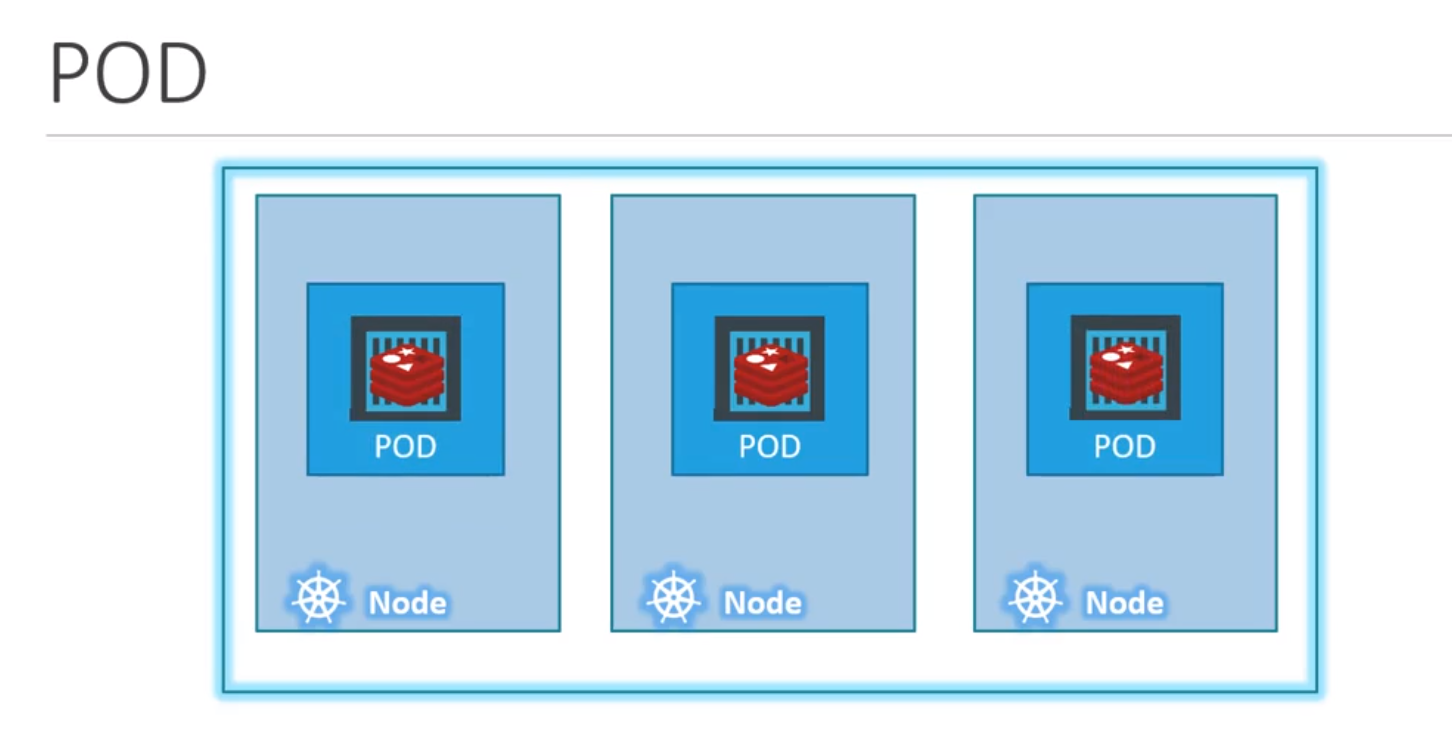
- Example/Use-case
- let us consider we have Single node k8 cluster, Single instance of our appln, which is running in a single docker container encapsulated in a pod
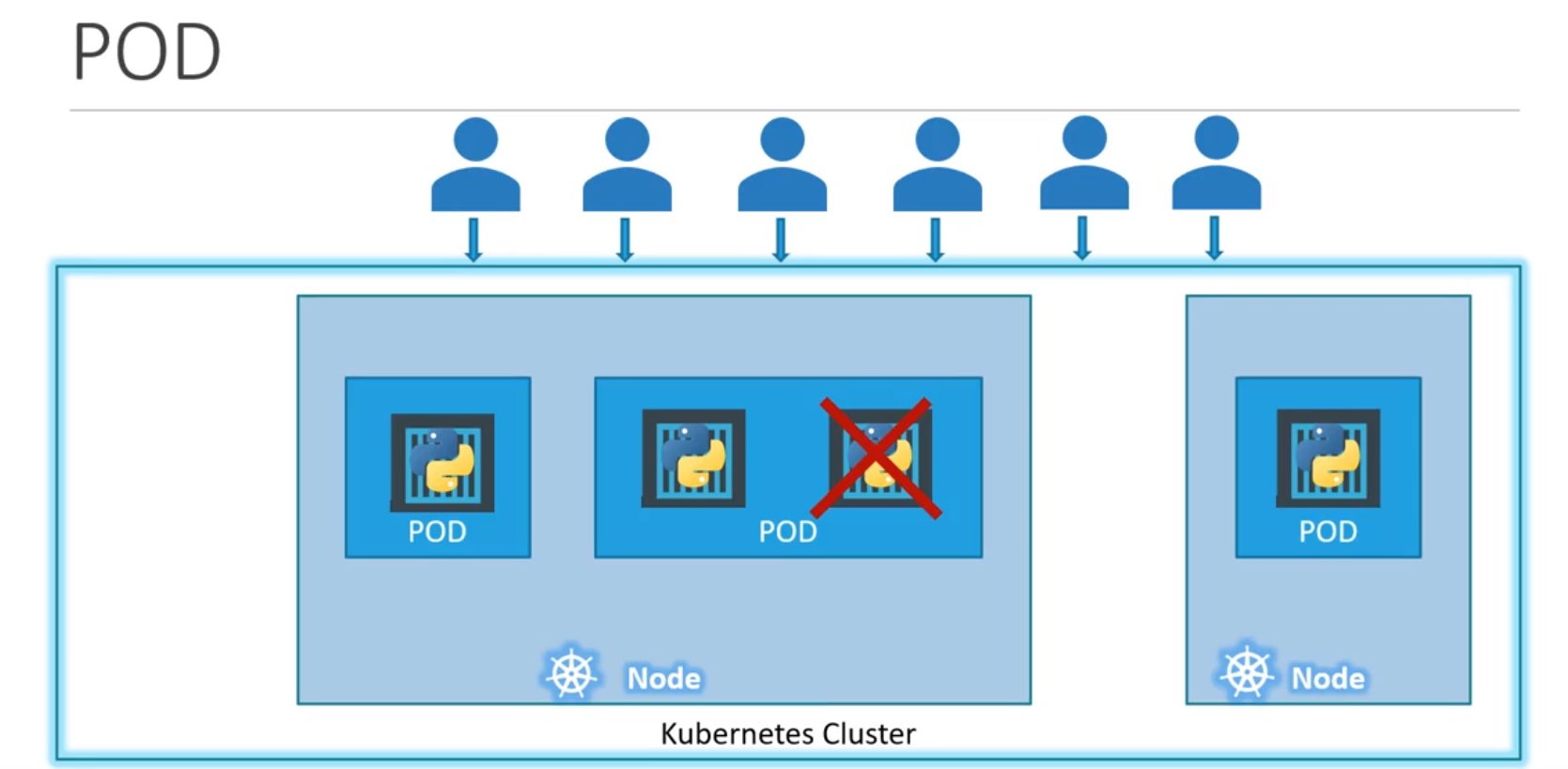
- But for above example let us consider If user/client load increases, then inorder to scale our appln:
- Let us say, current still increase such that current worker-node can no-more create a new instance of pod underneath (reach threshold), then soln->
- let us consider we have Single node k8 cluster, Single instance of our appln, which is running in a single docker container encapsulated in a pod
- Thus we can conclude that: Pods have one-2-one (or direct) relation with containers running your appln
- Also In-general for scaling:
- To scale-up (high load) --> Create/spin-up new pods
- To scale-down (no much load) --> Delete/spin-down exisiting pods
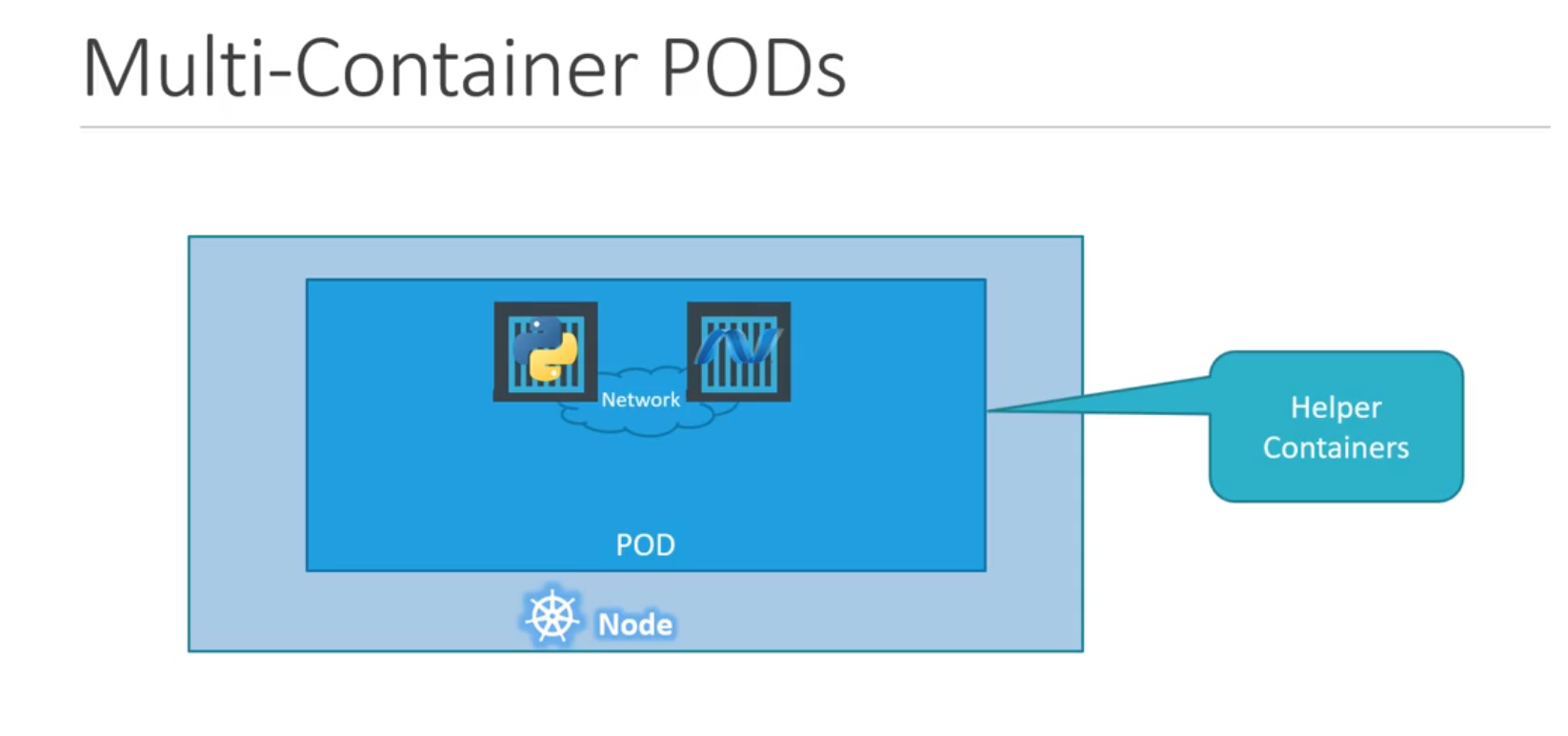
- Multi-container Pods (Rear use-case)
- In general we would always have each/one pod containg --> one instance of our appln (or - one container)
- But in-practice we can have helper containers within the same pod,
- i.e- one container for your appln + another container ex- monitoring/logging <-- Inside the same POD
- Helper container lives a long side with your appln container, If every new pod is created then both appln container & helper container is also created together, If pod dies both of them dies/destory too.
- NOTE: these 2 containers can communicate/speak with each other --using--> (localhost) as there in same network space
\$ kubectl run nginx --image nginx(Runs/deploy nginx image instance as a container inside a pod (which is inside a node)) [NOTE: --image nginx <== Image/Repositry name in dockerHub]\$ kubectl get pods(list of pods running) [NOTE: Container first would be in ContainerCreating status & then Running status]-

- https://kodekloud.com/lessons/kubernetes-for-beginners-labs/
- use the couponcode provided in Udemy Section-1, Accessing the labs