A PoC for an Ethereum transaction simulator, which compares two approaches:
- Use standard ETH RPC calls to fetch the needed state for the simulation and run the EVM code locally
- Use a local reth DB to fetch the data and run the EVM code locally
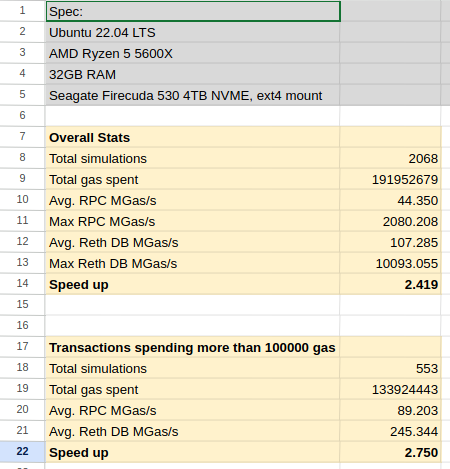
The local DB approach is much faster compared to using RPC, even when the RPC is running locally.
Here are some benchmark results of simulating mempool transactions using reth running locally on Ubuntu 22.04, Ryzen 5 5600X, 24GB RAM, Seagate FireCuda 530 4TB NVME.
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1lolaKiBNtQuFktuw8Pa2tnWLtJcWKG_gHQF06cMCrd4/edit?usp=sharing
You can see from the results that the Reth DB speed is over 2x faster, compare to using the RPC interface of the node.
In order to run the mempool simulator copy the .env.example file to .env. Set WS_RPC_URL and HTTP_RPC_URL to a node which supports fetching the pending transactions in the mempool. Also set RETH_DB_PATH to the location of the DB of a locally synced reth node.
$ cp .env.example .env
$ cargo run --releaseMake sure to run with --release, so that you can see the true performance of the reth DB simulator.