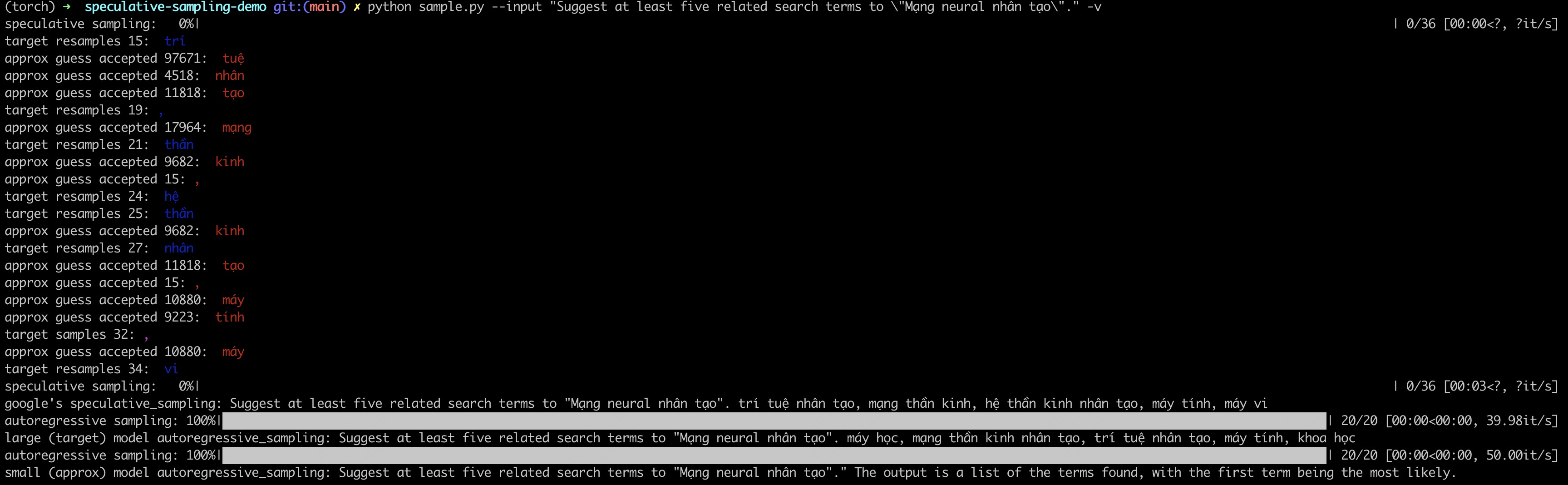
This repo implements a speculative sampling for large lauguage model(LLM) decoding. It uses two models during decoding: a target model and an approximation model. The apporximation model is a smaller model and target model is a larger one. The apporximation model guess tokens and the target model corrects the guesses. Therefore, it decodes by running the target model in parallel on the outputs of the approximation models, which is more efficient than decoding with the target model alone.
The speculative sampling is proposed by Google and Deepmind independently. So I implement two slightly different versions of speculative sampling: Google's and Deepmind's.
In the sample, I use bloomz-7b1 as the target model, bloom-560m as the approximation model.
python sample.py \
--input "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy " \
--target_model_name bigscience/bloomz-7b1 \
--approx_model_name bigscience/bloom-560mYou can also use --v args to see a token is generated by which model.
@inproceedings{leviathan2023fast,
title={Fast inference from transformers via speculative decoding},
author={Leviathan, Yaniv and Kalman, Matan and Matias, Yossi},
booktitle={International Conference on Machine Learning},
pages={19274--19286},
year={2023},
organization={PMLR}
}
@article{chen2023accelerating,
title={Accelerating large language model decoding with speculative sampling},
author={Chen, Charlie and Borgeaud, Sebastian and Irving, Geoffrey and Lespiau, Jean-Baptiste and Sifre, Laurent and Jumper, John},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.01318},
year={2023}
}
This repo is built for demostration purpose. Other optimizations such as batching and KV Caching are not included which are essential for efficiency.