GitHub Action for executing remote ssh commands.
Important: Only support Linux docker container.
See action.yml for more detailed information.
host- ssh hostport- ssh port, default is22username- ssh usernamepassword- ssh passwordpassphrase- the passphrase is usually to encrypt the private keysync- synchronous execution if multiple hosts, default is falsetimeout- timeout for ssh to remote host, default is30scommand_timeout- timeout for ssh command, default is10mkey- content of ssh private key. ex raw content of ~/.ssh/id_rsa, remember include the BEGIN and END lineskey_path- path of ssh private keyfingerprint- fingerprint SHA256 of the host public key, default is to skip verificationscript- execute commandsscript_stop- stop script after first failureenvs- pass environment variable to shell scriptdebug- enable debug modeuse_insecure_cipher- include more ciphers with use_insecure_cipher (see #56)cipher- the allowed cipher algorithms. If unspecified then a sensible
SSH Proxy Setting:
proxy_host- proxy hostproxy_port- proxy port, default is22proxy_username- proxy usernameproxy_password- proxy passwordproxy_passphrase- the passphrase is usually to encrypt the private keyproxy_timeout- timeout for ssh to proxy host, default is30sproxy_key- content of ssh proxy private key.proxy_key_path- path of ssh proxy private keyproxy_fingerprint- fingerprint SHA256 of the proxy host public key, default is to skip verificationproxy_use_insecure_cipher- include more ciphers with use_insecure_cipher (see #56)proxy_cipher- the allowed cipher algorithms. If unspecified then a sensible
Executing remote ssh commands.
name: remote ssh command
on: [push]
jobs:
build:
name: Build
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: executing remote ssh commands using password
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.PASSWORD }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
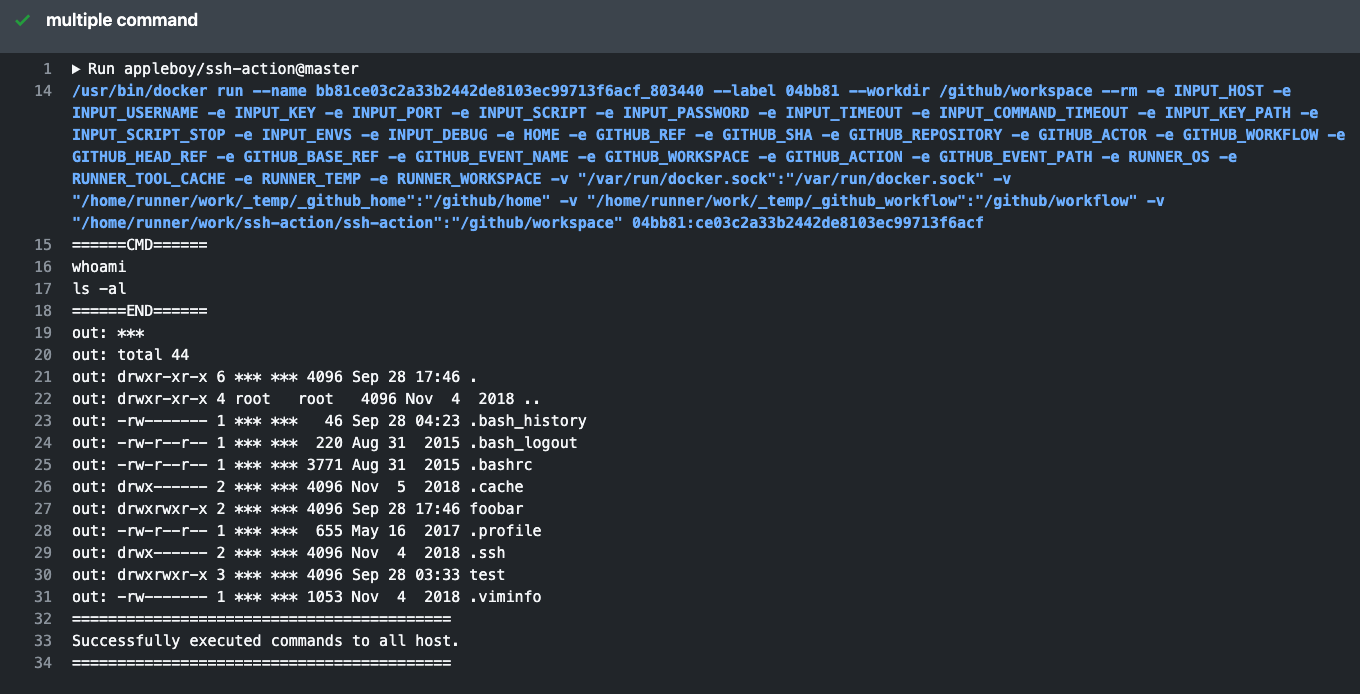
script: whoamioutput:
======CMD======
whoami
======END======
out: ***
==============================================
✅ Successfully executed commands to all host.
==============================================Make sure to follow the below steps while creating SSH Keys and using them. The best practice is create the SSH Keys on local machine not remote machine. Login with username specified in Github Secrets. Generate a RSA Key-Pair:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -a 200 -C "your_email@example.com"Add newly generated key into Authorized keys. Read more about authorized keys here.
cat .ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh b@B 'cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys'cat .ssh/id_ed25519.pub | ssh b@B 'cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys'Copy Private Key content and paste in Github Secrets.
clip < ~/.ssh/id_rsaclip < ~/.ssh/id_ed25519See the detail information about SSH login without password.
A note from one of our readers: Depending on your version of SSH you might also have to do the following changes:
- Put the public key in
.ssh/authorized_keys2 - Change the permissions of
.sshto 700 - Change the permissions of
.ssh/authorized_keys2to 640
If you are currently using OpenSSH and are getting the following error:
ssh: handshake failed: ssh: unable to authenticate, attempted methods [none publickey]Make sure that your key algorithm of choice is supported. On Ubuntu 20.04 or later you must explicitly allow the use of the ssh-rsa algorithm. Add the following line to your OpenSSH daemon file (which is either /etc/ssh/sshd_config or a drop-in file under /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/):
CASignatureAlgorithms +ssh-rsaAlternatively, ed25519 keys are accepted by default in OpenSSH. You could use this instead of rsa if needed:
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -a 200 -C "your_email@example.com"- name: executing remote ssh commands using password
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.PASSWORD }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
script: whoami- name: executing remote ssh commands using ssh key
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
script: whoami- name: multiple command
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
script: |
whoami
ls -al - name: multiple host
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
- host: "foo.com"
+ host: "foo.com,bar.com"
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
script: |
whoami
ls -al - name: multiple host
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
- host: "foo.com"
+ host: "foo.com:1234,bar.com:5678"
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.KEY }}
script: |
whoami
ls -al - name: multiple host
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
host: "foo.com,bar.com"
+ sync: true
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
script: |
whoami
ls -al - name: pass environment
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
+ env:
+ FOO: "BAR"
+ BAR: "FOO"
+ SHA: ${{ github.sha }}
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
+ envs: FOO,BAR,SHA
script: |
echo "I am $FOO"
echo "I am $BAR"
echo "sha: $SHA"Inside env object, you need to pass every environment variable as a string, passing Integer data type or any other may output unexpected results.
ex: missing
abcfolder
- name: stop script if command error
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
+ script_stop: true
script: |
mkdir abc/def
ls -aloutput:
======CMD======
mkdir abc/def
ls -al
======END======
2019/11/21 01:16:21 Process exited with status 1
err: mkdir: cannot create directory ‘abc/def’: No such file or directory
##[error]Docker run failed with exit code 1+--------+ +----------+ +-----------+
| Laptop | <--> | Jumphost | <--> | FooServer |
+--------+ +----------+ +-----------+in your ~/.ssh/config, you will see the following.
Host Jumphost
HostName Jumphost
User ubuntu
Port 22
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/keys/jump_host.pem
Host FooServer
HostName FooServer
User ubuntu
Port 22
ProxyCommand ssh -q -W %h:%p Jumphost - name: ssh proxy command
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
+ proxy_host: ${{ secrets.PROXY_HOST }}
+ proxy_username: ${{ secrets.PROXY_USERNAME }}
+ proxy_key: ${{ secrets.PROXY_KEY }}
+ proxy_port: ${{ secrets.PROXY_PORT }}
script: |
mkdir abc/def
ls -alThe purpose of the passphrase is usually to encrypt the private key. This makes the key file by itself useless to an attacker. It is not uncommon for files to leak from backups or decommissioned hardware, and hackers commonly exfiltrate files from compromised systems.
- name: ssh key passphrase
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
+ passphrase: ${{ secrets.PASSPHRASE }}
script: |
whoami
ls -alSetting up SSH host fingerprint verification can help to prevent Person-in-the-Middle attacks. Before setting this up, run the command below to get your SSH host fingerprint. Remember to replace ed25519 with your appropriate key type (rsa, dsa, etc.) that your server is using and example.com with your host.
In modern OpenSSH releases, the default key types to be fetched are rsa (since version 5.1), ecdsa (since version 6.0), and ed25519 (since version 6.7).
ssh example.com ssh-keygen -l -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key.pub | cut -d ' ' -f2Now you can adjust you config:
- name: ssh key passphrase
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v0.1.8
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
+ fingerprint: ${{ secrets.FINGERPRINT }}
script: |
whoami
ls -alWe would love for you to contribute to appleboy/ssh-action, pull requests are welcome!
The scripts and documentation in this project are released under the MIT License