This is the implementation for our paper "Ensemble of Narrow DNN Chains" (my Machine Learning course essay at Oxford).
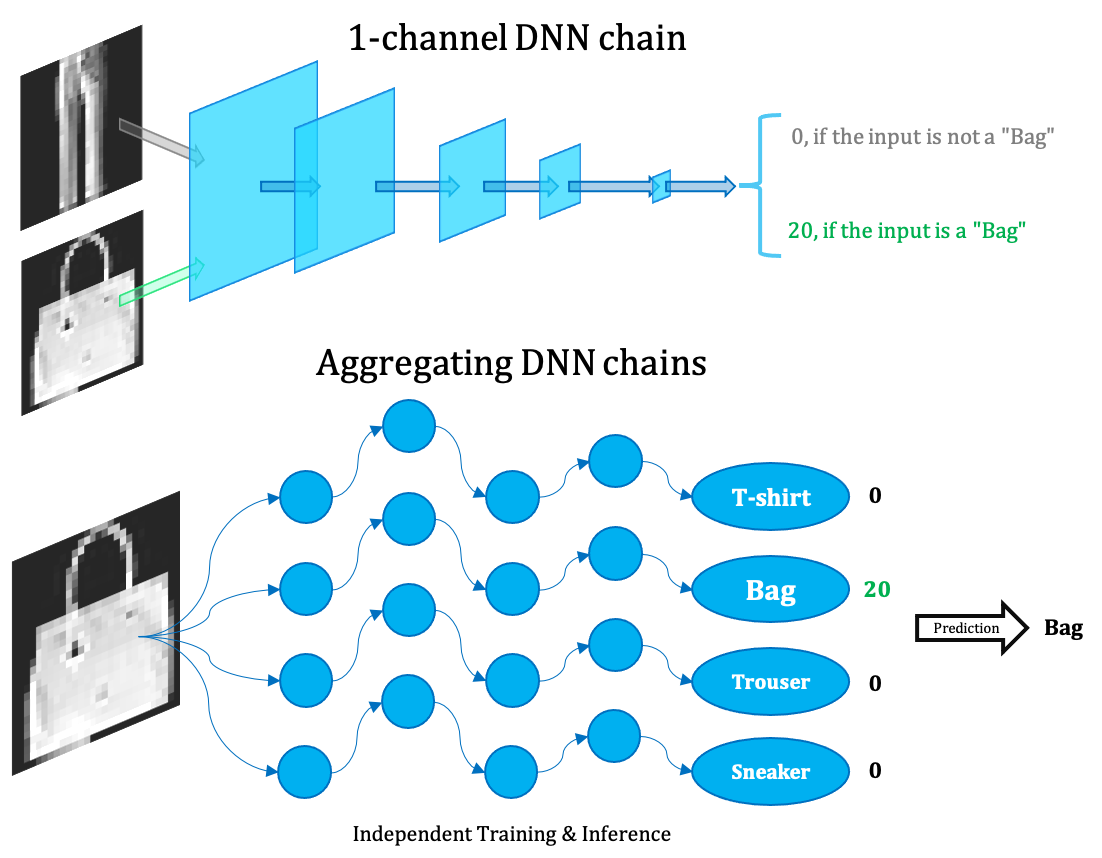
We propose the Ensemble of Narrow DNN Chains (ENDC) framework:
- first train such narrow DNN chains that perform well on one-vs-all binary classification tasks,
- then aggregate them together by voting to predict for the multiclassification task.
Our ensemble framework could:
- utilize the abstract interpretability of DNNs,
- outperform traditional ML significantly on CIFAR-10,
- while being 2-4 orders of magnitude smaller than normal DNN and 6+ times smaller than traditional ML models,
- furthermore compatible with full parallelism in both the training and deployment stage.
Our empirical study shows that a narrow DNN chain could learn binary classifications well. Moreover, our experiments on three MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, CIFAR-10 confirm the potential power of ENDC. Compared with traditional ML models, ENDC, with the smallest parameter number, could achieve similar accuracy on MNIST and Fashion-MNIST, and significantly better accuracy on CIFAR-10.
| Dataset | Accuracy | Arch | #Param |
|---|---|---|---|
| MNIST | 93.40% | 1-channel | 1300 |
| Fashion-MNIST | 80.39% | 1-channel | 1300 |
| CIFAR-10 | 47.72% | 2-channel | 4930 |
- Each binary classifier's parameter number is even smaller than the input entry (130 < 28x28 for MNIST and Fashion-MNIST, 493 < 3x32x32 for CIFAR-10)!
We compare ENDC with traditional ML models:
- Logistic Regression (LR)
- Support Vector Classifier (SVC)
and normal DNNs. Their results are referenced from internet, see our paper for sources and details.
MNIST
| Method | Accuracy (%) | # Param |
|---|---|---|
| ENDC (ours) | 93.4 | 1.3K |
| LR | 91.7 | 7.7K+ |
| SVC | 97.8 | 7.7K+ |
| Normal DNN (LeNet) | 99.3 | 0.41M |
Fashion-MNIST
| Method | Accuracy (%) | # Param |
|---|---|---|
| ENDC (ours) | 80.4 | 1.3K |
| LR | 84.2 | 7.7K+ |
| SVC | 89.7 | 7.7K+ |
| Normal DNN (VGG-16) | 93.5 | 26M |
CIFAR-10
| Method | Accuracy (%) | # Param |
|---|---|---|
| ENDC (ours) | 47.7 | 4.8K |
| LR | 39.9 | 30.0K+ |
| SVC (PCA) | 40.2 | 0.44M+ |
| Normal DNN (VGG-16-BN) | 93.9 | 15M |
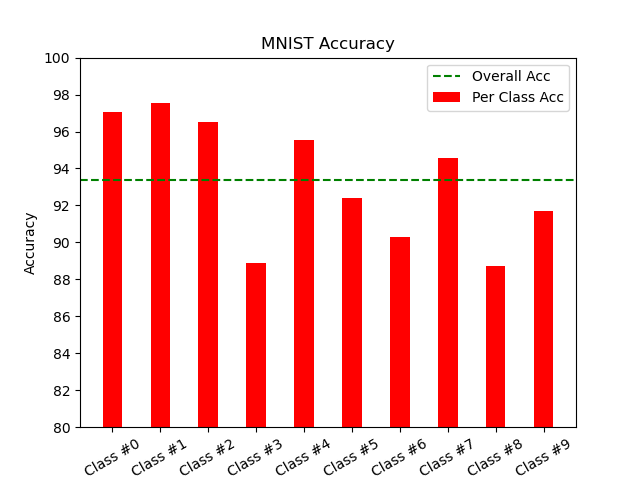
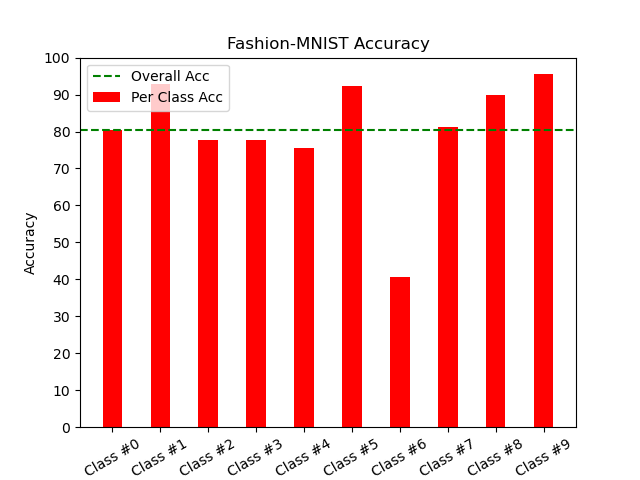
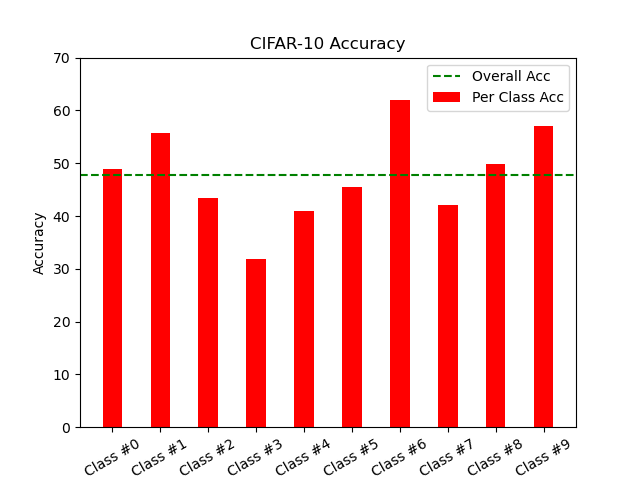
| Dataset | #0 (%) | #1 (%) | #2 (%) | #3 (%) | #4 (%) | #5 (%) | #6 (%) | #7 (%) | #8 (%) | #9 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNIST | 97.04 | 97.53 | 96.51 | 88.91 | 95.52 | 92.38 | 90.29 | 94.55 | 88.71 | 91.67 |
| Fashion-MNIST | 80.60 | 92.90 | 77.60 | 77.60 | 75.50 | 92.30 | 40.70 | 81.30 | 90.00 | 95.50 |
| CIFAR-10 | 48.90 | 55.70 | 43.50 | 31.80 | 41.00 | 45.40 | 61.90 | 42.00 | 49.90 | 57.10 |
- First run datasets/downloader.py to download the MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, and CIFAR-10 datasets under datasets/.
- Then follow the notebooks at notebooks/.
- Our trained narrow DNN chains are provided under checkpoints/, with their activation distribution histograms and ROC curves at assets/.
- Only convolution layers are adopted.
- The 1-channel DNN chain (for MNIST and Fashion-MNIST) architecture:
narrow_VGG( (features): Sequential( (0): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (1): ReLU(inplace=True) (2): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (3): ReLU(inplace=True) (4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) (5): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (6): ReLU(inplace=True) (7): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (8): ReLU(inplace=True) (9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) (10): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (11): ReLU(inplace=True) (12): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (13): ReLU(inplace=True) (14): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (15): ReLU(inplace=True) (16): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) (17): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (18): ReLU(inplace=True) (19): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (20): ReLU(inplace=True) (21): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (22): ReLU(inplace=True) (23): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) (24): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (25): ReLU(inplace=True) (26): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (27): ReLU(inplace=True) (28): Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (29): ReLU(inplace=True) (30): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) ) )
- The 2-channel DNN chain (for CIFAR-10) architecture:
narrow_VGG( (features): Sequential( (0): Conv2d(3, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (1): ReLU(inplace=True) (2): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (3): ReLU(inplace=True) (4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) (5): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (6): ReLU(inplace=True) (7): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (8): ReLU(inplace=True) (9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) (10): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (11): ReLU(inplace=True) (12): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (13): ReLU(inplace=True) (14): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (15): ReLU(inplace=True) (16): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) (17): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (18): ReLU(inplace=True) (19): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (20): ReLU(inplace=True) (21): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (22): ReLU(inplace=True) (23): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) (24): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (25): ReLU(inplace=True) (26): Conv2d(2, 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (27): ReLU(inplace=True) (28): Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)) (29): ReLU(inplace=True) (30): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) ) )