aiomonitor-ng is a (temporary) fork of aiomonitor with support for Python 3.10+ and additional usability & debuggability improvements.
aiomonitor is a module that adds monitor and cli capabilities for asyncio applications. Idea and code were borrowed from curio project. Task monitor that runs concurrently to the asyncio loop (or fast drop-in replacement uvloop) in a separate thread as result monitor will work even if the event loop is blocked for some reason.
This library provides a python console using aioconsole module. It is possible to execute asynchronous commands inside your running application. Extensible with you own commands, in the style of the standard library's cmd module
Installation process is simple, just:
$ pip install aiomonitor-ng
Monitor has context manager interface:
import aiomonitor
async def main():
loop = asyncio.get_running_loop()
run_forever = loop.create_future()
with aiomonitor.start_monitor(loop):
await run_forever
try:
asyncio.run(main())
except KeyboardInterrupt:
passNow from separate terminal it is possible to connect to the application:
$ telnet localhost 50101
or the included python client:
$ python -m aiomonitor.cli
Let's create a simple aiohttp application, and see how aiomonitor can
be integrated with it.
import asyncio
import aiomonitor
from aiohttp import web
# Simple handler that returns response after 100s
async def simple(request):
loop = request.app.loop
print('Start sleeping')
await asyncio.sleep(100)
return web.Response(text="Simple answer")
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
# create application and register route
app = web.Application()
app.router.add_get('/simple', simple)
# it is possible to pass a dictionary with local variables
# to the python console environment
host, port = "localhost", 8090
locals_ = {"port": port, "host": host}
# init monitor just before run_app
with aiomonitor.start_monitor(loop=loop, locals=locals_):
# run application with built-in aiohttp run_app function
web.run_app(app, port=port, host=host)Let's save this code in file simple_srv.py, so we can run it with the following command:
$ python simple_srv.py ======== Running on http://localhost:8090 ======== (Press CTRL+C to quit)
And now one can connect to a running application from a separate terminal, with
the telnet command, and aiomonitor will immediately respond with prompt:
$ telnet localhost 50101 Asyncio Monitor: 1 tasks running Type help for commands monitor >>>
Now you can type commands, for instance, help:
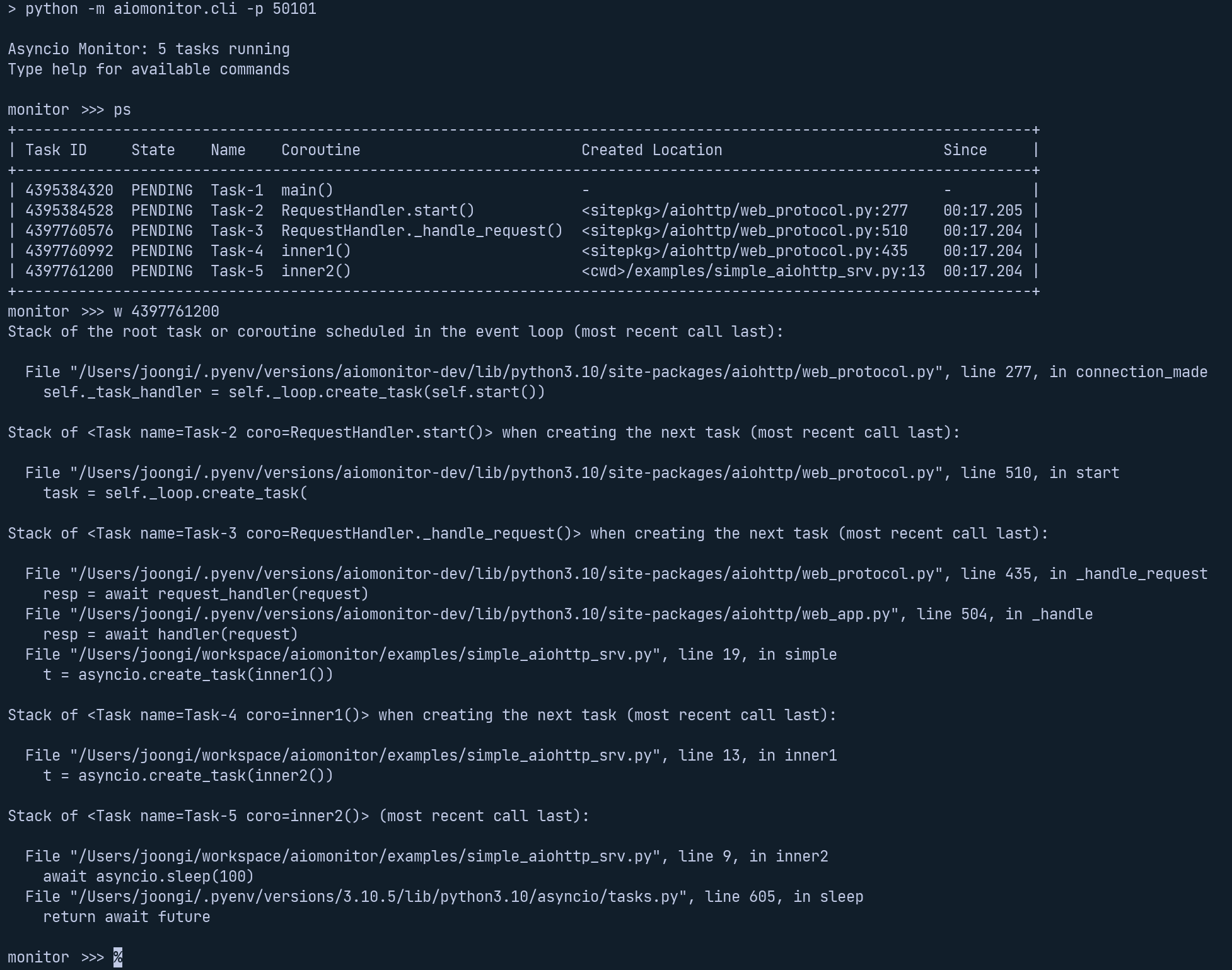
monitor >>> help Usage: help [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]... To see the usage of each command, run them with "--help" option. Commands: cancel Cancel an indicated task console Switch to async Python REPL exit (q,quit) Leave the monitor client session help (?,h) Show the list of commands ps (p) Show task table ps-terminated (pst,pt) List recently terminated/cancelled tasks signal Send a Unix signal stacktrace (st,stack) Print a stack trace from the event loop thread where (w) Show stack frames and the task creation chain of a task where-terminated (wt) Show stack frames and the termination/cancellation chain of a task
aiomonitor also supports async python console inside a running event loop
so you can explore the state of your application:
monitor >>> console Python 3.10.7 (main, Sep 9 2022, 12:31:20) [Clang 13.1.6 (clang-1316.0.21.2.5)] on darwin Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. --- This console is running in an asyncio event loop. It allows you to wait for coroutines using the 'await' syntax. Try: await asyncio.sleep(1, result=3) --- >>> await asyncio.sleep(1, result=3) 3 >>>
To leave the console type exit() or press Ctrl+D:
>>> exit() ✓ The console session is closed. monitor >>>
You may add more variables that can be directly referenced in the console command.
Refer the console-variables example code
aiomonitor is very easy to extend with your own console commands.
Refer the extension example code
- Python 3.8+ (3.10.7+ recommended)
- aioconsole
- Click
- prompt_toolkit
- uvloop (optional)