"Zero setup" cross compilation and "cross testing" of Rust crates
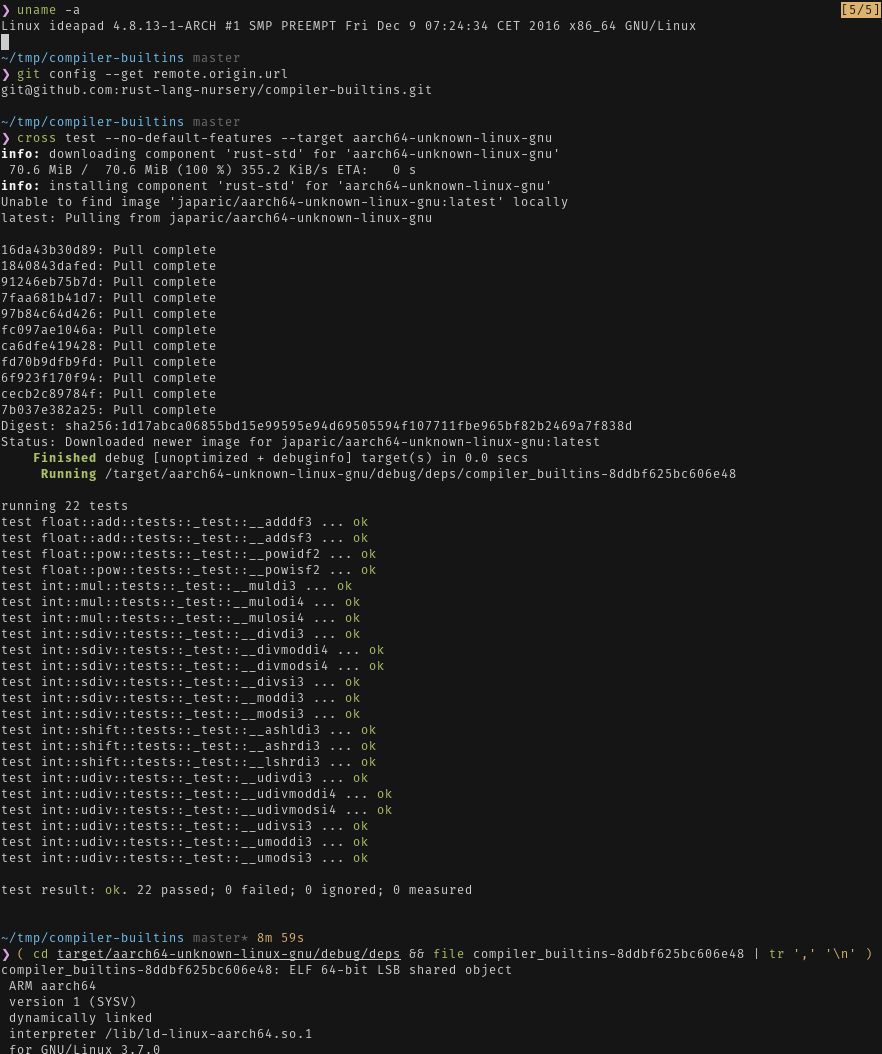
`cross test`ing a crate for the aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu target
Disclaimer: Only works on a x86_64 Linux host (e.g. Travis CI is supported)
-
crosswill provide all the ingredients needed for cross compilation without touching your system installation. -
crossprovides an environment, cross toolchain and cross compiled libraries (e.g. OpenSSL), that produces the most portable binaries. -
"cross testing",
crosscan test crates for architectures other than i686 and x86_64. -
The stable, beta and nightly channels are supported.
-
A Linux kernel with binfmt_misc support is required for cross testing.
$ cargo install cross
cross has the exact same CLI as Cargo
but as it relies on Docker you'll have to start the daemon before you can use
it.
# (ONCE PER BOOT)
# Start the Docker daemon, if it's not already running
$ sudo systemctl start docker
# MAGIC! This Just Works
$ cross build --target aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu
# EVEN MORE MAGICAL! This also Just Works
$ cross test --target mips64-unknown-linux-gnuabi64
# Obviously, this also Just Works
$ cross rustc --target powerpc-unknown-linux-gnu --release -- -C lto
You can place a Cross.toml file in the root of your Cargo project to tweak
cross's behavior:
The default Docker image that cross uses provides a C environment that tries
to cover the most common cross compilation cases. However, it can't cover every
single use case out there. When the default image is not enough, you can use the
target.$TARGET.image field in Cross.toml to use custom Docker image for a
specific target:
[target.aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu]
image = "my/image:tag"In the example above, cross will use a image named my/image:tag instead of
the default one. Normal Docker behavior applies, so:
-
Docker will first look for a local image named
my/image:tag -
If it doesn't find a local image, then it will look in Docker Hub.
-
If only
image:tagis specified, then Docker won't look in Docker Hub. -
If only
tagis omitted, then Docker will use thelatesttag.
It's recommended to base your custom image on the default Docker image that
cross uses: japaric/$TARGET:$VERSION (where $VERSION is cross's version).
This way you won't have to figure out how to install a cross C toolchain in your
custom image. Example below:
FROM japaric/aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu:v0.1.4
RUN dpkg --add-architecture arm64 && \
apt-get update && \
apt-get install libfoo:arm64$ docker build -t my/image:tag path/to/where/the/Dockerfile/resides
By default, cross uses cargo to build your Cargo project unless you are
building for one of the thumbv*-none-eabi* targets; in that case, it uses
xargo. However, you can use the build.xargo or target.$TARGET.xargo field
in Cross.toml to force the use of xargo:
# all the targets will use `xargo`
[build]
xargo = trueOr,
# only this target will use `xargo`
[target.aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu]
xargo = trueNote that xargo = false has no effect as you can't use cargo with targets
that only support xargo.
A target is considered as "supported" if cross can cross compile a
"non-trivial" (binary) crate, usually Cargo, for that target.
Testing support is more complicated. It relies on QEMU user emulation, so
testing may sometimes fail due to QEMU bug sand not because there's a bug in the
crate. That being said, cross test is assumed to "work" (test column in the
table below) if it can successfully
run compiler-builtins
test suite.
Also, testing is very slow. cross will actually run units tests sequentially
because QEMU gets upset when you spawn several threads. This also means that, if
one of your unit tests spawns several threads then it's more likely to fail or,
worst, "hang" (never terminate).
| Target | libc | GCC | OpenSSL | C++ | QEMU | test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
aarch64-linux-android |
N/A | 4.9 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | N/A | |
aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu |
2.19 | 4.8.2 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.8.0 | ✓ |
arm-linux-androideabi |
N/A | 4.9 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | N/A | |
arm-unknown-linux-gnueabi |
2.19 | 4.8.2 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.8.0 | ✓ |
arm-unknown-linux-musleabi |
1.1.15 | 5.3.1 | N/A | 2.8.0 | ✓ | |
armv7-linux-androideabi |
N/A | 4.9 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | N/A | |
armv7-unknown-linux-gnueabihf |
2.15 | 4.6.2 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.8.0 | ✓ |
armv7-unknown-linux-musleabihf |
1.1.15 | 5.3.1 | N/A | 2.8.0 | ✓ | |
i686-linux-android |
N/A | 4.9 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | N/A | |
i686-unknown-freebsd [1] |
10.2 | 5.3.0 | 1.0.2k | N/A | ||
i686-unknown-linux-gnu |
2.15 | 4.6.2 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | N/A | ✓ |
i686-unknown-linux-musl |
1.1.15 | 5.3.1 | N/A | N/A | ✓ | |
mips-unknown-linux-gnu |
2.23 | 5.3.1 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.8.0 | ✓ |
mips64-unknown-linux-gnuabi64 |
2.23 | 5.3.1 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.8.0 | ✓ |
mips64el-unknown-linux-gnuabi64 |
2.23 | 5.3.1 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.8.0 | ✓ |
mipsel-unknown-linux-gnu |
2.23 | 5.3.1 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.8.0 | ✓ |
powerpc-unknown-linux-gnu |
2.19 | 4.8.2 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.7.1 | ✓ |
powerpc64-unknown-linux-gnu |
2.19 | 4.8.2 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.7.1 | ✓ |
powerpc64le-unknown-linux-gnu |
2.19 | 4.8.2 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.7.1 | ✓ |
s390x-unknown-linux-gnu |
2.23 | 5.3.1 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.8.0 | |
sparc64-unknown-linux-gnu [2] |
2.23 | 5.3.1 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | 2.8.0 | ✓ |
thumbv6m-none-eabi [3] |
2.2.0 | 5.3.1 | N/A | N/A | ||
thumbv7em-none-eabi [3] |
2.2.0 | 5.3.1 | N/A | N/A | ||
thumbv7em-none-eabihf [3] |
2.2.0 | 5.3.1 | N/A | N/A | ||
thumbv7m-none-eabi [3] |
2.2.0 | 5.3.1 | N/A | N/A | ||
x86_64-pc-windows-gnu[1] |
N/A | 5.3.1 | ✓ | N/A | ||
x86_64-unknown-dragonfly [1] [2] |
4.6.0 | 5.3.0 | 1.0.2k | N/A | ✓ | |
x86_64-unknown-freebsd [1] |
10.2 | 5.3.0 | 1.0.2k | N/A | ||
x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu |
2.15 | 4.6.2 | 1.0.2k | ✓ | N/A | ✓ |
x86_64-unknown-linux-musl |
1.1.15 | 5.3.1 | 1.0.2k | N/A | ✓ | |
x86_64-unknown-netbsd[1] |
7.0 | 5.3.0 | 1.0.2k | N/A |
[1] For *BSD targets, the libc column indicates the OS release version from where libc was extracted.
[2] No std component available as of 2017-01-10
[3] libc = newlib
You can set the QEMU_STRACE variable when you use cross run to get a backtrace
of system calls from "foreign" (non x86_64) binaries.
$ cargo new --bin hello && cd $_
$ QEMU_STRACE=1 cross run --target aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu
9 brk(NULL) = 0x0000004000023000
9 uname(0x4000823128) = 0
(..)
9 write(1,0xa06320,14)Hello, world!
= 14
9 sigaltstack(0x4000823588,(nil)) = 0
9 munmap(0x0000004000b16000,16384) = 0
9 exit_group(0)
-
path dependencies (in Cargo.toml) that point outside the Cargo project won't work because
crossuse docker containers only mounts the Cargo project so the container doesn't have access to the rest of the filesystem. -
crosswill mount the Cargo project as READ ONLY. Thus, if any crate attempts to modify its "source", the build will fail. Well behaved crates should only ever write to$OUT_DIRand never modify$CARGO_MANIFEST_DIRthough.
Licensed under either of
- Apache License, Version 2.0 (LICENSE-APACHE or http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
- MIT license (LICENSE-MIT or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
at your option.
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the work by you, as defined in the Apache-2.0 license, shall be dual licensed as above, without any additional terms or conditions.

