[Node.js进阶系列]Koa源码精读二
webfansplz opened this issue · 0 comments
webfansplz commented
了解了 Koa 的一些核心实现**,我们最后来分析源码就会发现清晰很多,GO ~
'use strict';
/**
* Module dependencies.
*/
const isGeneratorFunction = require('is-generator-function');
const response = require('./response');
const compose = require('koa-compose');
const isJSON = require('koa-is-json');
const context = require('./context');
const request = require('./request');
const statuses = require('statuses');
const Emitter = require('events');
const util = require('util');
const Stream = require('stream');
const http = require('http');
const convert = require('koa-convert');
const deprecate = require('depd')('koa');
module.exports = class Application extends Emitter {
constructor() {
super();
this.proxy = false;
this.subdomainOffset = 2;
this.env = process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development';
// 装载中间件容器
this.middleware = [];
// 创建context对象
this.context = Object.create(context);
// 创建request对象
this.request = Object.create(request);
// 创建response对象
this.response = Object.create(response);
if (util.inspect.custom) {
this[util.inspect.custom] = this.inspect;
}
}
// 创建http服务
listen(...args) {
const server = http.createServer(this.callback());
return server.listen(...args);
}
toJSON() {
return only(this, ['subdomainOffset', 'proxy', 'env']);
}
inspect() {
return this.toJSON();
}
// use中间件
use(fn) {
if (typeof fn !== 'function') throw new TypeError('middleware must be a function!');
if (isGeneratorFunction(fn)) {
deprecate(
'Support for generators will be removed in v3. ' +
'See the documentation for examples of how to convert old middleware ' +
'https://github.com/koajs/koa/blob/master/docs/migration.md'
);
fn = convert(fn);
}
this.middleware.push(fn);
return this;
}
callback() {
// 前面我们提到的"洋葱模型",中间件流程控制
const fn = compose(this.middleware);
/*
events模块的listenerCount方法,
判断error事件的监听数量为0时,监听error事件。
*/
if (!this.listenerCount('error')) this.on('error', this.onerror);
const handleRequest = (req, res) => {
// 创建上下文对象,传入http模块的req(请求对象),res(响应对象)
const ctx = this.createContext(req, res);
// 请求处理
return this.handleRequest(ctx, fn);
};
return handleRequest;
}
handleRequest(ctx, fnMiddleware) {
const res = ctx.res;
res.statusCode = 404;
/*
调用context.js的onerror函数
context.js的onerror函数里,有这样一句代码 this.app.emit('error', err, this);
其实就是我们之前提到的Eventemitter,所以这里会触发this.onerror方法.
所以这里虽然调用的是context.js的onerror函数,但会触发两个error函数进行异常处理.
*/
const onerror = err => ctx.onerror(err);
// 对响应内容进行处理
const handleResponse = () => respond(ctx);
// 确保一个流在完成,关闭,报错时都会执行响应的回调函数
onFinished(res, onerror);
// 执行中间件,并处理对应响应
return fnMiddleware(ctx)
.then(handleResponse)
.catch(onerror);
}
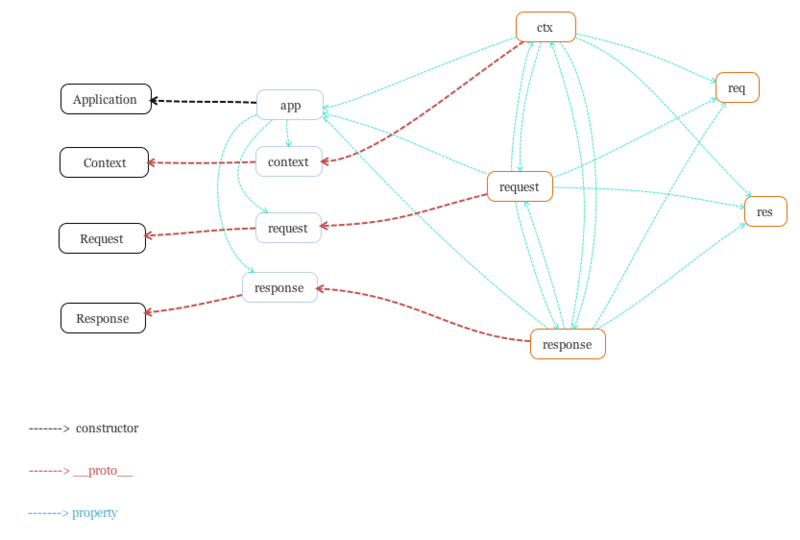
// 创建上下文对象, 看完如果觉得萌比的话,可看下方流程图
createContext(req, res) {
const context = Object.create(this.context);
const request = (context.request = Object.create(this.request));
const response = (context.response = Object.create(this.response));
context.app = request.app = response.app = this;
context.req = request.req = response.req = req;
context.res = request.res = response.res = res;
request.ctx = response.ctx = context;
request.response = response;
response.request = request;
context.originalUrl = request.originalUrl = req.url;
context.state = {};
return context;
}
// 错误处理
onerror(err) {
// 判断 err 是否是 Error 实例
if (!(err instanceof Error)) throw new TypeError(util.format('non-error thrown: %j', err));
// 是否 404 错误
if (404 == err.status || err.expose) return;
// 是否有静默设置,
if (this.silent) return;
// 打印出出错堆栈,方便对问题进行定位
const msg = err.stack || err.toString();
console.error();
console.error(msg.replace(/^/gm, ' '));
console.error();
}
};
// 响应内容处理
function respond(ctx) {
// allow bypassing koa
if (false === ctx.respond) return;
// 是否为可写流
if (!ctx.writable) return;
const res = ctx.res;
let body = ctx.body;
const code = ctx.status;
// 如果响应的Status Code是body 为空的类型,将 body 置为 null并响应
// ignore body
if (statuses.empty[code]) {
// strip headers
ctx.body = null;
return res.end();
}
// 如果是HEAD方法
if ('HEAD' == ctx.method) {
// http 响应头部是否已经被发送且body是否为json,未发送的话,添加 length 头部
if (!res.headersSent && isJSON(body)) {
ctx.length = Buffer.byteLength(JSON.stringify(body));
}
return res.end();
}
// status body
// body值为空
if (null == body) {
// HTTP 版本>=2
if (ctx.req.httpVersionMajor >= 2) {
// body值为code
body = String(code);
} else {
// body值为 context 中的 message 属性或 code
body = ctx.message || String(code);
}
// 未发送响应头部,添加length和type
if (!res.headersSent) {
ctx.type = 'text';
ctx.length = Buffer.byteLength(body);
}
return res.end(body);
}
// responses
// 处理buffer类型的body
if (Buffer.isBuffer(body)) return res.end(body);
// 处理字符串类型的body
if ('string' == typeof body) return res.end(body);
// body是流类型,合并处理
if (body instanceof Stream) return body.pipe(res);
// body: json
// body是json类型,序列化
body = JSON.stringify(body);
// 未发送响应头部,添加length
if (!res.headersSent) {
ctx.length = Buffer.byteLength(body);
}
res.end(body);
}下面,引用某位大佬整理的流程图,� 希望可以帮助你更清晰的理解 Koa 上下文对象~
结语
欢乐的时光总是这么短暂,到了跟大家说再见的时候啦,如果你觉得有帮助到你的话,请给我小星星~
上一节:Koa 源码精读一