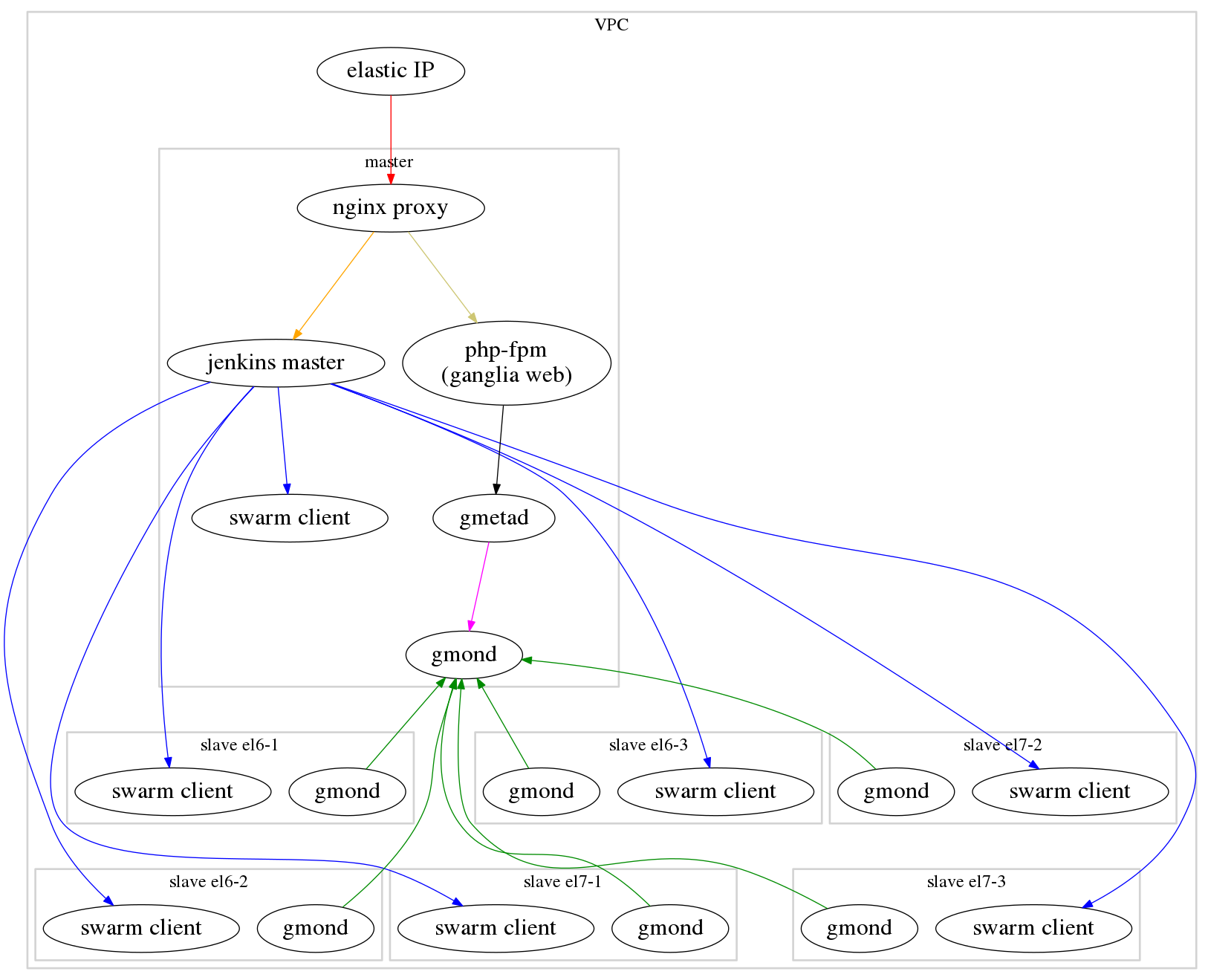
LSST Jenkins deployment
Synopsis
This is a demonstration of deploying a complete
jenkins master + build agent environment to
AWS EC2 which is pre-configured to build the LSST
Stack. The principle goal is to demonstrate a possible migration path away
from LSST DM's existing CI infrastructure. The key feature improvements over
the existing buildbot driven system are:
- concurrently running a build on multiple operating systems
- multiple independent builds of the same job occurring in parallel
A secondary objective is provide an example of deploying a moderately complex application onto a modern cloud infrastructure.
High level architecture
The instances running the jenkins master and agent processes are deployed into an AWS "Virtual Private Cloud" or VPC. Using a non-default VPC (historically, AWS had separate classic and VPC environments; all newly created AWS accounts have a default VPC in each region that more or less emulates the "classic" behavior) allows for direct control over the RFC1918 private address space. A benefit of this is that the master instance can have a fixed IP address which the agents can locate by convention instead of requiring either the address to be injected or use of a service discovery mechanism.
Tooling
packer
The Centos project supplies "official" x86_64 HVM Amazon Machine Images
(AMIs) for both Centos 6 and 7 in all EC2 regions. However, the images are
slightly out of date, 6.5 vs. 6.7 and 7.0 vs. 7.1, and the Centos 6 image does
not include cloud-init or is
it compatible with vagrant. The popular
chef/bento packer
templates were modified to install/configure cloud-init for Centos 6, update
the images to the current minor releases, and make both images more friendly
for usage with vagrant.
terraform
As with any network environment, a VPC requires a fair amount of configuration.
Instead of requiring manual interaction via the AWS console,
terraform is used to configure fully configure
the VPC. Note that terraform has the capability to spawn EC2 instances and
could completely replace vagrant at the expense of loosing a convenient
development/debugging mechanism.
The terraform configuration files are under the 'tf' directory.
vagrant
EC2 instances are created/destroyed via
vagrant. Vagrant is also used to pass "User
Data" to cloud-init and to run puppet on each node in "masterless" mode.
Vagrant is configured via the 'Vagrantfile'.
cloud-init
There are a number of low-level configurations needed in a cloud environment. Including:
- ssh key injection / sudo management
- dynamic resizing of the instance's block storage
- hostname/host file management
cloud-init is relied upon to
provide those functions in demo.
puppet
The bulk of the "heavy lifting" (configuring the instances) in this demo is
done by a composition of puppet modules. This is
implemented via a bundled "site" module that implements the Roles and
Profiles pattern.
- The puppet modules in use are listed in the Puppetfile.
- The site module is under the
jenkins_demodirectory.
metric collection
A full production deployment would likely involve additional jenkins plugins for metric collection and instance level metrics collected external to jenkins which are then made available to end users via a web interface.
ganglia
The ganglia monitoring system is used to collect
general host metrics from the build agents and are accessible from the web
interface as https://<jenkins-master>/ganglia/.
A possible improvement would be to create gmetric values from jenkins when
certain events occur, such as the start and finish of jobs.
AWS cloud watch
The demo enables cloud watch metric collection about the instances which is completely external to jenkins and not visible without AWS account credentials.
backups
A simple backup solution is provided via a jenkins job named
jenkins-ec2-snapshot that will create EBS snapshots of the jenkins-master
using the ec-snapshot script.
Note that this requires valid AWS credientials to be present in
common.yaml.
Notable omissions
jenkins security
jenkins does not have any access control enabled. This means that anyone can change anything, include the jenkins configuration, essentially allowing arbitrary code to be executed under the jenkins role account.
There is on going development to improve the
rtyle/jenkins puppet module so
that is can handle the complete set of security configuration needed for a
production deployment without requiring manual configuration by the
administrator.
DNS
The demo attaches an elastic IP address (public IP) but does not manage DNS configuration for this address. There are a number of ways of automatically handling this including via the terraform AWS provider.
jenkins plugins
There are a number of plugins that are not configured via this demo as it would require exposing secrets. This includes github oauth integration and email notifications.
Prerequisites
- Vagrant 1.7.x
git- needed to clone this repo
Only needed to use hiera-eyaml to decrypt/edit common.eyaml
- ruby 1.9.3+
- bundler
Vagrant plugins
These are required:
- vagrant-puppet-install
- vagrant-librarian-puppet '~> 0.9.0'
- vagrant-aws '~> 0.7.0'
Setup and Deployment
Build updated and vagrant friendly AMIs
Download & prepare packer
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<...>
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<...>
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=us-east-1
git clone -b builder/aws https://github.com/jhoblitt/bento.git
cd bento
mkdir bin
cd bin
wget https://dl.bintray.com/mitchellh/packer/packer_0.8.6_linux_amd64.zip
unzip packer_0.8.6_linux_amd64.zip
cd ..
Select Official Centos AMI to use as base image
EC2 AMI IDs are per region so you need to select the correct AMI ID for the region in which you plan to build. Note that it is possible to copy AMIs between EC2 regions after they are built. However, each region will still have a unique AMI ID
CentOS 6 (x86_64) - with Updates HVM
AMI IDs for version 6 - 2015-09-28:
| Region | ID |
|---|---|
| US East (N. Virginia) | ami-57cd8732 |
| US West (Oregon) | ami-1255b321 |
| US West (N. California) | ami-45844401 |
CentOS 7 (x86_64) with Updates HVM
AMI IDs for version 7 - 2015-09-28:
| Region | ID |
|---|---|
| US East (N. Virginia) | ami-61bbf104 |
| US West (Oregon) | ami-d440a6e7 |
| US West (N. California) | ami-f77fbeb3 |
Build centos 6.7 AMI
./bin/packer build --only amazon-ebs -var 'source_ami=ami-c2a818aa' centos-6.7-x86_64.json
Build 'amazon-ebs' finished.
==> Builds finished. The artifacts of successful builds are:
--> amazon-ebs: AMIs were created:
us-east-1: ami-974d85fc
--> amazon-ebs: 'aws' provider box: builds/__unset_box_basename__.aws.boxBuild centos 7.1 AMI
./bin/packer build --only amazon-ebs -var 'source_ami=ami-96a818fe' centos-7.1-x86_64.json
Build 'amazon-ebs' finished.
==> Builds finished. The artifacts of successful builds are:
--> amazon-ebs: AMIs were created:
us-east-1: ami-3331f958
--> amazon-ebs: 'aws' provider box: builds/__unset_box_basename__.aws.boxDeclare new AMI IDs
To be used by vagrant.
export CENTOS6_AMI=ami-974d85fc
export CENTOS7_AMI=ami-3331f958
export MASTER_AMI=$CENTOS7_AMI
cd ..
Clone & prepare demo
git clone git@github.com:jhoblitt/deploy-jenkins.git
cd deploy-jenkins
Edit hiera data as necessary
This demo uses a simple hiera
configuration for providing configuration data to the puppet manifests used to
provision the nodes. The literal configuration file used by hiera/puppet, if
present, is hieradata/common.yaml.
However, some configuration data, such as the hipchat API token, must be kept
confidential. A rubygem named
hiera-eyaml is used to maintain
a "shadow" hiera configuration
hieradata/common.eyaml that contains mixed
plaintext and encrypted values. Confidential data that is specific to LSST/DM
is present in this file and the correct private key ring needs to be present
under the ./keys/ directory in order to decrypt it.
keys/
├── private_key.pkcs7.pem
└── public_key.pkcs7.pem
$ rsync -av /<path to keys>/keys/ keys/
sending incremental file list
created directory keys
./
private_key.pkcs7.pem
public_key.pkcs7.pem
sent 2,949 bytes received 84 bytes 6,066.00 bytes/sec
total size is 2,725 speedup is 0.90If you do not have access to LSST/DM keys, you can either copy common.yaml to
common.eyaml and manually edit it or generate a new eyaml key set to
maintain your own version of common.eyaml (the LSST/DM encrypted values would
need to be removed).
It is essential that the eyaml keys are kept confidential and not published in this repository.
eyaml setup
A Gemfile is provided to install hiera-eyaml. A working ruby + bundler
install is assumed.
bundle install
provided rake convenience tasks
bundle exec rake -T
rake createkeys # generate new eyaml keys
rake decrypt # decrypt common.eyaml -> common.yaml
rake edit # edit common.eyaml (requires keys)
decrypt common.eyaml
bundle exec rake decrypt
Generate ssh key pair
The ssh key pair is required for both terraform and vagrant.
(cd jenkins_demo/templates; make)
Run terraform to configure AWS VPC
cd terraform
make
export TF_VAR_aws_access_key=$AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
export TF_VAR_aws_secret_key=$AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
export TF_VAR_aws_default_region=$AWS_DEFAULT_REGION
export TF_VAR_env_name=${USER}-demo
export TF_VAR_aws_zone_id=Z3TH0HRSNU67AM
export TF_VAR_domain_name=lsst.codes
# sanity check
./bin/tf plan
./bin/tf apply
cd ..
Create AWS EC2 instances with vagrant
Install required vagrant plugins
vagrant plugin install vagrant-puppet-install
vagrant plugin install vagrant-librarian-puppet --plugin-version '~> 0.9.0'
vagrant plugin install vagrant-aws --plugin-version '~> 0.6.0'
# sanity check
vagrant plugin list
Disable parallel actions
One of the vagrant plugins currently in use is not compatible with vagrant parallel providers. That means vagrant is unable to create EC2 instances in parallel.
export VAGRANT_DEFAULT_PROVIDER='aws'
export VAGRANT_NO_PARALLEL='yes'
create pre-provisoined base images
Start up the build agents first so there isn't state created by the master attempting to create jobs.
vagrant up el6-1 el7-1
# sanity check
vagrant provision el6-1 el7-1
vagrant package el6-1
rm package.box
vagrant package el7-1
rm package.box
vagrant destroy -f el6-1 el7-1
vagrant up master
# sanity check
vagrant provision master
vagrant package master
rm package.box
vagrant destroy -f master
# sanity check
vagrant check
$ vagrant package el6-1
==> el6-1: Burning instance i-bc806b6f into an ami
==> el6-1: Waiting for the AMI 'ami-ff18e494' to burn...
==> el6-1: Burn was successful in 60s
==> el6-1: Compressing package to: /home/jhoblitt/tmp/deploy-jenkins/package.box
$ rm package.box
$ vagrant package el7-1
==> el7-1: Burning instance i-a4ef0477 into an ami
==> el7-1: Waiting for the AMI 'ami-0515e96e' to burn...
==> el7-1: Burn was successful in 146s
==> el7-1: Compressing package to: /home/jhoblitt/tmp/deploy-jenkins/package.box
$ rm package.box
$ vagrant destroy -f el6-1 el7-1
==> el7-1: Terminating the instance...
==> el7-1: Running cleanup tasks for 'puppet' provisioner...
==> el6-1: Terminating the instance...
==> el6-1: Running cleanup tasks for 'puppet' provisioner...
$ vagrant package master
==> master: Burning instance i-7c0de6af into an ami
==> master: Waiting for the AMI 'ami-d312eeb8' to burn...
==> master: Burn was successful in 417s
==> master: Compressing package to: /home/jhoblitt/tmp/deploy-jenkins/package.box
$ rm package.box
$ vagrant destroy -f master
==> master: Terminating the instance...
==> master: Running cleanup tasks for 'puppet' provisioner...Save env vars
The shell snippet below will store all of the important environment variables
that have been set into a script called creds.sh, intended to be sourced
before performing vagrant/terraform operations in a clean shell.
cat > creds.sh <<END
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=$AWS_DEFAULT_REGION
export CENTOS6_AMI=$CENTOS6_AMI
export CENTOS7_AMI=$CENTOS7_AMI
export MASTER_AMI=$MASTER_AMI
export VAGRANT_DEFAULT_PROVIDER='aws'
export VAGRANT_NO_PARALLEL='yes'
export TF_VAR_aws_access_key=$TF_VAR_aws_access_key
export TF_VAR_aws_secret_key=$TF_VAR_aws_secret_key
export TF_VAR_aws_default_region=$TF_VAR_aws_default_region
export TF_VAR_env_name=$TF_VAR_env_name
export TF_VAR_aws_zone_id=$TF_VAR_aws_zone_id
export TF_VAR_domain_name=$TF_VAR_domain_name
END
Start all demo instances
. ./creds.sh
vagrant up