This project was bootstrapped with Create React App, Metamask, Rainbowkit, Wagmi, Ethers.
Runs the app in the development mode.
Open http://localhost:3000 to view it in the browser.
 Message signing using MetaMask is a process that involves using the MetaMask wallet to verify that you are the originator of a transaction or message. It provides a way to prove ownership of a specific Ethereum address and allows the transaction or message to be added to the blockchain.
Message signing using MetaMask is a process that involves using the MetaMask wallet to verify that you are the originator of a transaction or message. It provides a way to prove ownership of a specific Ethereum address and allows the transaction or message to be added to the blockchain.
Message signing with MetaMask is commonly used for various purposes, such as authentication, authorization, and secure exchanges of information . It provides a way to prove the ownership of an Ethereum address without revealing the private key.
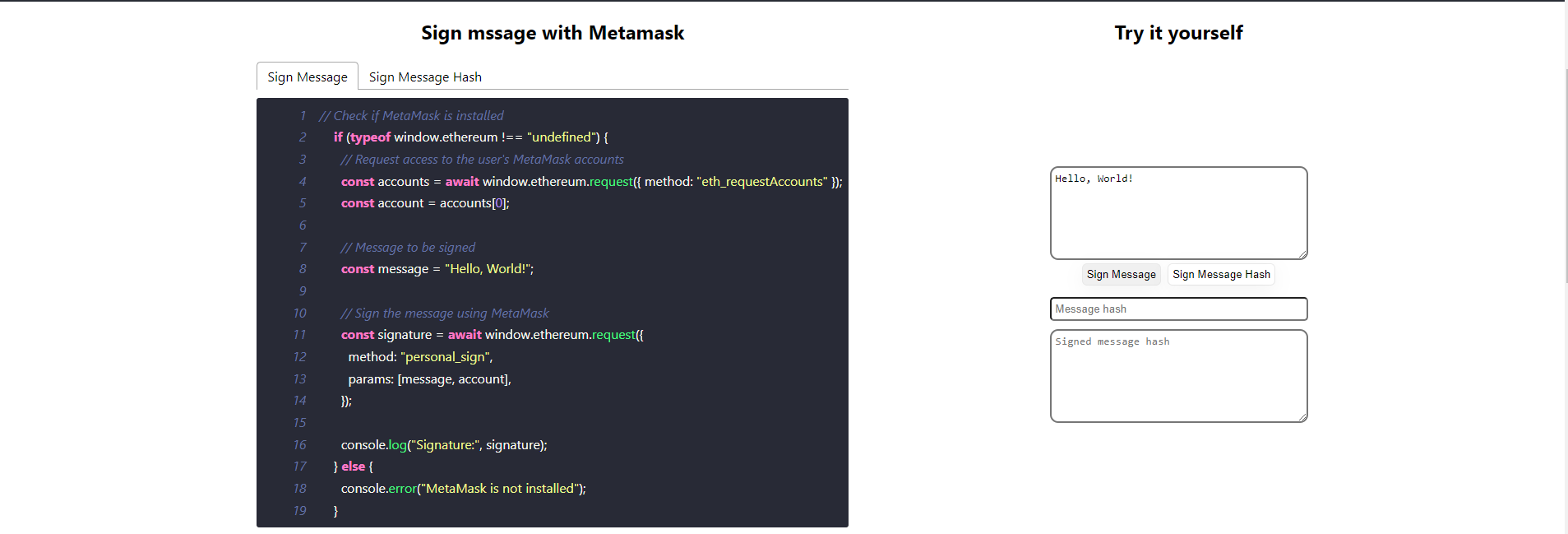
Following code shows how does Metamask sign plan message in Javascript.
// Check if MetaMask is installed
if (typeof window.ethereum !== "undefined") {
// Request access to the user's MetaMask accounts
const accounts = await window.ethereum.request({ method: "eth_requestAccounts" });
const account = accounts[0];
// Message to be signed
const message = "Hello, World!";
// Sign the message using MetaMask
const signature = await window.ethereum.request({
method: "personal_sign",
params: [message, account],
});
console.log("Signature:", signature);
} else {
console.error("MetaMask is not installed");
}Following code shows how does Metamask sign hashed message in Javascript.
// Check if MetaMask is installed
if (typeof window.ethereum !== "undefined") {
// Request access to the user's MetaMask accounts
const accounts = await window.ethereum.request({ method: "eth_requestAccounts" });
const account = accounts[0];
// Message to be signed
const message = "Hello, World!";
// Message hash
const messageHash = ethers.keccak256(ethers.toUtf8Bytes(message))
// Sign the message using MetaMask
const signature = await window.ethereum.request({
method: "personal_sign",
params: [messageHash, account],
});
console.log("Signature:", signature);
} else {
console.error("MetaMask is not installed");
}Message signing using Wagmi involves using the Wagmi library, which provides React hooks for working with Ethereum. With Wagmi, you can sign messages to prove control of a specific Ethereum address securely.
It's important to note that before signing a message, the user's wallet needs to be connected to the browser and the application. This typically involves using a wallet connection provider like Rainbowkit.
Following code shows how to sign plan message with Wagmi in Javascript.
try {
//Get wallet client
const walletClient = await getWalletClient();
// Message to be signed
const message = "Hello, World!";
//Sign message
const signature = await walletClient?.signMessage({ message });
}
catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}Following code shows how to sign hashed message with Wagmi in Javascript.
try {
//Get wallet client
const walletClient = await getWalletClient();
// Message to be signed
const message = "Hello, World!";
// Message hash
const messageHash = ethers.keccak256(ethers.toUtf8Bytes(message))
//Sign message
const signature = await walletClient?.signMessage({ message: { raw: messageHash } });
}
catch (error) {
console.error(error);
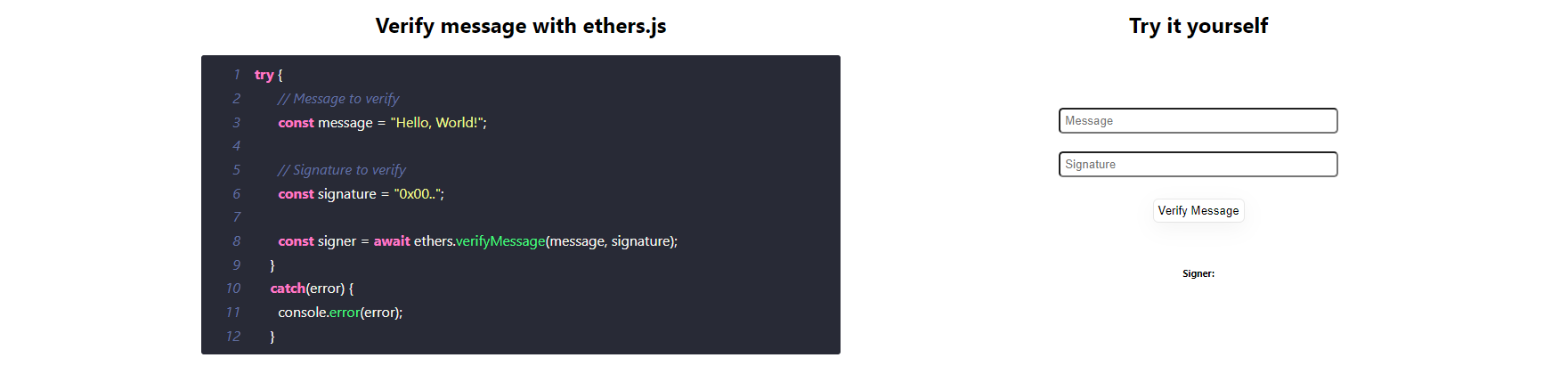
}Message verification using ethers involves verifying the signature of a message to ensure its authenticity.
try {
// Message to verify
const message = "Hello, World!";
// Signature to verify
const signature = "0x00..";
const signer = await ethers.verifyMessage(message, signature);
}
catch(error) {
console.error(error);
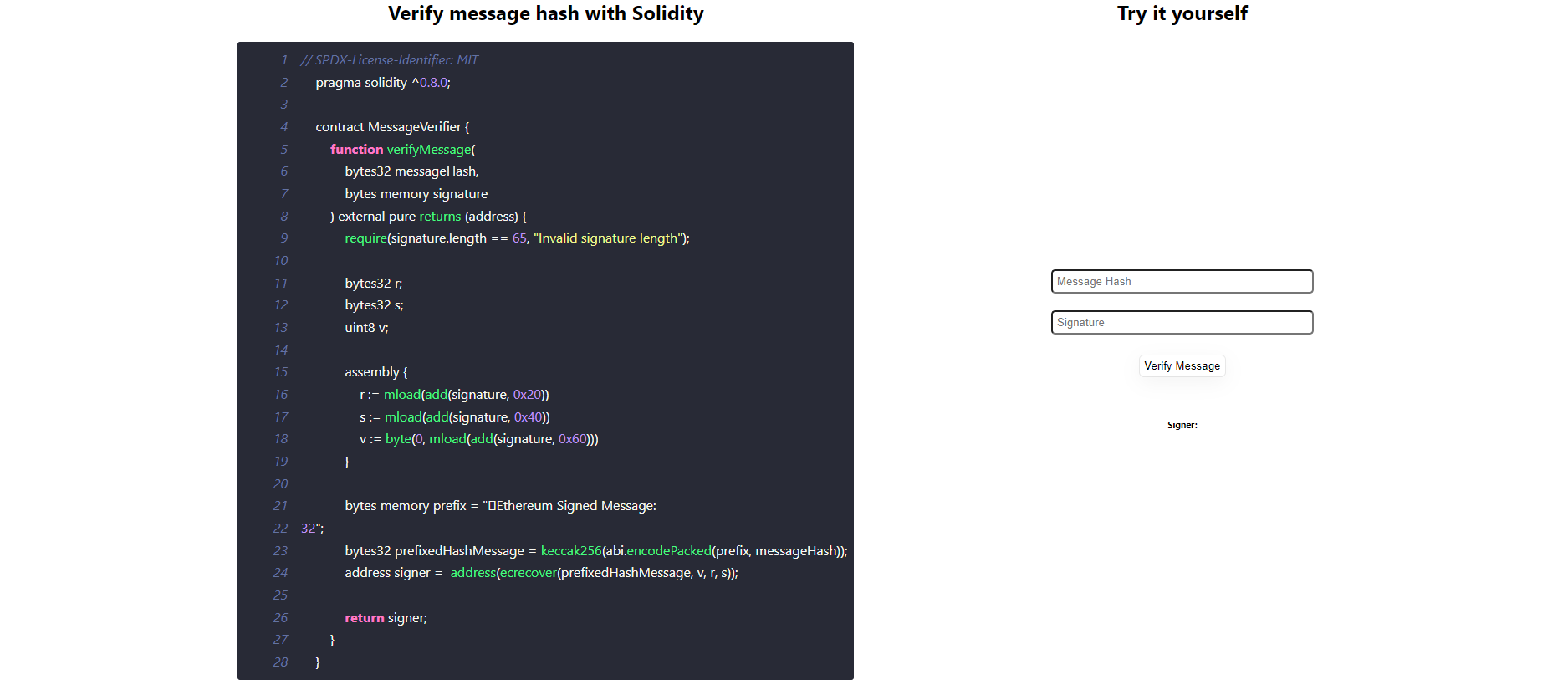
}Message hash verification in Solidity involves the process of verifying the integrity and authenticity of a signed message on the Ethereum blockchain.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract MessageVerifier {
function verifyMessage(
bytes32 messageHash,
bytes memory signature
) external pure returns (address) {
require(signature.length == 65, "Invalid signature length");
bytes32 r;
bytes32 s;
uint8 v;
assembly {
r := mload(add(signature, 0x20))
s := mload(add(signature, 0x40))
v := byte(0, mload(add(signature, 0x60)))
}
bytes memory prefix = "\x19Ethereum Signed Message:\n32";
bytes32 prefixedHashMessage = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(prefix, messageHash));
address signer = address(ecrecover(prefixedHashMessage, v, r, s));
return signer;
}
}Made with ❤ by CYBER STORM