ELMo: Embeddings from Language Models, which comes from the paper "Deep contextualized word representations".
This resource includes various methods of using ELMo, visual analysis of ELMo, and paper interpretation.
NAACL 2018最佳论文 Deep contextualized word representations:艾伦人工智能研究所提出新型深度语境化词表征(研究者使用从双向 LSTM 中得到的向量,该 LSTM 是使用成对语言模型(LM)目标在大型文本语料库上训练得到的。因此,该表征叫作 ELMo(Embeddings from Language Models)表征。)。
| name | description |
|---|---|
| elmo_tfhub_use_methods.ipynb | Summarize four usage methods of Elmo embedding. |
| IMDB_ELMo_As_Embedding_Layer.ipynb | IMDB movie review sentiment analysis example |
| elmo_sentence_level_embedding.ipynb | Kaggle's movie review sentiment analysis example |
| elmo_word_level_embedding.ipynb | Kaggle's movie review sentiment analysis example |
| IMDB_ELMo_Preprocessing_Data.ipynb | Preprocessing data with Elmo |
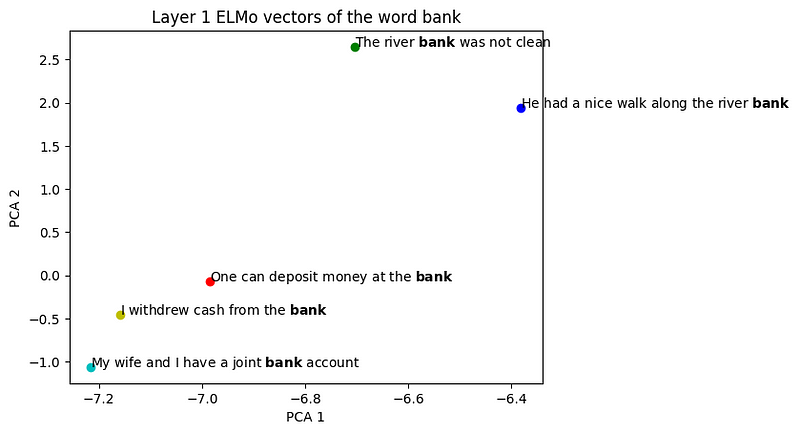
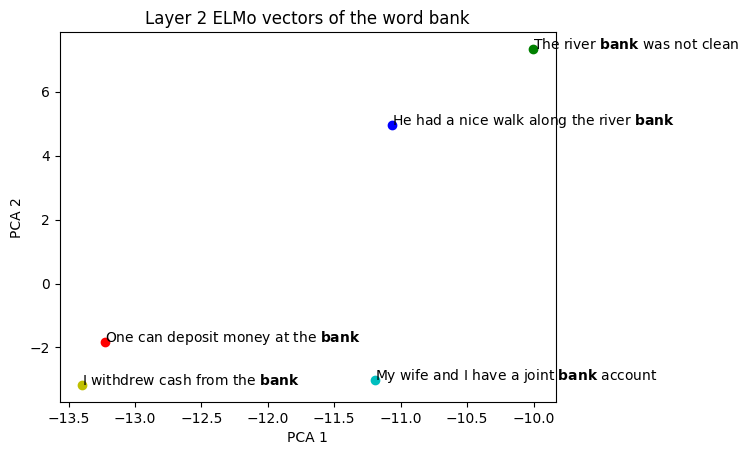
| Visualizing ELMo Contextual Vectors | Visualizing... |
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
# elmo_url="https://tfhub.dev/google/elmo/2"
# hub.Module(elmo_url, trainable=True)
# You can either use the URL directly or download the file locally and then use it.
# hub.Module(path_to_elmo_model, trainable=True)
tokens_input = [["the", "cat", "is", "on", "the", "mat"],
["dogs", "are", "in", "the", "fog", ""]]
tokens_length = [6, 5]
max_length = max(tokens_length)
def tokens_elmo(path_to_hub_elmo_model="https://tfhub.dev/google/elmo/2"):
elmo_tokens_input = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.string, shape=[None, max_length], name="tokens_input")
elmo_sequence_length_input = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=[None,], name="tokens_length")
module = hub.Module(path_to_hub_elmo_model, trainable=True)
module_features = module(inputs={"tokens":elmo_tokens_input, "sequence_len":elmo_sequence_length_input},
signature='tokens', as_dict=True)
elmo_embedding = module_features["elmo"] #[batch_size, max_length, 1024], the weighted sum of the 3 layers, where the weights are trainable.
return elmo_tokens_input, elmo_sequence_length_input, elmo_embedding
elmo_tokens_input, elmo_sequence_length_input, elmo_embedding = tokens_elmo(path_to_hub_elmo_model="/home/b418/jupyter_workspace/B418_common/袁宵/tfhub_modules/elmo")
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run([tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.tables_initializer()])
out_elmo_embedding = sess.run(elmo_embedding,feed_dict={elmo_tokens_input:tokens_input,
elmo_sequence_length_input:tokens_length})
print("out_elmo_shape:\t", out_elmo_embedding.shape)
Create a semantic search engine
Matthew E. Peters, Mark Neumann, Mohit Iyyer, Matt Gardner, Christopher Clark, Kenton Lee, Luke Zettlemoyer
Our word vectors are learned functions of the internal states of a deep bidirectional language model (biLM), which is pre-trained on a large text corpus. We show that these representations can be easily added to existing models and significantly improve the state of the art across six challenging NLP problems, including question answering, textual entailment and sentiment analysis. We also present an analysis showing that exposing the deep internals of the pre-trained network is crucial, allowing downstream models to mix different types of semi-supervision signals.
在本论文中,我们介绍了一种新型深度语境化词表征,可对词使用的复杂特征(如句法和语义)和词使用在语言语境中的变化进行建模(即对多义词进行建模)。我们的词向量是深度双向语言模型(biLM)内部状态的函数,在一个大型文本语料库中预训练而成。本研究表明,这些表征能够被轻易地添加到现有的模型中,并在六个颇具挑战性的 NLP 问题(包括问答、文本蕴涵和情感分析)中显著提高当前最优性能。此外,我们的分析还表明,揭示预训练网络的深层内部状态至关重要,可以允许下游模型综合不同类型的半监督信号。
Comments: NAACL 2018. Originally posted to openreview 27 Oct 2017. v2 updated for NAACL camera ready Subjects: Computation and Language (cs.CL) Cite as: arXiv:1802.05365 [cs.CL] (or arXiv:1802.05365v2 [cs.CL] for this version)