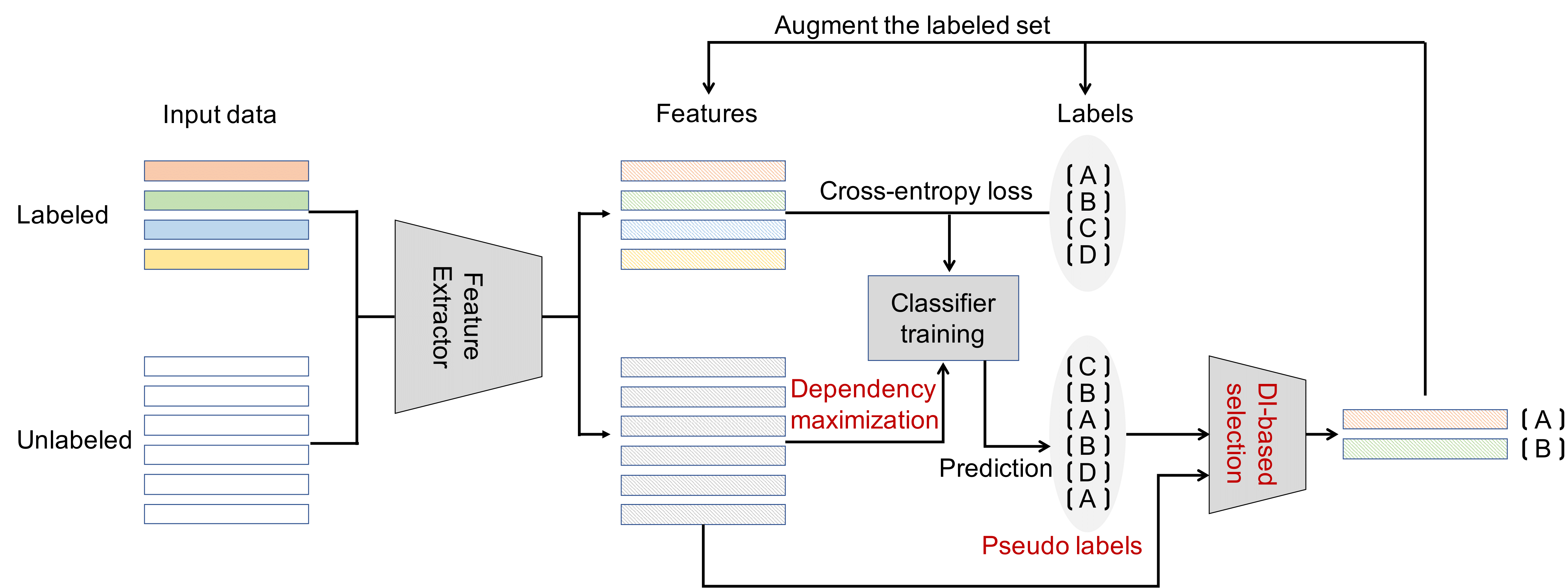
This repository contains the PyTorch implementation of the paper Semi-Supervised Few-Shot Learning Via Dependency Maximization and Instance Discriminant Analysis (Journal of Signal Processing Systems 2022).
In few-shot learning (FSL), the model learns to recognize new objects with extremely few labeled training data per category. Most of previous FSL approaches resort to the meta-learning paradigm, where the model accumulates inductive bias through learning many training tasks so as to solve a new unseen few-shot task. In contrast, we propose a simple semi-supervised FSL approach to exploit unlabeled data accompanying the few-shot task for improving few-shot performance. Firstly, we propose a Dependency Maximization method based on the Hilbert-Schmidt norm of the cross-covariance operator, which maximizes the statistical dependency between the embedded features of those unlabeled data and their label predictions, together with the supervised loss over the support set. We then use the obtained model to infer the pseudo-labels of the unlabeled data. Furthermore, we propose an Instance Discriminant Analysis to evaluate the credibility of each pseudo-labeled example and select the most faithful ones into an augmented support set to retrain the model as in the frst step. We iterate the above process until the pseudo-labels of the unlabeled set become stable. The proposed method outperforms previous state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods on widely used few-shot classifcation benchmarks.
This code requires the following:
- python: 3.x
- Pytorch: 0.4+
-
We use Mini-ImageNet dataset, which is the most widely used few-shot classification benchmark. Download the data from here.
-
The train/val/test spliting can be downloaded from here.
-
Extract the data as following format:
miniimagenet/
├── images
├── n0210891500001298.jpg
├── n0287152500001298.jpg
...
├── test.csv
├── val.csv
└── train.csv-
Download the pretrained WRN-28-10 checkpoint from here to initlize the model.
-
Run 5-way 1-shot tasks:
python train.py \
--test_batch 600 \
--update_lr 1e-4 \
--update_step 1000 \
--sigma 0.5 \
--loss_type hybrid \
--DM_factor 0.01 \
--classifier_init \
--temperature 64 \
--k_spt 1 \
--k_ub 60 \
--component 10 \
--rho 1e-3 \
--round 60 \
--mode semi- Run 5-way 5-shot tasks:
python train.py \
--test_batch 10 \
--update_lr 1e-4 \
--update_step 1000 \
--sigma 0.5 \
--loss_type hybrid \
--DM_factor 0.01 \
--classifier_init \
--temperature 32 \
--k_spt 5 \
--k_ub 60 \
--component 10 \
--rho 1e-3 \
--round 60 \
--mode semiIf you find this repository helpful, please consider citing:
@article{hou2022semi,
title={Semi-Supervised Few-Shot Learning Via Dependency Maximization and Instance Discriminant Analysis},
author={Hou, Zejiang and Kung, Sun-Yuan},
journal={Journal of Signal Processing Systems},
pages={1--12},
year={2022},
publisher={Springer}
}