The neweast version of PolyAcaller has been deposited in https://github.com/ZhaiLab-SUSTech/FLEPSeq, please use th neweast one.
Predicate potential poly(A) regions from Nanopore fast5 file which has been basecalled by guppy with flipflop mode.
Maintained by Jinbu Jia, Weipeng Mo, Zhijian Liu.
git clone https://github.com/zhailab/polyAcaller.git
cd polyAcaller
python setup.py install
cd example #you need run not in git install package
polyAcaller test_sample1.fast5 test_run.out
polyAcaller test_sample1.fast5 test_run.out 0 #default 1
polyAcaller test_sample2.fast5 test_run_.out 0 test_sample2.search_region.txt
It's better to limit the polyA search region in a specific region. Such as the region between adapter and genome mapping region. It's better to set some padding region, such as:
genome mapping region (|) unmapping region (-) 3' adapter (*)
read: ---***----|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||-------------------------***************----
search region: ||||||||||-------------------------*****
|--10nt--| |5nt|
The next version will include adaper searching and genome mapping. But now you can use minimap2 to perform genome mapping and use blastn or other tools to find adapter, and then set the search region based on the mapping information.
test_sample2.search_region.txt (tab sperated):
read_id base search_start_base search_end_base
000478c6-4c63-4cb7-baca-ca4954a12ee6 A 266 274
read_id read_length polya_start polya_end polya_start_base polya_end_base polya_length polya_score polya_type
05c92581-89a8-4813-ac46-25ea1f00f6a2 2473 1242 2841 69 79 149.39605848696758 1555 polyT
05d86bb1-209a-4d1b-bd84-85853824a4a4 1232 1288 2965 63 72 140.56731451269684 1678 polyT
05e2c771-9cfe-4d04-95ec-3aae5f8cea67 1278 20864 22089 1207 1222 92.1577325939618 1226 polyA
from polyacaller import Fast5ReadWrapper
read = Fast5ReadWrapper("test_sample1.fast5")
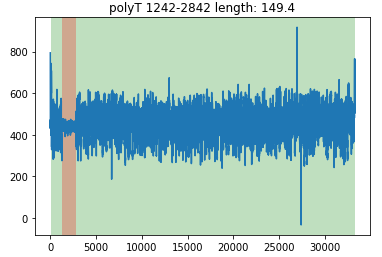
read.plot()
The cyan-blue region indicates the sequence region. The grown region indicates the longer polyA region.
The parameters of plot method:
figsize = None #such as [10, 5]
plot_all_polyA_region=False
plot_base=False
plot_base_line=False
xlim=None
ylim=None
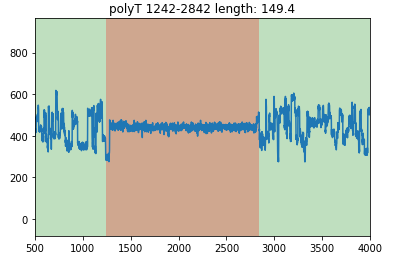
You can set xlim to zoom in:
read.plot(xlim=[500,4000])
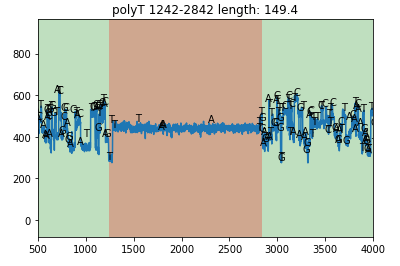
You can add the base sequence above the raw signal. But this will be slower.
read.plot(xlim=[500,4000], plot_base=True)
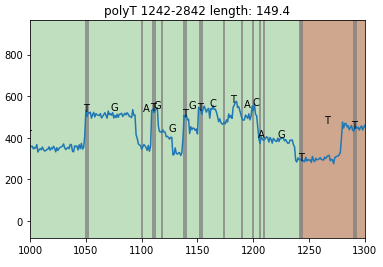
You also can add the border line of bases.
read.plot(xlim=[1000,1300], plot_base=True, plot_base_line=True)
You can save the figure like this:
read.plot(xlim=[500,4000])
read.savefig("test_data/example.pdf")
Furthermore, the matplotlib object fig and ax has been
stored in read.fig, read.ax.
help(Fast5ReadWrapper)
pA_val = scale * (raw + offset)
raw (event) index 012345..... --------------------------------------------------------------------------- init. - adpater ---- primer ----- polyA ------- RNA ----------------------
frist_template_start |
move (stride = 4) index 0 1 2 3 4 .... | | | | | .... value 1 0 0 0 1 .... base index 0 1 ... value C T ..
flip index 0 1 2 3 4 ... 4 column value A C G T flop index 0 1 2 3 4 ... 4 column value A C G T flip: the probability of one move belongs to A, C, G, T flop: the probability of one move belongs to continous A, continous C, continous G, continous T