This project implements a Stock Trading Bot, trained using Deep Reinforcement Learning, specifically Deep Q-learning. Implementation is kept simple and as close as possible to the algorithm discussed in the paper, for learning purposes.
Generally, Reinforcement Learning is a family of machine learning techniques that allow us to create intelligent agents that learn from the environment by interacting with it, as they learn an optimal policy by trial and error. This is especially useful in many real world tasks where supervised learning might not be the best approach due to various reasons like nature of task itself, lack of appropriate labelled data, etc.
The important idea here is that this technique can be applied to any real world task that can be described loosely as a Markovian process.
This work uses a Model-free Reinforcement Learning technique called Deep Q-Learning (neural variant of Q-Learning). At any given time (episode), an agent abserves it's current state (n-day window stock price representation), selects and performs an action (buy/sell/hold), observes a subsequent state, receives some reward signal (difference in portfolio position) and lastly adjusts it's parameters based on the gradient of the loss computed.
There have been several improvements to the Q-learning algorithm over the years, and a few have been implemented in this project:
- Vanilla DQN
- DQN with fixed target distribution
- Double DQN
- Prioritized Experience Replay
- Dueling Network Architectures
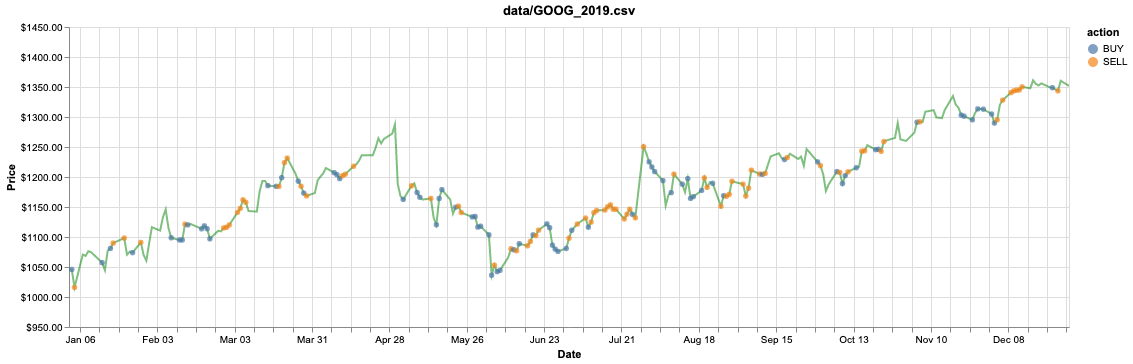
Trained on GOOG 2010-17 stock data, tested on 2019 with a profit of $1141.45 (validated on 2018 with profit of $863.41):
You can obtain similar visualizations of your model evaluations using the notebook provided.
- At any given state, the agent can only decide to buy/sell one stock at a time. This is done to keep things as simple as possible as the problem of deciding how much stock to buy/sell is one of portfolio redistribution.
- The n-day window feature representation is a vector of subsequent differences in Adjusted Closing price of the stock we're trading followed by a sigmoid operation, done in order to normalize the values to the range [0, 1].
- Training is prefferably done on CPU due to it's sequential manner, after each episode of trading we replay the experience (1 epoch over a small minibatch) and update model parameters.
You can download Historical Financial data from Yahoo! Finance for training, or even use some sample datasets already present under data/.
In order to use this project, you'll need to install the required python packages:
pip3 install -r requirements.txtNow you can open up a terminal and start training the agent:
python3 train.py data/GOOG.csv data/GOOG_2018.csv --strategy t-dqnOnce you're done training, run the evaluation script and let the agent make trading decisions:
python3 eval.py data/GOOG_2019.csv --model-name model_GOOG_50 --debugNow you are all set up!
- @keon for deep-q-learning
- @edwardhdlu for q-trader