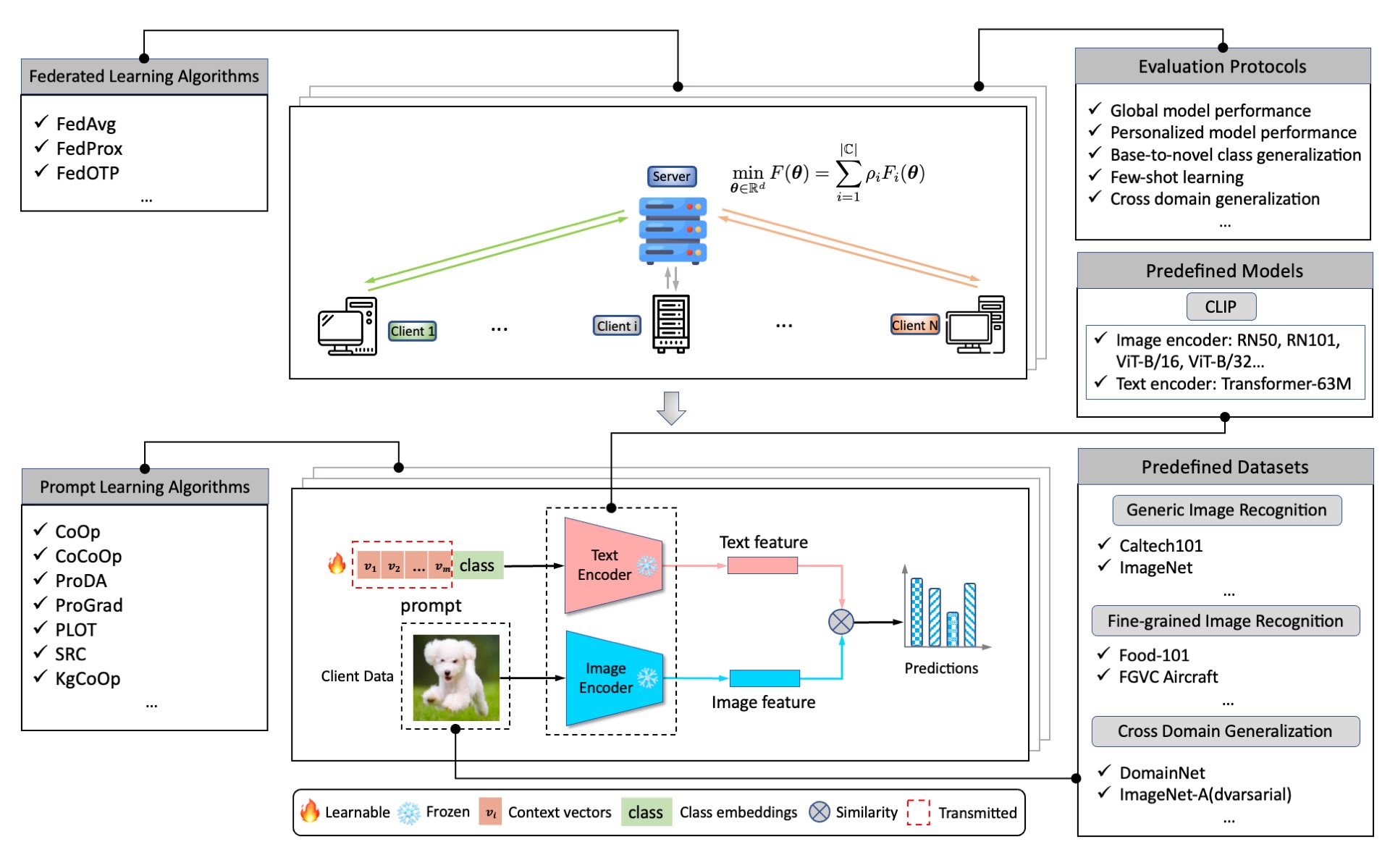
FLiP is a comprehensive benchmark suite for large-scale evaluation of federated prompt learning methods, particularly on vision tasks. It integrates a rich set of federated prompt learning algorithms to provide a reproducible benchmark with aligned experimental settings to track the cutting-edge advancements in this field. FLiP also offers off-the-shelf highly-reusable functionalities for flexible customization and agile developing of novel federated prompt learning algorithms. Blessed by the decoupled design of federated learning and prompt learning modules, it can be readily extended to harvest the progress from federated learning and prompt learning communities. FLiP is also remarkably more convenient to use than modifying centralized prompt learning repos to adapt to federated settings.
FLiP offers modularized design of each components. In this way, it is capable of integrating a rich collection of federated learning and prompt learning algorithms, providing unified data loading interface on a wide variety of datasets under comprehensive evaluation protocols. It is also under active development and will continuously include more models, tasks, and functionalities for federated prompt learning.
FLiP
├── flcore
│ ├── clients # local training algorithms for clients
│ │ ├── client_base.py
│ │ ├── client_fedavg.py
│ │ └── client_fedotp.py
│ ├── datasets # dataset partition and processing
│ │ ├── base.py
│ │ ├── caltech101.py
│ │ ├── domain_net.py
│ │ ├── imagenet.py
│ │ ├── ...
│ │ ├── imageloader.py
│ │ ├── info.py
│ │ ├── randaugment.py
│ │ ├── randtransform.py
│ │ └── utils.py
│ ├── models # model configurations
│ │ ├── clip # CLIP models and prompt learning algorithms
│ │ ├── cnn
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── text
│ │ └── utils.py
│ ├── optimizers # customizable optimizers
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── sam.py
│ │ └── utils.py
│ ├── pretty
│ │ ├── history.py
│ │ └── logger.py
│ ├── servers # global aggregation algorithms on server
│ │ ├── ground_metric.py
│ │ ├── server_base.py
│ │ ├── server_fedavg.py
│ │ └── server_fedotp.py
│ └── utils.py
├── main.py
├── scripts # shell scripts for reproducing results
│ └── run_batch.sh
└── tools # misc tools for building envs, dataset processing, etc
└── install_pt_2100.sh
We use Anaconda to install and manage the required Python packages.
We provide the shell script for setting up the environments, which is /tools/install_pt_2100.sh shown as follows:
conda create -n pt-2100 python=3.10.14 -y
source ${HOME}/app/anaconda3/bin/activate pt-2100 # need customization
conda install -y pytorch==2.1.0 torchvision==0.16.0 torchaudio==2.1.0 pytorch-cuda=12.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia
conda install -y matplotlib pandas
conda install -y tensorboard tensorboardx
conda install -y tqdm scikit-learn termcolor
conda install -c conda-forge opencv -y
conda install -y numpy==1.23.5
pip install h5py ftfy regex
Notably, the default installation path of anaconda is ${HOME}/app/anaconda3,
which may requires customization to activate the created conda env.
The instructions for downloading and preparing datasets can be found here.
By default, we use SLURM for job scheduling in order to achieve large-scale evaluation.
For example, the shell script for running experiments for evalation of global model performance that sweeps the combination of
various algorithms and datasets is /scripts/run_batch.sh.
To run experiments without SLURM,
turn off the SLURM option in run_batch.sh to --slurm=false.
cd ../
mkdir outputs
prefix="srun --exclusive -n 1 -c 8 --gpus-per-task=1 --mem=15G"
for algo in CLIP CoOp CoCoOp PromptSRC OTP KgCoOp PLOT ProDA ProGrad; do
for dataset in caltech101 fgvc_aircraft food101 oxford_flowers oxford_pets stanford_cars ucf dtd; do
$prefix python main.py \
--times=3 \
--benchmark=global \
--data_root=~/data/prompt \
--num_workers=6 \
--precision=amp \
--dataset=$dataset \
--image_backbone=RN50 \
--prompt_algo=$algo \
--optim_name=sgd \
--lr_scheduler='cos' \
--split_alpha=0.1 \
--loss_type=ce \
--central=false \
--num_clients=10 \
--num_shot=8 \
--optim_momentum=0.9 \
--local_learning_rate=0.002 \
--batch_size=16 \
--eval_scaler=2 \
--num_prompt=1 \
--local_epochs=1 \
--global_rounds=50 \
--prompt_batch_size=2 \
--eval_multi=false \
--client_eval=false \
--slurm=true \
--verbose2 > outputs/"${algo}_${dataset}.out" &
sleep 5
done
done
wait
echo "All jobs done!"
The meaning of each argument can be found in the help information of argparse:
usage: main.py [-h] [-bench {dual,global,personal,base2novel,xdomain,multidomain,xdataset}] [-falg {FedAvg,FedOTP}]
[-palg {CLIP,CoOp,CoCoOp,PLOT,ALIGN,ProDA,ProGrad,PromptSRC,BPL,KgCoOp,OTP}] [-ctr CENTRAL]
[-did DEVICE_ID] [-t TIMES] [-slurm {true,false}] [-detm {true,false}] [--verbose] [--verbose2]
[-ibb {RN50,ViT-B/16}] [-data DATASET] [-tdata TARGET_DATASET] [-root DATA_ROOT] [-dnt NUM_SHOT]
[-dns NUM_SHARDS] [-dsm {dirichlet,iid}] [-dsa SPLIT_ALPHA] [-dsb SPLIT_BETA] [-dtf {default,randaug}]
[-ddl {true,false}] [-dpl {true,false}] [-dnw NUM_WORKERS] [-nc NUM_CLIENTS] [-cevl {true,false}]
[-gr GLOBAL_ROUNDS] [-le LOCAL_EPOCHS] [-tf TRAIN_FRACTION] [-cdr CLIENT_DROP_RATE] [-opn OPTIM_NAME]
[-orho OPTIM_RHO] [-lrs {,cos}] [-lbs BATCH_SIZE] [-lvbs EVAL_SCALER] [-evrds EVAL_ROUNDS]
[-lr LOCAL_LEARNING_RATE] [-omt OPTIM_MOMENTUM] [-owd OPTIM_WEIGHT_DECAY] [-prec {fp32,fp16,amp}]
[-iws INIT_WEIGHTS] [-lst {ce,bce}] [-gcn GRAD_CLIPPING_NORM] [-seed SEED] [-npt NUM_PROMPT]
[-nptv NUM_PROMPT_VISION] [-nctx NUM_CONTEXT] [-ctp CLASS_TOKEN_POSITION] [-csc {true,false}]
[-cti CTX_INIT] [-pbsz PROMPT_BATCH_SIZE]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-bench, --benchmark {dual,global,personal,base2novel,xdomain,multidomain,xdataset}
benchmark metrics for algorithms evaluation
-falg, --fed_algo {FedAvg,FedOTP}
federated learning algorithms
-palg, --prompt_algo {CLIP,CoOp,CoCoOp,PLOT,ALIGN,ProDA,ProGrad,PromptSRC,BPL,KgCoOp,OTP}
prompt learning algorithms
-ctr CENTRAL, --central CENTRAL
centralized training mode
-did DEVICE_ID, --device_id DEVICE_ID
the device id for GPU
-t TIMES, --times TIMES
number of times of experimental run
-slurm, --slurm {true,false}
whether to use SLURM as the job scheduler
-detm, --deterministic {true,false}
deterministic run (for debug)
--verbose verbose debug message
--verbose2 verbose2 debug message
-ibb {RN50,ViT-B/16}, --image_backbone {RN50,ViT-B/16}
pretrained backbone models from CLIP
-data DATASET, --dataset DATASET
source dataset for training
-tdata TARGET_DATASET, --target_dataset TARGET_DATASET
target dataset for testing (on xdomain and xdataset metric)
-root DATA_ROOT, --data_root DATA_ROOT
dataset root folder
-dnt NUM_SHOT, --num_shot NUM_SHOT
number of shots of each class
-dns NUM_SHARDS, --num_shards NUM_SHARDS
number of dataset shards
-dsm {dirichlet,iid}, --split_mode {dirichlet,iid}
dataset split mode
-dsa SPLIT_ALPHA, --split_alpha SPLIT_ALPHA
alpha parameter for dirichlet split mode
-dsb SPLIT_BETA, --split_beta SPLIT_BETA
beta parameter for dataset split
-dtf, --data_transform {default,randaug}
data augmentation approaches
-ddl, --drop_last {true,false}
whether drop the last batch data
-dpl, --parallel {true,false}
whether use parallel data loading
-dnw NUM_WORKERS, --num_workers NUM_WORKERS
number of workers for data loading
-nc NUM_CLIENTS, --num_clients NUM_CLIENTS
number of total clients
-cevl, --client_eval {true,false}
whether perform local client evaluation on test set
-gr GLOBAL_ROUNDS, --global_rounds GLOBAL_ROUNDS
number of global training rounds
-le LOCAL_EPOCHS, --local_epochs LOCAL_EPOCHS
number of local epochs
-tf TRAIN_FRACTION, --train_fraction TRAIN_FRACTION
fraction of subsapling clients
-cdr CLIENT_DROP_RATE, --client_drop_rate CLIENT_DROP_RATE
ratio of stragglers
-opn OPTIM_NAME, --optim_name OPTIM_NAME
name of optimizer
-orho OPTIM_RHO, --optim_rho OPTIM_RHO
hyper-parameter for SAM optimizer
-lrs, --lr_scheduler {'',cos}
learning rate scheduler
-lbs BATCH_SIZE, --batch_size BATCH_SIZE
batch size for local training
-lvbs EVAL_SCALER, --eval_scaler EVAL_SCALER
scaling parameter of larger batch size for faster evaluation
-evrds EVAL_ROUNDS, --eval_rounds EVAL_ROUNDS
interval of rounds for global evaluation
-lr LOCAL_LEARNING_RATE, --local_learning_rate LOCAL_LEARNING_RATE
local learning rate
-omt OPTIM_MOMENTUM, --optim_momentum OPTIM_MOMENTUM
optimizer momentum
-owd OPTIM_WEIGHT_DECAY, --optim_weight_decay OPTIM_WEIGHT_DECAY
optimizer weight decay
-prec, --precision {fp32,fp16,amp}
full / mixed precision training
-iws INIT_WEIGHTS, --init_weights INIT_WEIGHTS
path of checkpoint weights
-lst, --loss_type {ce,bce}
type of loss
-gcn GRAD_CLIPPING_NORM, --grad_clipping_norm GRAD_CLIPPING_NORM
grad clipping norm
-seed SEED, --seed SEED
random seed
-npt NUM_PROMPT, --num_prompt NUM_PROMPT
number of learnable prompt
-nptv NUM_PROMPT_VISION, --num_prompt_vision NUM_PROMPT_VISION
number of vision prompt
-nctx NUM_CONTEXT, --num_context NUM_CONTEXT
number of text prompt
-ctp CLASS_TOKEN_POSITION, --class_token_position CLASS_TOKEN_POSITION
class token position in a prompt
-csc, --class_specific_context {true,false}
whether use class specific context
-cti CTX_INIT, --ctx_init CTX_INIT
context initialization string
-pbsz PROMPT_BATCH_SIZE, --prompt_batch_size PROMPT_BATCH_SIZE
prompt batch size for ProDA
Each experimental run will create a results folder to save benchmarked metrics,
an output folder to keep training logs and a summaries folder to store
tensorboard logs for visualization.