ADMiner is an Active Directory audit tool that leverages cypher queries to crunch data from the BloodHound graph database (neo4j) and gives you a global overview of existing weaknesses through a web-based static report, including detailed listing, dynamic graphs, key indicators history, along with risk ratings.
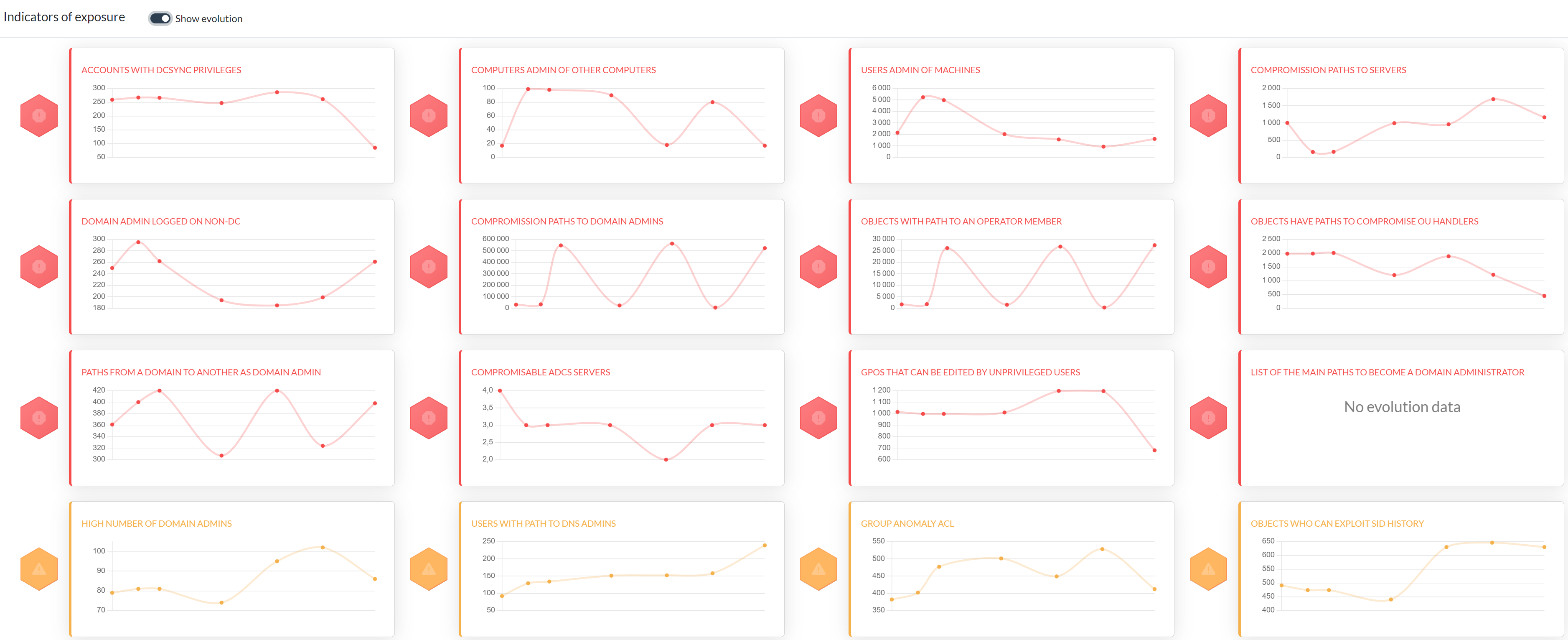
You can also observe indicators over time to help measuring mitigation efficiency.
ADMiner was created and is maintained by the Mazars Cybersecurity Audit & Advisory team.
Prerequisites: Python3
pip install -r requirements.txt
Run the tool:
./main.py [-h] [-b BOLT] [-u USERNAME] [-p PASSWORD] [-e EXTRACT_DATE] [-r RENEWAL_PASSWORD] [-a] [-c] [-l LEVEL] -cf CACHE_PREFIX [-ch NB_CHUNKS] [-co NB_CORES] [--rdp] [--evolution EVOLUTION] [--cluster CLUSTER]
Example:
./main.py -c -cf My_Report -u neo4j -p mypassword
To better handle large data sets, it is possible to enable multi-threading and also to use a cluster of neo4j databases, as shown in the following example (where server1 handles 32 threads and server2 handles 16) :
./main.py -c -cf My_Report -b bolt://server1:7687 -u neo4j -p mypassword --cluster server1:7687:32,server2:7687:16
Options:
-h, --help Show this help message and exit
-b, --bolt Neo4j bolt connection (default: bolt://127.0.0.1:7687)
-u, --username Neo4j username (default : neo4j)
-p, --password Neo4j password (default : neo5j)
-e, --extract_date Extract date (e.g., 20220131). Default: last logon date
-r, --renewal_password Password renewal policy in days. Default: 90
-a, --azure Use Azure relations
-c, --cache Use local file for neo4j data
-l, --level Recursive level for path queries
-cf, --cache_prefix Cache file to use (in case of multiple company cache files)
-ch, --nb_chunks Number of chunks for parallel neo4j requests. Default : number of CPU
-co, --nb_cores Number of cores for parallel neo4j requests. Default : number of CPU
--rdp Include the CanRDP edge in graphs
--evolution Evolution over time : location of json data files. ex : '../../tests/'
--cluster Nodes of the cluster to run parallel neo4j queries. ex : host1:port1:nCore1,host2:port2:nCore2,...
The following provides a list controls that have already been implemented in AD Miner :
| Dormant accounts | Tier 0 sessions violation | Control path cross domain from DA to DA |
| Ghost computers | Machine accounts with admin privs | Control paths to GPOs |
| Accounts without password expiration | Obsolete OS | Control paths to servers |
| Accounts with old passwords | Inadequate number of domain admins | Control paths to OU |
| Accounts with clear-text passwords | RDP access | Control paths to GMSA passwords |
| Kerberoastable accounts | Domain functional level | Control path to AdminSDHolder container |
| AS-REP Roastable accounts | Users with admin privs | Users with path to DNS Admins |
| Accounts with SID history | Machine accounts with high privs | ACL anomalies on group objects |
| LAPS status | Non tier 0 with DCSync capabilities | Objects with path to an Operator Member |
| LAPS access | Unconstrained delegations | ADCS local admin privs |
| KRBTGT password age | Constrained delegations | Empty groups/OU |
| DC Shadow to DA | Role-based constrained delegations | |
| DC Shadow to all | Control paths to domain admins |
Check out how to contribute here.