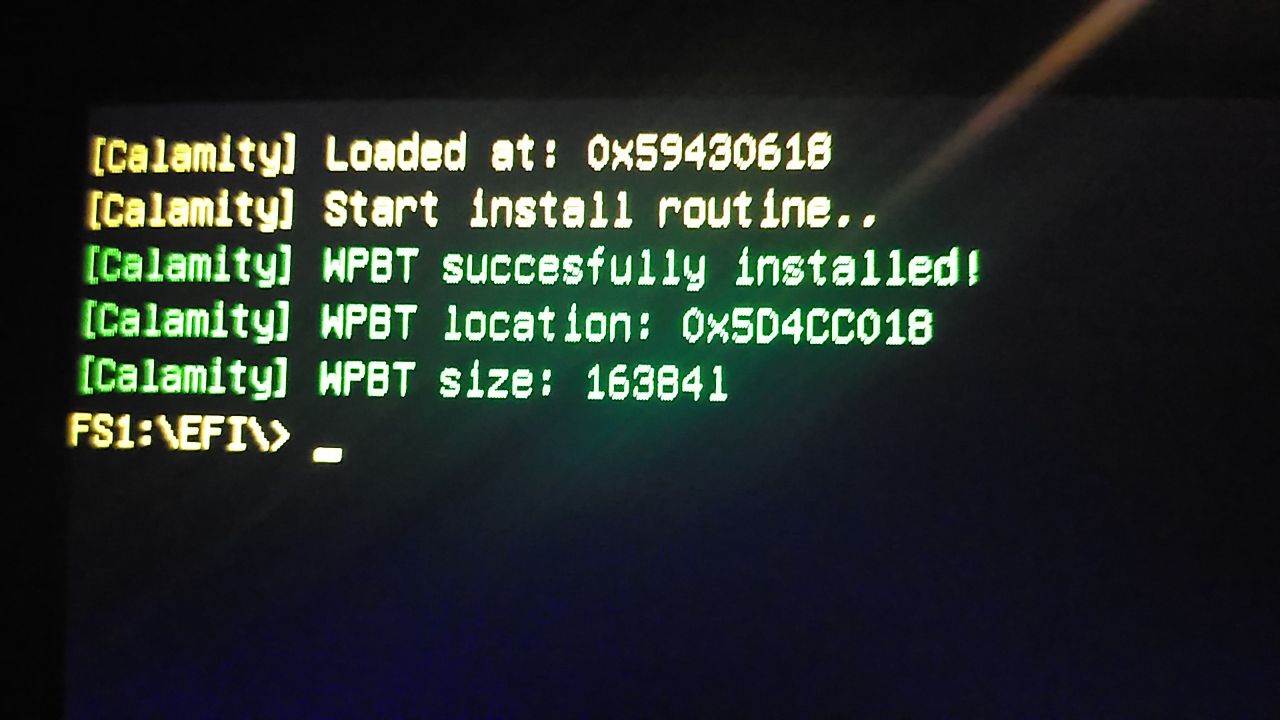
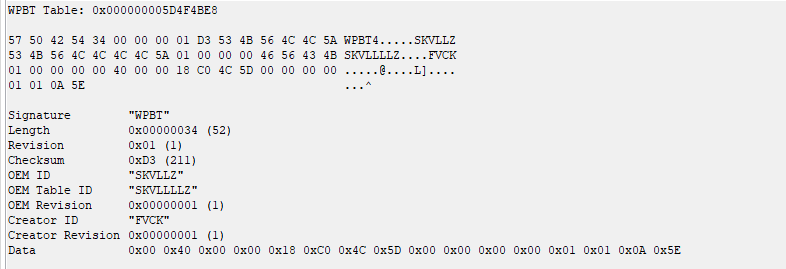
Calamity is a project that was written to better understand how the Windows Platform Binary Table (WPBT) works.
WPBT is a persistent Windows mechanism that allows to keep vendor applications even if the operating system is completely reinstalled. This is achieved by moving the application from anywhere (ideally in ROM) to ACPI memory. For example, anti-theft applications can use WPBT.
Calamity tries to be the easiest and friendliest implementation. You simply copy your application into the Driver.h header file and compile the EFI driver itself. After compiling, transfer the driver itself to the USB, then create an EFI\Boot partition and transfer the Shell.efi file from the repository, previously renamed bootx64.efi, to the created partition on the USB. Applications that use WPBT have their own limitations, which are described below.
PE files that use the WPBT mechanism must be built with the NATIVE subsystem, and they must necessarily be Ring 3 (User Mode) applications. Also, for such applications, only functions from ntdll (and no more!) can be used as dependencies. Also, the application must be signed, you can use your own certificate or use certificates from different leaks (also, don't forget to set /INTEGRITYCHECK in the linker settings). An example of a native application is in the repository.
The project uses VisualUefi to make working with EDKII easier. You may have to change the paths for header files and libraries in the project.
WPBT documentation is available on MSDN in .docx format.
SKVLLZ. (2023)