Features • Install • Usage • API Setup • Library • Join Discord
Subfinder is a subdomain discovery tool that discovers valid subdomains for websites by using passive online sources. It has a simple modular architecture and is optimized for speed. subfinder is built for doing one thing only - passive subdomain enumeration, and it does that very well.
We have designed subfinder to comply with all passive sources licenses, and usage restrictions, as well as maintained a consistently passive model to make it useful to both penetration testers and bug bounty hunters alike.
- Fast and powerful resolution and wildcard elimination module
- Curated passive sources to maximize results
- Multiple Output formats supported (Json, File, Stdout)
- Optimized for speed, very fast and lightweight on resources
- STDIN/OUT support for integrating in workflows
subfinder -hThis will display help for the tool. Here are all the switches it supports.
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -all | Use all sources (slow) for enumeration | subfinder -d uber.com -all |
| -config | Configuration file for API Keys, etc | subfinder -config config.yaml |
| -d | Domain to find subdomains for | subfinder -d uber.com |
| -dL | File containing list of domains to enumerate | subfinder -dL hackerone-hosts.txt |
| -exclude-sources | List of sources to exclude from enumeration | subfinder -exclude-sources archiveis |
| -max-time | Minutes to wait for enumeration results (default 10) | subfinder -max-time 1 |
| -nC | Don't Use colors in output | subfinder -nC |
| -nW | Remove Wildcard & Dead Subdomains from output | subfinder -nW |
| -ls | List all available sources | subfinder -ls |
| -o | File to write output to (optional) | subfinder -o output.txt |
| -oD | Directory to write enumeration results to (optional) | subfinder -oD ~/outputs |
| -oI | Write output in Host,IP format | subfinder -oI |
| -oJ | Write output in JSON lines Format | subfinder -oJ |
| -r | Comma-separated list of resolvers to use | subfinder -r 1.1.1.1,1.0.0.1 |
| -rL | Text file containing list of resolvers to use | subfinder -rL resolvers.txt |
| -recursive | Enumeration recursive subdomains | subfinder -d news.yahoo.com -recursive |
| -silent | Show only subdomains in output | subfinder -silent |
| -sources | Comma separated list of sources to use | subfinder -sources shodan,censys |
| -t | Number of concurrent goroutines for resolving (default 10) | subfinder -t 100 |
| -timeout | Seconds to wait before timing out (default 30) | subfinder -timeout 30 |
| -v | Show Verbose output | subfinder -v |
| -version | Show current program version | subfinder -version |
Subfinder requires go1.14+ to install successfully. Run the following command to get the repo -
▶ GO111MODULE=on go get -v github.com/projectdiscovery/subfinder/v2/cmd/subfinderSubfinder will work after using the installation instructions however to configure Subfinder to work with certain services, you will need to have setup API keys. The following services do not work without an API key:
- Binaryedge
- Certspotter
- Censys
- Chaos
- DnsDB
- Github
- Intelx
- Passivetotal
- Recon.dev
- Robtex
- SecurityTrails
- Shodan
- Spyse
- Threatbook
- Virustotal
- Zoomeye
Theses values are stored in the $HOME/.config/subfinder/config.yaml file which will be created when you run the tool for the first time. The configuration file uses the YAML format. Multiple API keys can be specified for each of these services from which one of them will be used for enumeration.
For sources that require multiple keys, namely Censys, Passivetotal, they can be added by separating them via a colon (:).
An example config file -
resolvers:
- 1.1.1.1
- 1.0.0.1
sources:
- binaryedge
- bufferover
- censys
- passivetotal
- sitedossier
binaryedge:
- 0bf8919b-aab9-42e4-9574-d3b639324597
- ac244e2f-b635-4581-878a-33f4e79a2c13
censys:
- ac244e2f-b635-4581-878a-33f4e79a2c13:dd510d6e-1b6e-4655-83f6-f347b363def9
certspotter: []
passivetotal:
- sample-email@user.com:sample_password
securitytrails: []
shodan:
- AAAAClP1bJJSRMEYJazgwhJKrggRwKA
github:
- d23a554bbc1aabb208c9acfbd2dd41ce7fc9db39
- asdsd54bbc1aabb208c9acfbd2dd41ce7fc9db39To run the tool on a target, just use the following command.
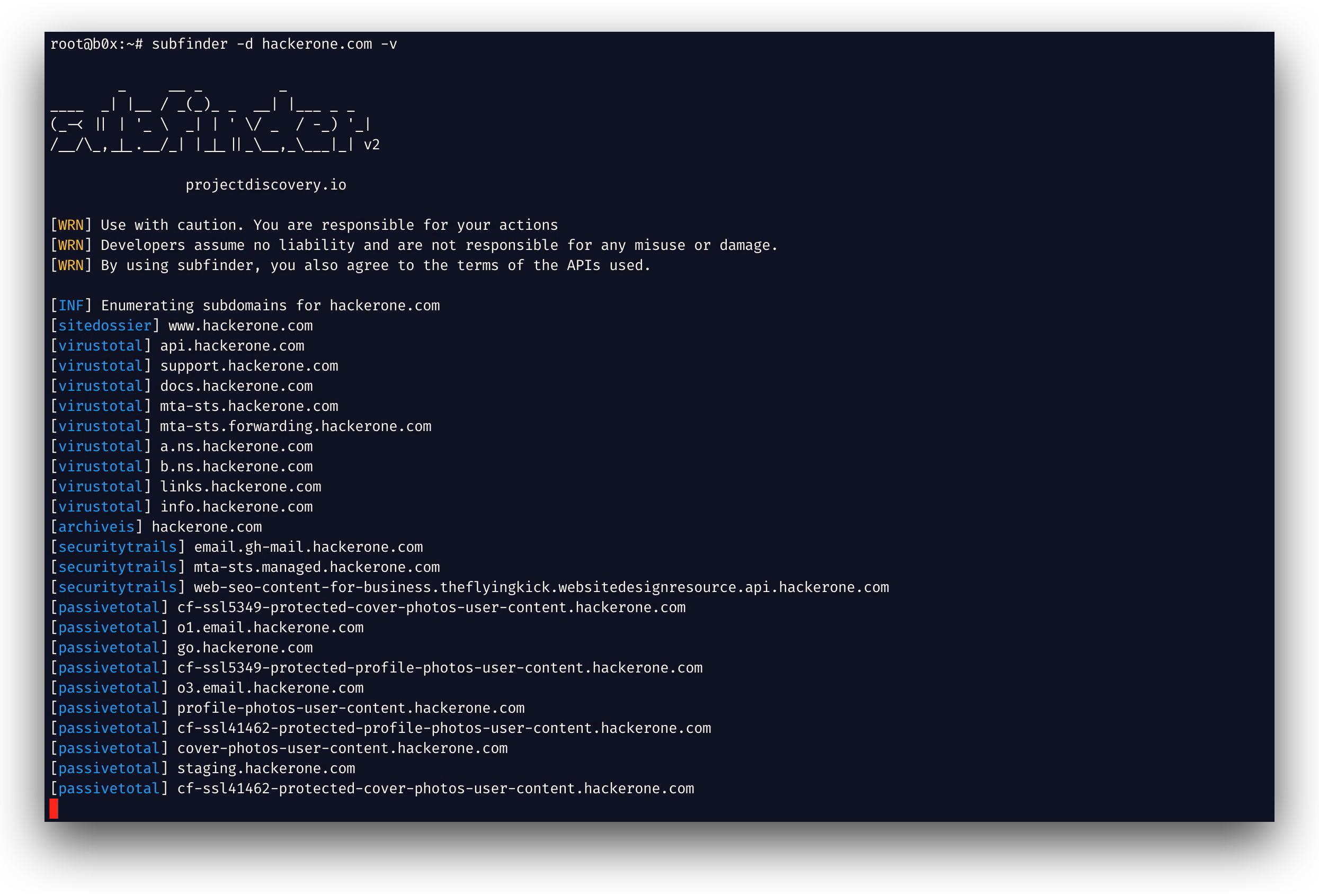
▶ subfinder -d example.comThe verbose flag v can be used to display verbose information.
[bufferover] lutin.dima.example.com
[bufferover] izosimdima.example.com
[bufferover] glazkovdima.example.com
[bufferover] dengshima.example.com
[bufferover] wwwkima.example.com
[bufferover] proxima.example.com
[bufferover] mma.example.com
[bufferover] damidoma.example.com
[bufferover] nomerdoma.example.com
[bufferover] soti.croma.example.com
The -o command can be used to specify an output file.
▶ subfinder -d example.com -o output.txtTo run the tool on a list of domains, -dL option can be used. This requires a directory to write the output files. Subdomains for each domain from the list are written in a text file in the directory specified by the -oD flag with their name being the domain name.
▶ cat domains.txt
hackerone.com
google.com
▶ subfinder -dL domains.txt -oD ~/path/to/output
▶ ls ~/path/to/output
hackerone.com.txt
google.com.txtYou can also get output in json format using -oJ switch. This switch saves the output in the JSON lines format.
If you use the JSON format, or the Host:IP format, then it becomes mandatory for you to use the -nW format as resolving is essential for these output format. By default, resolving the found subdomains is disabled.
▶ subfinder -d hackerone.com -o output.json -oJ -nW
▶ cat output.json
{"host":"www.hackerone.com","ip":"104.16.99.52"}
{"host":"mta-sts.hackerone.com","ip":"185.199.108.153"}
{"host":"hackerone.com","ip":"104.16.100.52"}
{"host":"mta-sts.managed.hackerone.com","ip":"185.199.110.153"}The subdomains discovered can be piped to other tools too. For example, you can pipe the subdomains discovered by subfinder to httpx httpx which will then find running http servers on the host.
▶ echo hackerone.com | subfinder -silent | httpx -silent
http://hackerone.com
http://www.hackerone.com
http://docs.hackerone.com
http://api.hackerone.com
https://docs.hackerone.com
http://mta-sts.managed.hackerone.com|
You can use the official dockerhub image at subfinder. Simply run - ▶ docker pull projectdiscovery/subfinderThe above command will pull the latest tagged release from the dockerhub repository. If you want to build the container yourself manually, git clone the repo, then build and run the following commands
docker build -t projectdiscovery/subfinder .If you are using docker, you need to first create your directory structure holding subfinder configuration file. After modifying the default config.yaml file, you can run: ▶ mkdir -p $HOME/.config/subfinder
▶ cp config.yaml $HOME/.config/subfinder/config.yaml
▶ nano $HOME/.config/subfinder/config.yamlAfter that, you can pass it as a volume using the following sample command. ▶ docker run -v $HOME/.config/subfinder:/root/.config/subfinder -it projectdiscovery/subfinder -d example.comFor example, this runs the tool against example.com and output the results to your host file system: docker run -v $HOME/.config/subfinder:/root/.config/subfinder -it projectdiscovery/subfinder -d example.com > example.com.txt |
|
Usage example: package main
import (
"bytes"
"context"
"fmt"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"github.com/projectdiscovery/subfinder/v2/pkg/passive"
"github.com/projectdiscovery/subfinder/v2/pkg/resolve"
"github.com/projectdiscovery/subfinder/v2/pkg/runner"
)
func main() {
config := runner.ConfigFile{
// Use the default list of resolvers by marshaling it to the config
Resolvers: resolve.DefaultResolvers,
// Use the default list of passive sources
Sources: passive.DefaultSources,
// Use the default list of all passive sources
AllSources: passive.DefaultAllSources,
// Use the default list of recursive sources
Recursive: passive.DefaultRecursiveSources,
}
runnerInstance, err := runner.NewRunner(&runner.Options{
Threads: 10, // Thread controls the number of threads to use for active enumerations
Timeout: 30, // Timeout is the seconds to wait for sources to respond
MaxEnumerationTime: 10, // MaxEnumerationTime is the maximum amount of time in mins to wait for enumeration
YAMLConfig: config,
})
buf := bytes.Buffer{}
err = runnerInstance.EnumerateSingleDomain(context.Background(), "projectdiscovery.io", []io.Writer{&buf})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
data, err := ioutil.ReadAll(&buf)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%s", data)
} |
subfinder is made with 🖤 by the projectdiscovery team. Community contributions have made the project what it is. See the Thanks.md file for more details.
Read the disclaimer for usage at DISCLAIMER.md and contact us for any API removal.