A novel machine learning method to cluster and identify damage modes in CFRP in compression-after-impact tests
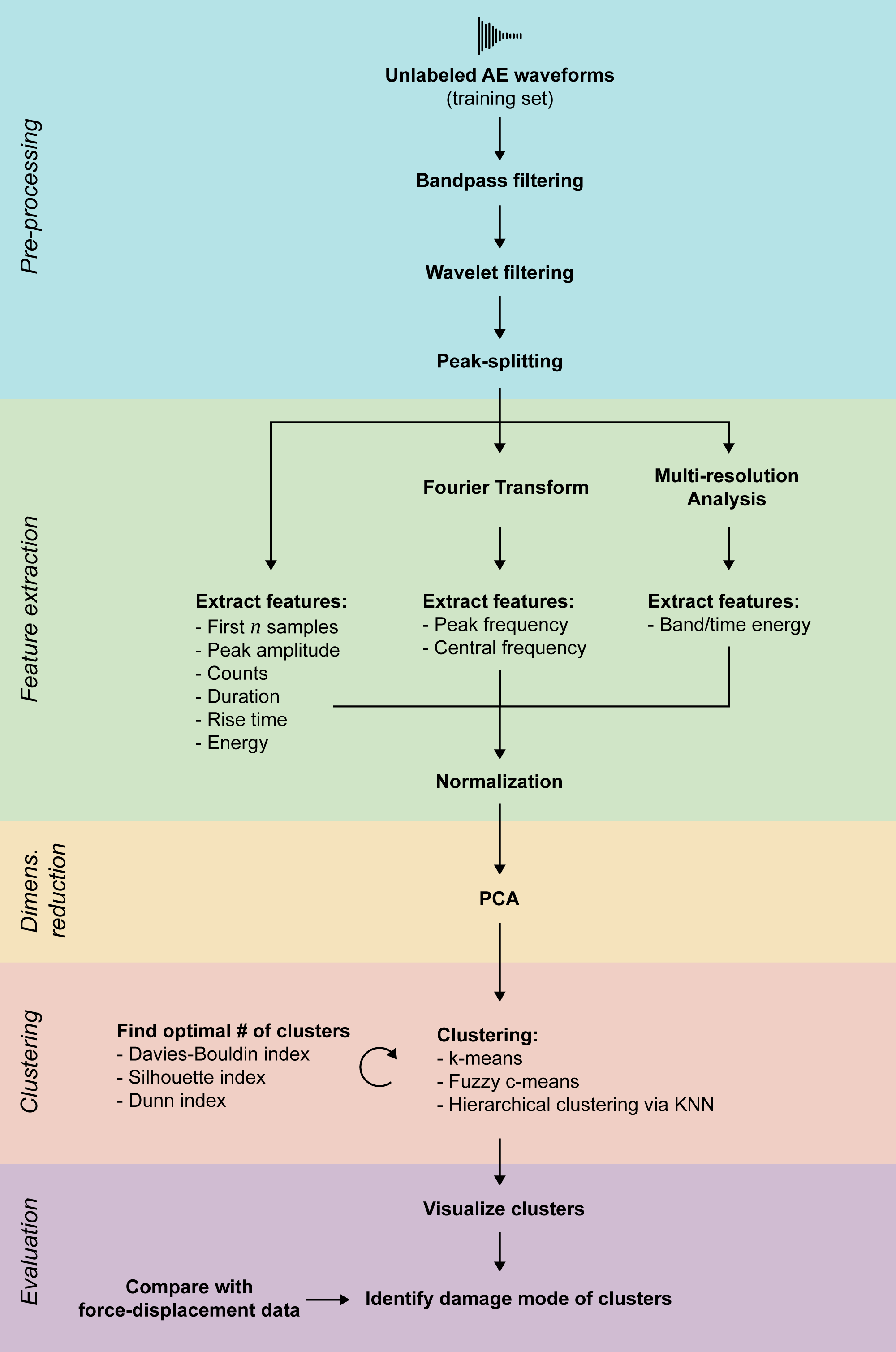
This is the repository for the TU Delft AE2223-I research project of group D5. The goal is the identification of the damage mode in composites under compression after impact based on acoustic emission measurements. A data analysis pipeline consisting of pre-processing, feature extraction, dimensionality reduction and clustering performs this task.
Links:
- See the research plan for more details on the project
- See the paper for the research results
- See the developer's guidelines if you want to contribute
To get started with development:
- Ensure that Python 3.9 is installed.
- Clone the GitHub repository by clicking on the green "Code" button above and follow the instructions.
- Open the cloned folder in PyCharm (other IDEs can be used, adjust the following instructions accordingly).
- Add a new interpreter in a Virtualenv environment. This ensures isolation so that the packages for this project do not conflict with your preinstalled ones.
- Install all required packages by opening
requirements.txtand clicking "Install requirements". This ensures that everyone uses the same package versions, preventing bugs that might be hard to find. - Read the code and Git guidelines in this document so the code stays consistent and clear.
To run the code from the console, make sure you are in the project directory and activated the virtual environment (<venv>\Scripts\activate.bat on Windows, source <venv>/bin/activate on Linux).
The main script can then be executed using python -m damage_identification [mode] where possible modes are:
train: train the pipeline (mostly feature extraction, PCA and clustering) on a training data setpredict: predict the damage mode of one or multiple examples using a trained pipeline and show evaluation results--help: show a help message with all possible command line options. This can also be appended to every mode to show mode-specific options.
Alternatively, the scripts in bin can be used which automatically activate the virtual environment and offer the same parameters.
The dataset(s) are specified as positional argument. Multiple data files can be given, separated by commas. Multiple files is only recommended for training. During prediction, issues may occur if predicting on multiple datasets simultaneously. For example, metadata normalization (force, displacement) will be inconsistent.
The trained pipelines and prediction results are stored in data/. The folder of a trained pipeline (data/pipeline_...) can be copied to run the pipeline to another computer. The data/ folder is also the recommended folder to store training and prediction datasets, since it is not committed to Git.
Train the pipeline on data/dataset.tradb, finding the optimal number of clusters between 2 and 5, and requiring 90% of explained variance for PCA:
python -m damage_identification train --n_clusters 2...5 --explained_variance 0.9 data/dataset.tradb
Predict the cluster memberships of the first 1000 examples in data/other_dataset.csv and associate with metadata:
python -m damage_identification predict --limit_data 1000 data/other_dataset.csv \
--metadata_file data/other_dataset_metadata.pickle
Ensure that the virtual environment with Python 3.9 and all dependencies is activated before running these commands.
Configurable parameters are passed to the pipeline as command line arguments
using --parameter_name value. The following parameters are available in every mode:
limit_data(int): only process the firstlimit_datarows of the specified datasetskip_shuffling: shuffling of dataset is skipped if flag is presentenable_peak_splitting: enable splitting of waveform if multiple peaks are detected (slow!)pipeline_name/-n: name of the pipeline model, enables training on different data
The following parameters are available during training:
sampling_rate(float, default: 2 048 000): the sampling rate/frequency of the examplesskip_filter: bandpass and wavelet filtering is skipped if flag is presentskip_saturation_detection: saturation detection is skipped if flag is presentfiltering_wavelet_family(str): the wavelet family name for wavelet filtering, either db for Daubechies or coif for Coifletfiltering_wavelet_scale(int): the magnification scale of the wavelet family for wavelet filtering, must be 3-38 for Daubechies or 1-17 for Coifletfiltering_wavelet_threshold(str or float): the threshold for wavelet filtering, either a numerical value or a threshold optimization method (optimal, iqr or sd)bandpass_low(float, default: 100): the low cutoff for the bandpass filter in kHzbandpass_high(float, default: 900): the high cutoff for the bandpass filter in kHzbandpass_order(int, default: 25): the order for the Butterworth bandpass filterdirect_features_threshold(float between 0 and 1): threshold for direct features like counts and duration, as fraction of the peak amplitudedirect_features_n_samples(int): how many raw firstnsamples should be used as features, without further transformationmra_wavelet_family(str): the wavelet family name for MRA (multi-resolution analysis), either db for Daubechies or coif for Coifletmra_wavelet_scale(int, default: 3): the magnification scale of the wavelet family for MRA, must be 3-38 for Daubechies or 1-17 for Coifletmra_time_bands(int, default: 4): the amount of time bands to split the energy information intomra_levels(int, default: 3): the decomposition level of the signaln_clusters(int or "start...end"): number of clusters (e.g. for k-means), determined based on multiple indices if range of k is specifiedexplained_variance(float between 0 and 1): desired level of explained variance for PCA selection, mutually exclusive withn_principal_componentsn_principal_components(int): desired number of components for PCA selection, mutually exclusive withexplained_variancen_neighbors(int): desired number of neighbors to be utilised in the KNN algorithm in the hierarchical clustering (should be an odd value)
The following parameters are available during prediction:
skip_visualization: plotting is skipped if flag is presentskip_statistics: printing of cluster and PCA statistics is skipped if flag is presentenable_identification: enable identification of damage mode based on cluster membershipsmetadata_file: path of metadata files generated with metadata extraction script (see below), separated by commas. Order must match the order of data files.
Next to the main program, this project contains some standalone scripts.
Some AE waveforms actually contain multiple hits, which can be detected by their initial peaks. Splitting waveforms by their peaks can be enabled in the pipeline using enable_peak_splitting. However, since it takes long, it is usually more efficient to perform peak-splitting before, so the pipeline can operate on an already peak-split dataset. This will also generate an index file ending in _idx.npy, associating the split examples with the original one.
Usage:
python damage_identification/preprocessing/peak_splitter.py [data_file]
data_file: the dataset to split
Each example of AE measurements has associated metadata. These include the timestamp, displacement and applied force, stored in the .pridb file. This script can extract these metadata, using interpolation and the index file in case of a peak-split dataset.
Usage:
python damage_identification/metadata.py [index_file] [pridb_file]
index_file: a file containing the indexes of the dataset. Either the datas et file (.tradb or .csv) itself for unsplit data, or the index file_idx.npyfor a peak-split dataset.pridb_file: the .pridb file containing the metadata
At the end of prediction, all plots are generated and saved to the results folder. However, in some cases, it is necessary to regenerate these plots from the numerical prediction results, which are saved in the results folder as well in the data.pickle file. This script allows this regeneration based on the saved prediction results.
Usage:
python damage_identification/evaluation/visualization.py [results_folder]
results_folder: a folder with prediction results containing adata.picklefile (e.g.data/results/2022-05-23T14-04-17)
The quality of clustering, for example how well clustering actually separates data, can be measured by indexes. This script can calculate the Davies, Silhouette, Dunn and Calinski-Harabasz indexes for different numbers of clusters. Note that only the first 10000 training examples are used for index calculations. The pipeline has to be trained with more examples than that.
Usage:
python damage_identification/evaluation/cluster_indexes.py [pipelines]
pipelines: a comma-separated list of pipeline directories (e.g.data/pipeline_DS0_3,data/pipeline_DS0_5). These pipelines should have been trained on the same dataset with different--n_clusters.
This script prints information about a trained pipeline. This includes the parameters used for training and information about PCA.
Usage:
python damage_identification/pipeline.py [pipeline]
pipeline: a pipeline directory (e.g.data/pipeline_DS0)
While using the pipeline, you will encounter different file types, identified by their suffix and extension:
.tradb: "transient database" stored by the Vallen AE data acquisition system, internally an SQLite database. Contains the AE signals for each hit..csv: alternative format for AE signals, e.g., when they were already pre-processed by another script_split.npy: signals to which peak splitting has been applied, generated from.tradbor.csvusingdamage_identification/preprocessing/peak_splitter.py._split_idx.npy: index file mapping the peak-split signals in_split.npyto their original signal, necessary for metadata mapping..pridb: "primary database" stored by the Vallen AE data acquisition system, internally an SQLite database. Contains the metadata for each hit._metadata.pickle: metadata file corresponding to a_split.npyfile (if extension is_split_metadata.pickle), or to a non-peak-split file such as.tradbotherwise. Extracted from.pridbusingdamage_identification/metadata.py. Can be loaded during prediction using--metadata_file.
- Acoustic emission: a non-destructive evaluation technique for composites, recording elastic waves emitted when damage occurs
- Example: a single waveform, term is commonly used in machine learning
- Pipeline: the collective term for all components and the flow of data between them, starting from raw waveforms and ending at the identified damage mode
- Sample: a single data point in a waveform, associated with a certain time
- Training set: the set of examples used to train the pipeline
- Validation set: the set of examples used to evaluate the performance of the pipeline
- Waveform: the acoustic emission measurement recorded by the sensor, made up of samples