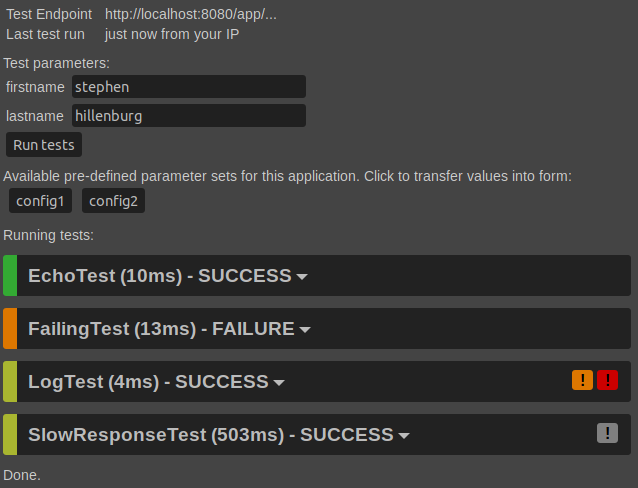
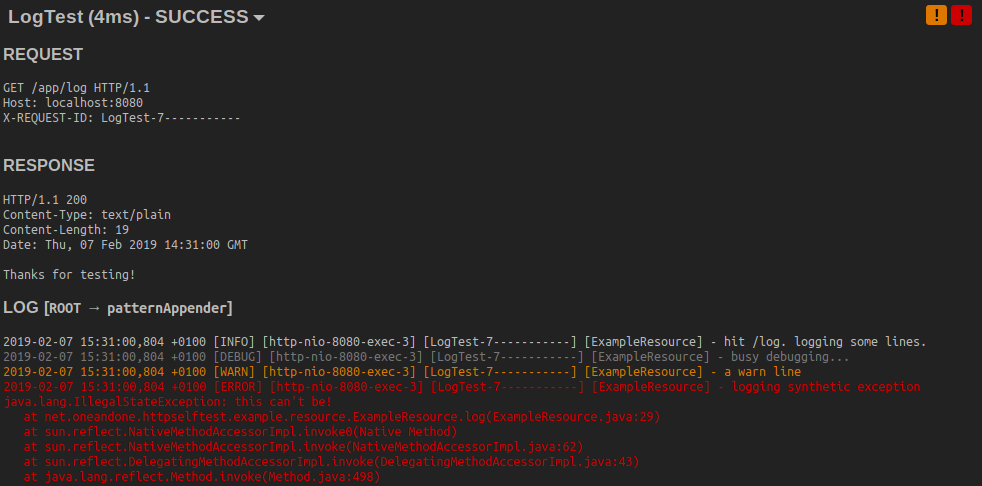
This repo implements a base servlet and surrounding infrastructure to enable semi-automatic tests against a running application in any development stage. The tests are deployed with the application and run against itself. Test parameters can be pre-defined or provided by the user. This allows to have meaningful test parameters across multiple stages and environments.
The intended use is not clear-cut. The servlet can be used for e.g.
- basic integration tests,
- smoke tests before general release,
- incident response,
- definitive insight into interface behavior.
public class MinimalSelftestServlet extends SelftestServlet {
@Override
protected TestConfigs getConfigs() {
return new TestConfigs("param1");
}
public static class TestEcho implements TestCase {
@Override
public TestRequest prepareRequest(TestValues config, Context ctx) throws Exception {
return new TestRequest("echo", "GET");
}
@Override
public void verify(TestValues config, TestResponse response, Context ctx) throws Exception {
Assertions.assertEqual("status code", 200, response.getStatus());
}
}
}You can easily play around with a simple test suite. Just launch the example app in the spring-boot-example module.
git clone https://github.com/1and1/httpselftest.git
cd httpselftest/selftest-springboot-example/
mvn spring-boot:run
# point your browser to the actuator endpoint: http://localhost:8081/actuator/selftest
# OR to the application port http://localhost:8080/selftest<dependency>
<groupId>net.oneandone.httpselftest</groupId>
<artifactId>selftest-core</artifactId>
<version>$VERSION</version>
</dependency>- Since HTTP Selftest is implemented as a Servlet, there is an implicit dependency on the javax Servlet API.
- HTML rendering is done using j2html. The dependency is co-packaged and shaded to avoid conflicts with production dependencies.
- JSON handling is done using json-simple. The dependency is co-packaged and shaded to avoid conflicts with production dependencies.
- In case Logback logging support is used, logback dependencies need to be on the classpath (
logback-classicandlogback-core).
The servlet is not supposed to be exposed to the internet. This is an internal developer tool. Additionally, you may want to set selftest.credentials.
If your application is a Spring Boot 2 app, the servlet can be registered as a @ServletEndpoint. In this case the application port and base path may need to be provided manually. The servlet will be running on the management port.
@ServletEndpoint(id = "selftest")
public class SelftestEndpoint implements Supplier<EndpointServlet> {
@Override
public EndpointServlet get() {
return new EndpointServlet(YourSelftestServlet.class)
.withInitParameter(SelftestServlet.PROP_OVERRIDE_PORT, "8080")
.withInitParameter(SelftestServlet.PROP_OVERRIDE_PATH, "/rest");
}
}If your application is a Spring Boot app, the servlet can be registered by the way of ServletRegistrationBean. This way it will be running on the application port.
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean<YourSelftestServlet> onProductionPort() {
return new ServletRegistrationBean<>(new YourSelftestServlet(), "/selftest");
}If your application has a web.xml, the servlet containing your test cases can be registered there.
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SelfTestServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>${SUBCLASS_OF_SelftestServlet}</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SelfTestServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/selftest</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>If you want to collect log messages and your application is not already collecting request tracking IDs in the MDC, you can do so by registering a SelftestMDCFilter.
The filter can be registered in Spring Boot apps by the way of FilterRegistrationBean.
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean selftestFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean filter = new FilterRegistrationBean();
filter.setFilter(new SelftestMDCFilter());
filter.addUrlPatterns("/*");
filter.setName("selftestFilter");
filter.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return filter;
}If you have a web.xml you can register it there.
<filter>
<filter-name>SelftestMDCFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>net.oneandone.httpselftest.servlet.SelftestMDCFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>SelftestMDCFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>| Servlet init parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
selftest.credentials |
Credentials for HTTP Basic authentication. Supports plain or SHA-256 (prefix with plain| or sha256|). |
no authentication |
selftest.logger |
Logging framework to be used for log message extraction. Possible values: [none, logback] |
logback |
selftest.configgroups |
Config groups can be used to filter out pre-defined configs that are irrelevant to the current environment. The values will be matched against the current hostname. Example: "local, staging". Check the example application for usage. |
no groups |
selftest.override.port |
Override for application port. Necessary if the httpselftest servlet runs on another port. | application port |
selftest.override.contextpath |
Override for application context path. Necessary if the httpselftest servlet runs on another port. | application path |
selftest.override.mdckey |
Override for MDC key storing the request tracking id. | X-REQUEST-ID |