This repository contains a Python implementation of the YIN algorithm for fundamental frequency estimation. The YIN algorithm is a widely used method for estimating the fundamental frequency (pitch) of an audio signal. Based on the paper by Alain de Cheveigné and Hideki Kawahara, "YIN, a fundamental frequency estimator for speech and music", J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 111, 1917 (2002); https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1458024
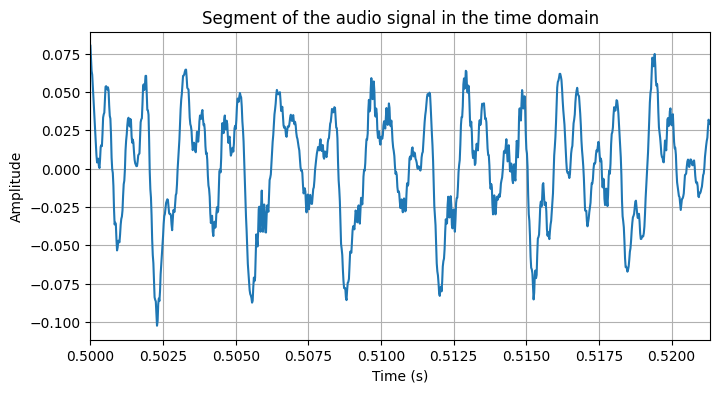
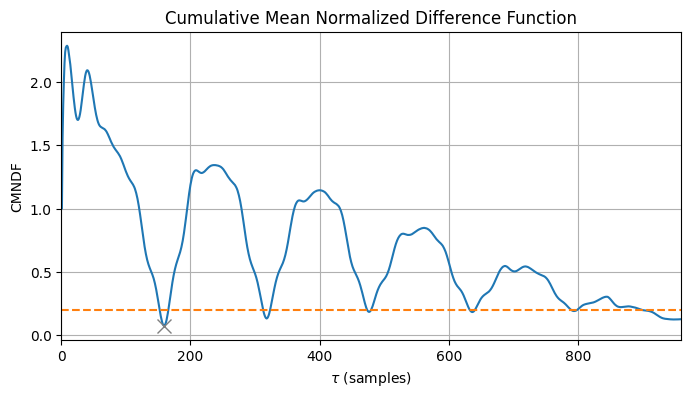
The YIN algorithm is a time-domain method based on the computation of the Cumulative Mean Normalized Difference Function (CMNDF) to find the fundamental frequency of a given audio signal.
This implementation includes the following components:
- Calculation of the difference function and the CMNDF
- Threshold-based candidate for the fundamental frequency
- Parabolic interpolation to refine the estimate of the fundamental frequency
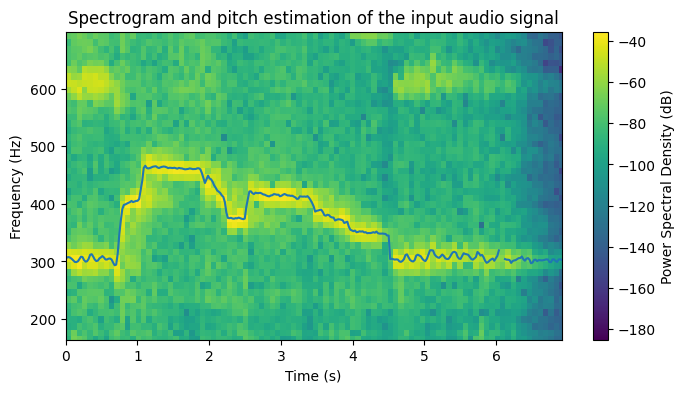
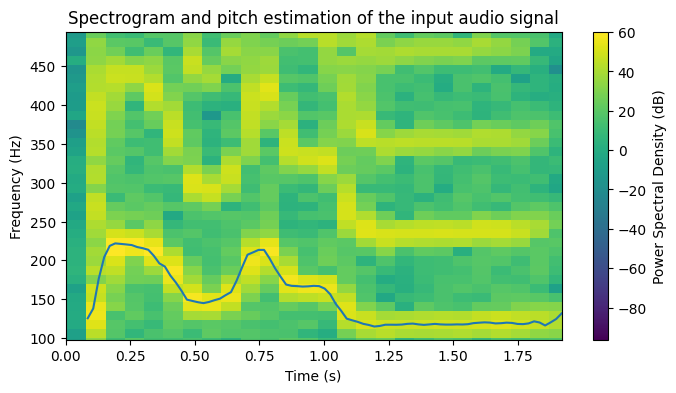
- Visualization of the pitch contour over a spectrogram
Predicted tau: 159.15 samples
Predicted fundamental frequency: 301.61 Hz
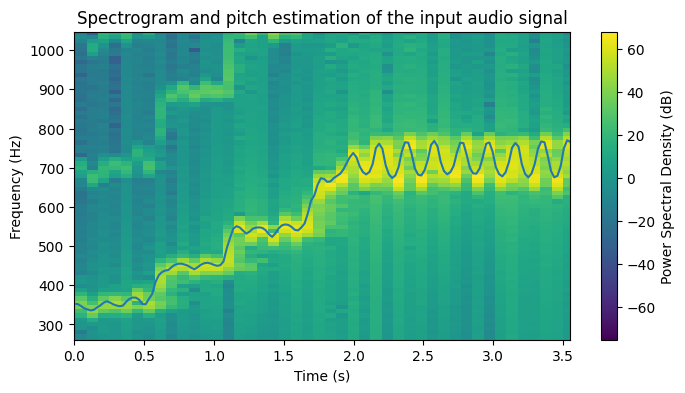
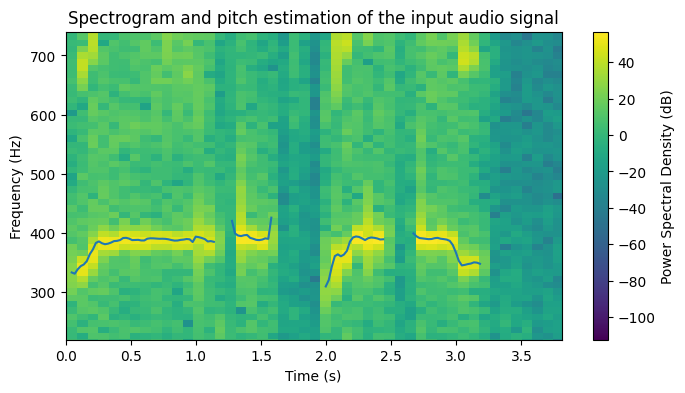
The script computes the estimated f0 values for the input signal and plots them on top of the spectrogram. The results of the pitch estimation for the different input audios (taken from freesound.org) are included next:
Sound 1: https://freesound.org/people/TheScarlettWitch89/sounds/427200/
Sound 2: https://freesound.org/people/daalvinz/sounds/367215/
Sound 3: https://freesound.org/people/HerbertBoland/sounds/30084/
Sound 4: https://freesound.org/people/TheScarlettWitch89/sounds/417938/
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/ABSounds/YIN-Pitch.git- Install the required packages:
pip install numpy scipy matplotlib tqdm- Run the
YIN_pitch.ipynbJupyter Notebook
For more information on the YIN pitch estimation algorithm, please refer to the following paper:
-
De Cheveigné, A., & Kawahara, H. (2002). YIN, a fundamental frequency estimator for speech and music. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 111(4), 1917–1930. DOI: 10.1121/1.1458024
-
Sounds taken from freesound.org: