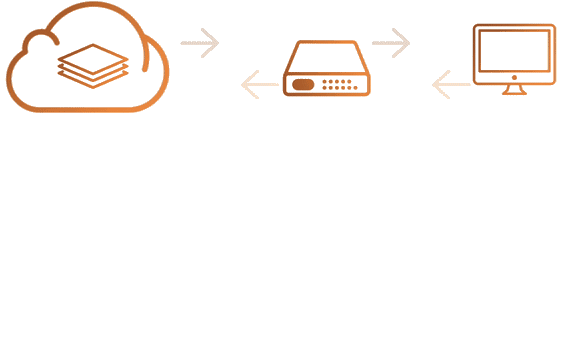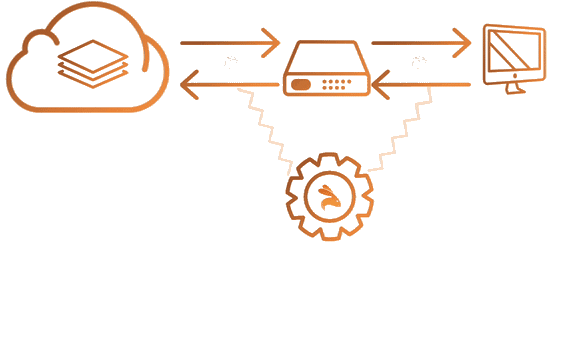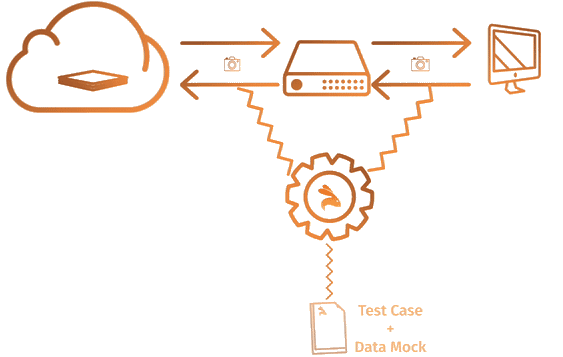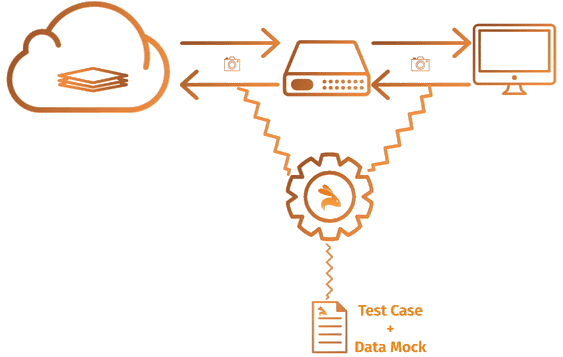
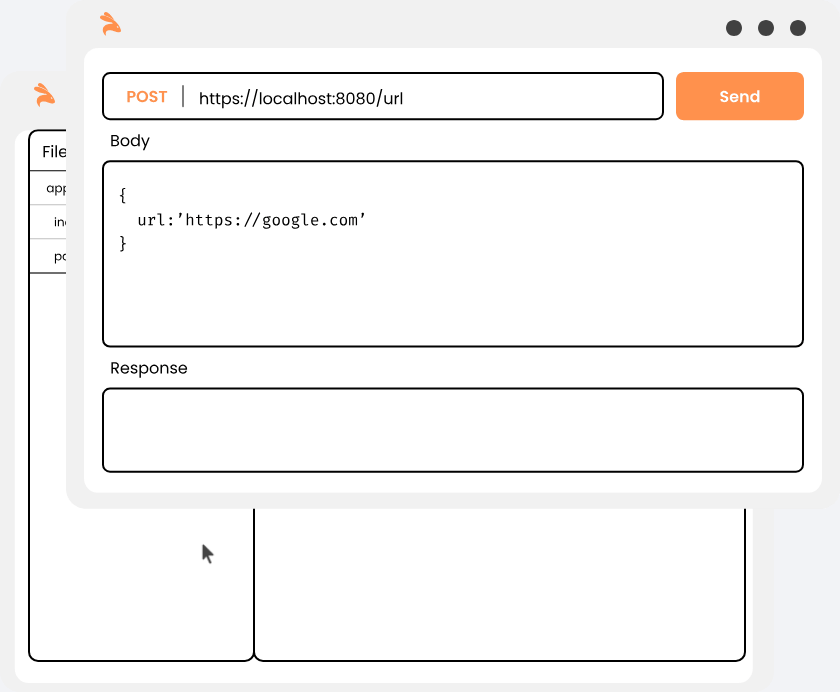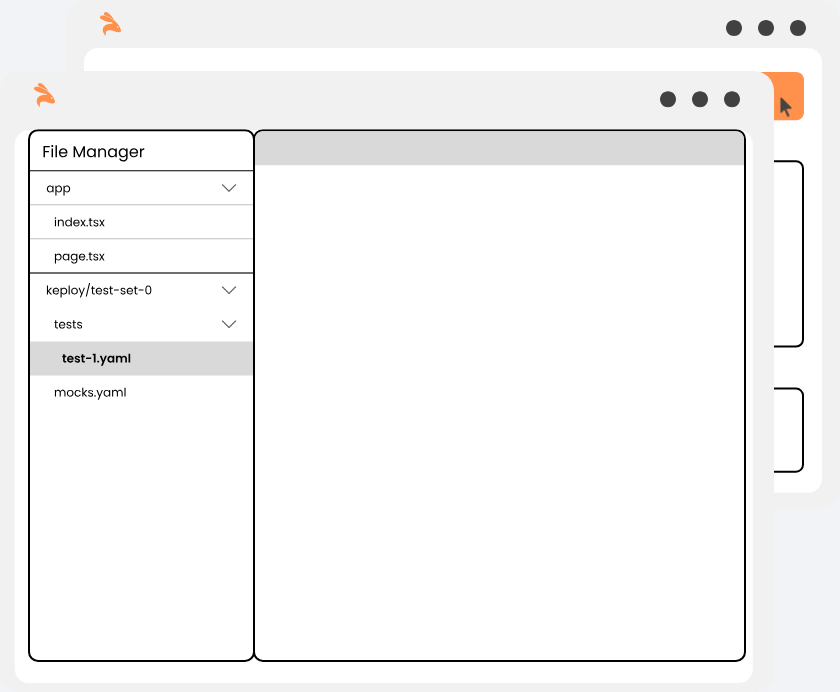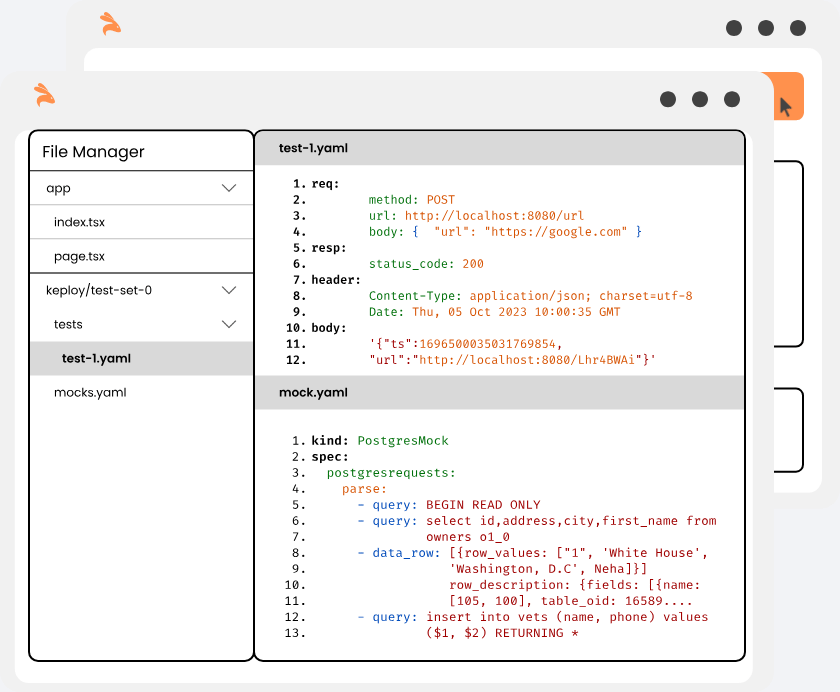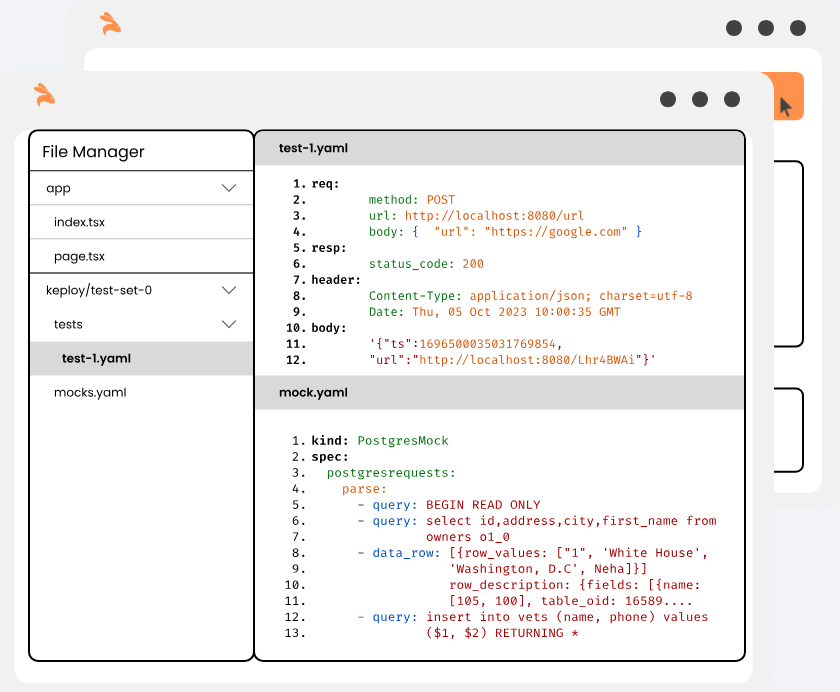
Keploy is a functional testing toolkit for developers. It generates E2E tests for APIs (KTests) along with mocks or stubs(KMocks) by recording real API calls. KTests can be imported as mocks for consumers and vice-versa.
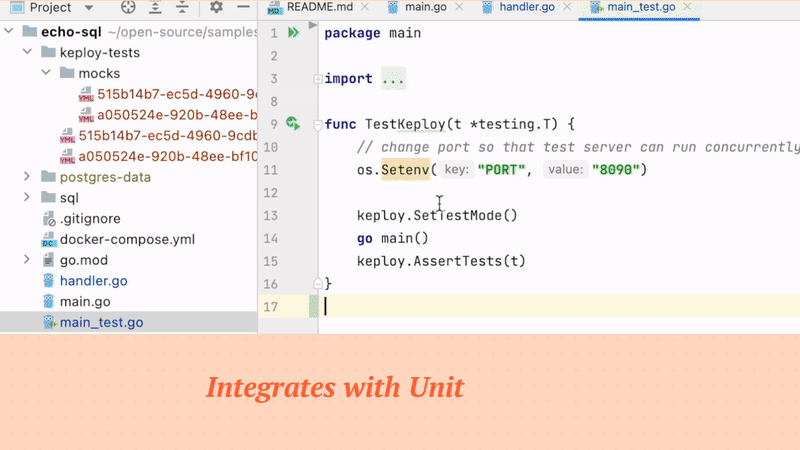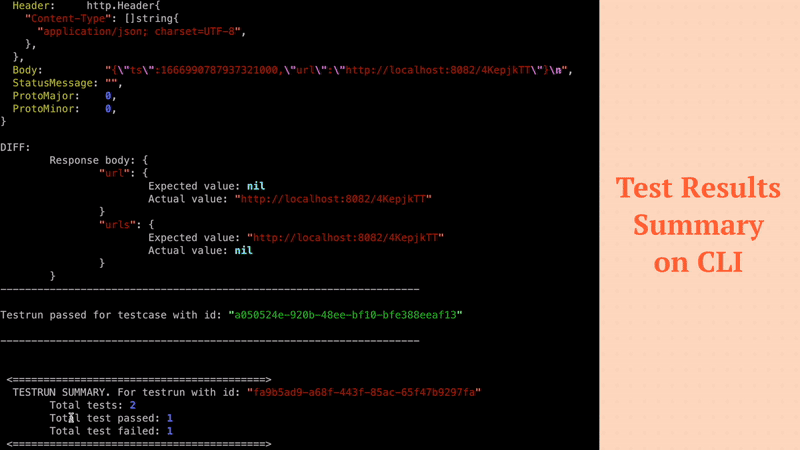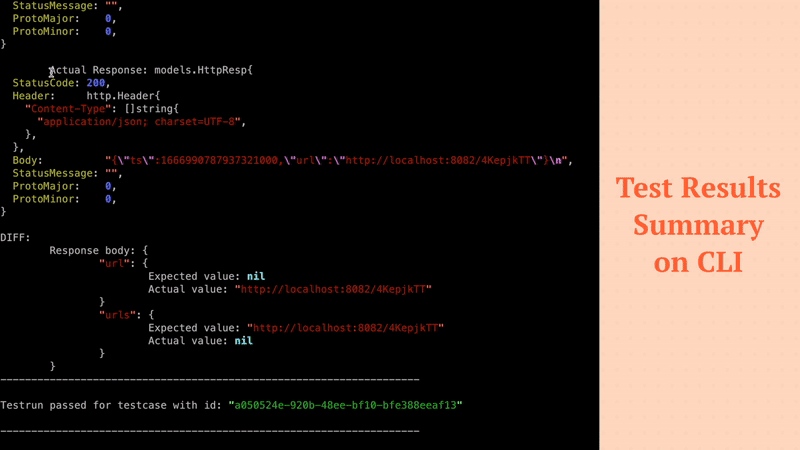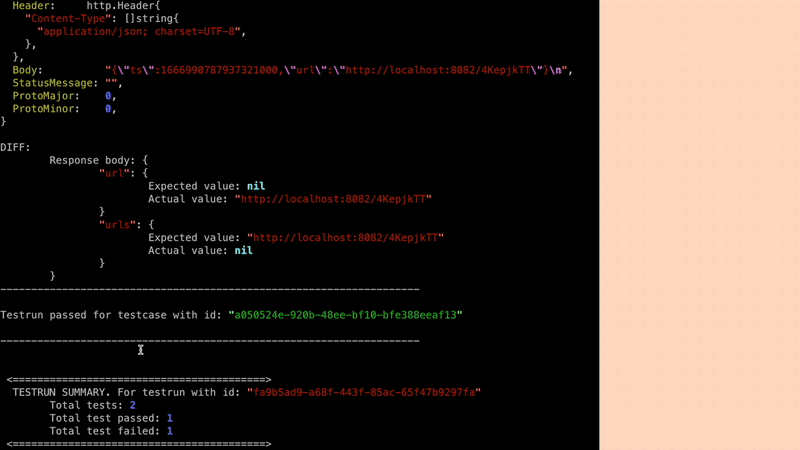
Merge KTests with unit testing libraries(like Go-Test, JUnit..) to track combined test-coverage.
KMocks can also be referenced in existing tests or use anywhere (including any testing framework). KMocks can also be used as tests for the server.
Keploy is testing itself with
without writing many test-cases or data-mocks. 😎
Keploy act as a proxy in your application that captures and replays all network interaction served to application from any source.
Visit How Keploy Works ? to read more in detail.
Here you can find the complete Documentation which you can refer.
Whether you are a community member or not, we would love your point of view! Feel free to first check out our:-
- Contribution Guidelines - The guide outlines the process for creating an issue and submitting a pull request.
- Code of Conduct - By following the guide we've set, your contribution will more likely be accepted if it enhances the project.
Keploy has native interoperability as it integrates with popular testing libraries like go-test, junit.
Code coverage will be reported with existing plus KTests. It'll also be integrated in CI pipelines/infrastructure automatically if you already have go-test, junit integrated.
Filters noisy fields in API responses like (timestamps, random values) to ensure high quality tests.
Ensures that redundant testcases are not generated.
Keploy can be used on Linux &
Windows through Docker.
We need to create a custom network for Keploy since we are using the Docker.
docker network create keploy-networkOnce the Custom Network is created, now we have to create the alias for the Keploy.
alias keploy='sudo docker run --name keploy-v2 -p 16789:16789 --network keploy-network --privileged --pid=host -it -v "$(pwd)":/files -v /sys/fs/cgroup:/sys/fs/cgroup -v /sys/kernel/debug:/sys/kernel/debug -v /sys/fs/bpf:/sys/fs/bpf -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --rm ghcr.io/keploy/keploy'Now, we will use the newly created Alias keploy to record the testcases. Run the following command in root directory of the you're application.
Note :- add the
container_nameunder your application service inside the 'docker-compose.yaml'if you are running viadocker-compose up.
keploy record -c "Docker_CMD_to_run_user_container --network keploy-network" --containerName "<contianerName>"Make API Calls using Hoppscotch, Postman or cURL command.
Keploy will capture the API calls you had made to generate the test-suites which will contain the testcases and data mocks into YAML format.
Now, we will use the newly created Alias keployV2 to test the testcases.Run the following command in root directory of the you're application.
keploy test -c "Docker_CMD_to_run_user_container --network keploy-network" --containerName "<contianerName>" --delay 20Docker_CMD_to_run_user_container is the docker command to run the application.
If you are using
docker-composecommand to start the application,--containerNameis required.
Note :- add the
container_nameunder your application service inside the 'docker-compose.yaml'if you are running viadocker-compose up.
Voilà! 🧑🏻💻 We have the server running!
Keploy can be used on Linux natively and via WSL on Winodows. Support for MacOS using Colima is work in progress.
Guide for native Installation
AMD Architecture
curl --silent --location "https://github.com/keploy/keploy/releases/latest/download/keploy_linux_amd64.tar.gz" | tar xz -C /tmp
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/bin && sudo mv /tmp/keploy /usr/local/bin && keployARM Architecture
curl --silent --location "https://github.com/keploy/keploy/releases/latest/download/keploy_linux_arm64.tar.gz" | tar xz -C /tmp
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/bin && sudo mv /tmp/keploy /usr/local/bin && keployRun this command on your terminal to start the recording of API calls:-
sudo -E keploy record -c "CMD_TO_RUN_APP"for example, if you are golang framework then the command would be:-
sudo -E keploy record -c "relative_path_of_go_binary of your application"Run this command on your terminal to run the testcases and generate the test coverage report:-
sudo -E keploy test -c "CMD_TO_RUN_APP" --delay 10
for example, if you are golang framework then the command would be:-
sudo -E keploy test -c "relative_path_of_go_binary of your application" --delay 10There are 2 Keploy modes:
-
Record mode :
- Record requests, response and all external calls and sends to Keploy server.
- After keploy server removes duplicates, it then runs the request on the API again to identify noisy fields.
- Sends the noisy fields to the keploy server to be saved along with the testcase.
-
Test mode :
- Fetches testcases for the app from keploy server.
- Calls the API with same request payload in testcase.
- Mocks external calls based on data stored in the testcase.
- Validates the responses and uploads results to the keploy server
-
Unit Testing: While Keploy is designed to run alongside unit testing frameworks (Go test, JUnit..) and can add to the overall code coverage, it still generates E2E tests.
-
Production usage Keploy is currently focused on generating tests for developers. These tests can be captured from any environment, but we have not tested it on high volume production environments. This would need robust deduplication to avoid too many redundant tests being captured. We do have ideas on building a robust deduplication system #27
🤔 FAQs
🕵️️ Why Keploy
We'd love to collaborate with you to make Keploy great. To get started: