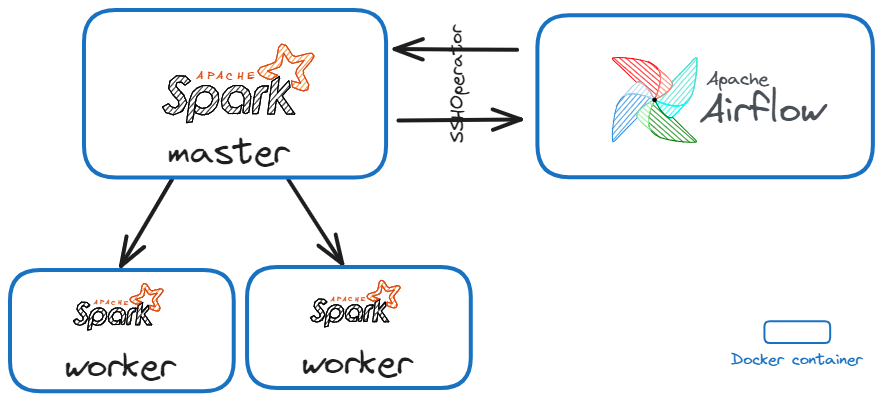
Welcome to this demo repository to show how to run pyspark applications on remote spark clusters using SSHOperator 🚀.
This Airflow pipeline will trigger the execution of a basic pyspark application that can be tested on other applications.
Run this Airflow project without installing anything locally.
- Fork this repository.
- Create a new GitHub codespaces project on your fork. Make sure it uses at least 4 cores!
- After creating the codespaces project the Astro CLI will automatically start up all necessary Airflow components. This can take a few minutes.
- Once the Airflow project has started access the Airflow UI by clicking on the Ports tab and opening the forward URL for port 8080.
-
Install the Gitpod extension for your browser:
-
Click on the Gitpod button that appears in your browser after installing the extension. This will open the project in Gitpod.
-
After Gitpod initializes, the Astro CLI will automatically start up all necessary Airflow components. This can take a few minutes.
-
Once the Airflow project has started, access the Airflow UI by clicking on the Ports tab and opening the forward URL for port 8080.
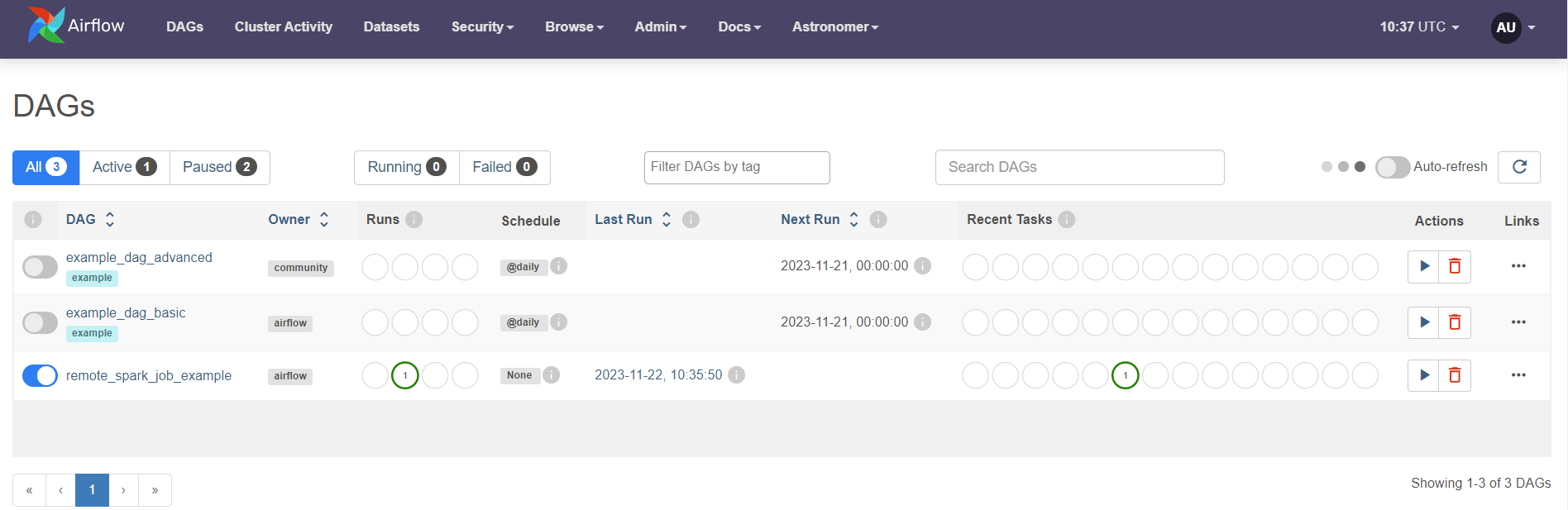
- Unpause
remote_spark_job_exampleDAG, by clicking on the toggle on the left hand side. Once theremote_spark_job_exampleDAG is unpaused it will run once, starting the pipeline.
-
To open the Spark UI app, go to the Ports tab and open the URL of the forwarded port
8081. -
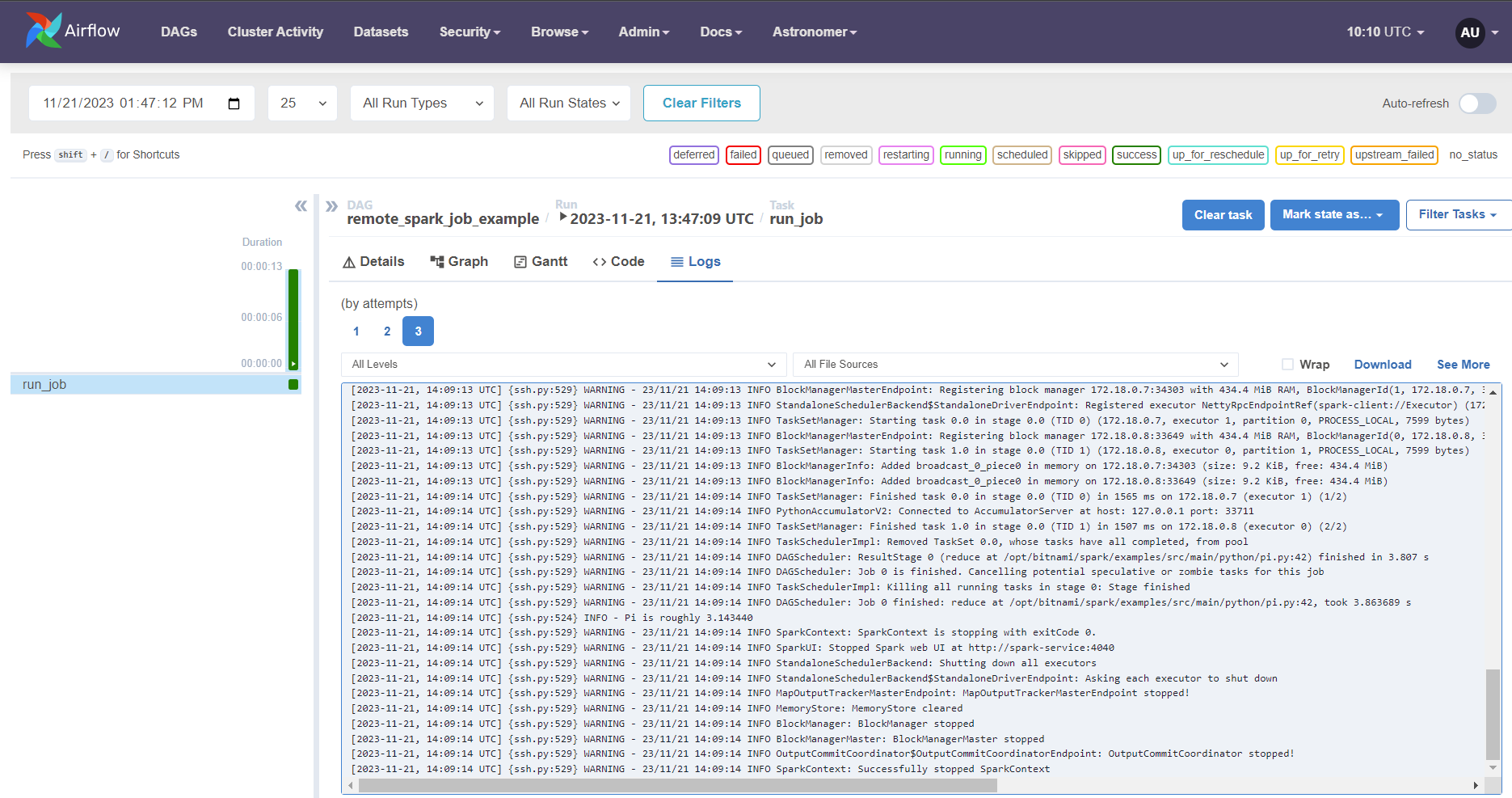
To see the logs of the execution of the spark job, access the logs of the
run_jobtask.
This repository uses a custom codespaces container to install the Astro CLI. The GH codespaces post creation command will start up the Astro project by running astro dev start.
5 Docker containers will be created and relevant ports will be forwarded:
-
The Airflow scheduler
-
The Airflow webserver
-
The Airflow metastore
-
The Airflow triggerer
-
A Spark master
-
2 Spark workers
This repository contains the following files and folders:
.astro: files necessary for Astro CLI commands..devcontainer: the GH codespaces configuration.dags: all DAGs in your Airflow environment.plugins: folder to place Airflow plugins. Empty.tests: folder to place pytests running on DAGs in the Airflow instance. Contains default tests..dockerignore: list of files to ignore for Docker..env: environment variables. Contains the definition for the SSH Spark connection..gitignore: list of files to ignore for git. Note that.envis not ignored in this project.docker-compose-spark.yml: Config file a Spark cluster with a master node and two workers.Dockerfile-spark: Configures Spark image with SSH, adds user, and starts SSH server.packages.txt: system-level packages to be installed in the Airflow environment upon building of the Dockerimage.README.md: this Readme.requirements.txt: python packages to be installed to be used by DAGs upon building of the Dockerimage..gitpod.yml: This file instructs Gitpod on how to prepare and build the project in case you run it on gitpod.