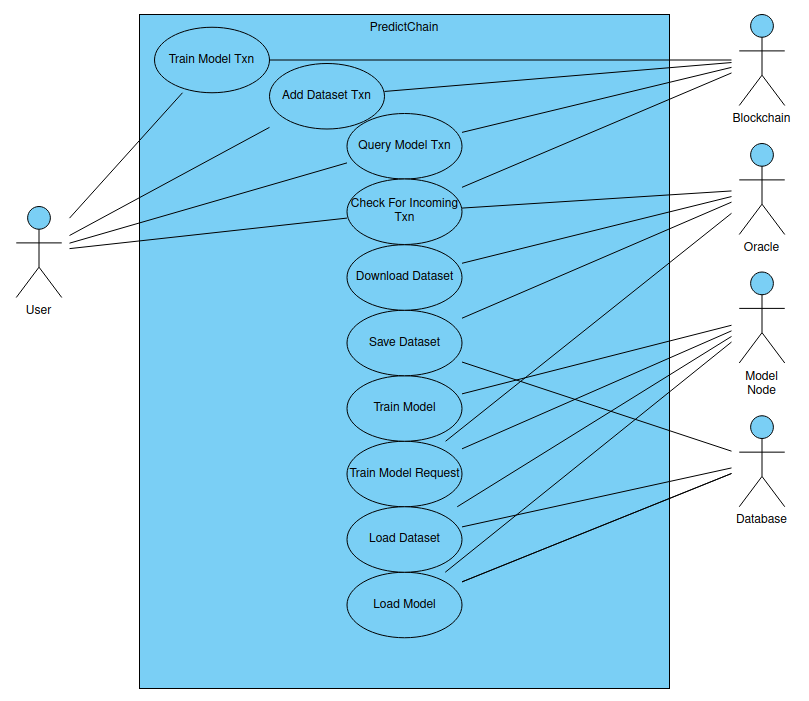
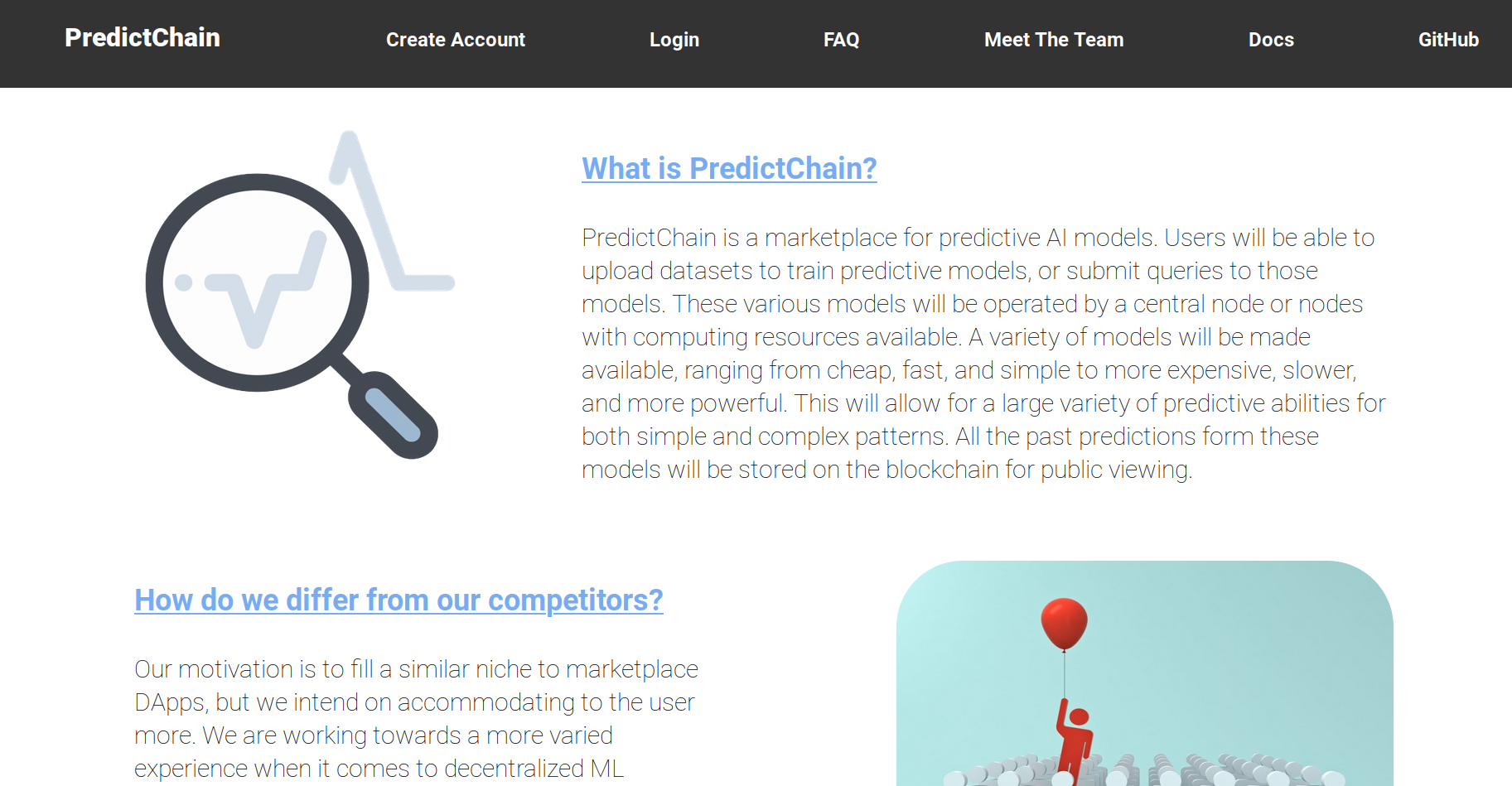
PredictChain is a marketplace for predictive AI models. Our goal is to make predictive models more accessible to more potential users. We do this through the ease of use and transparency of PredictChain. Users will be able to upload datasets, request the training of predictive models, or submit queries to those models. These various models will be operated by a central node with computing resources available.
A variety of models will be made available, ranging from cheap, fast, and simple to more expensive,
slower, and more powerful. This will allow for a large variety of predictive abilities for both
simple and complex patterns. All the past transactions will be stored on the blockchain for public viewing.
These include dataset creation, model training, model queries, and the results of these queries.
If you use this GitHub Code, please cite our work in the following way:
@inproceedings{pisano2023predictchain, title={PredictChain: Empowering Collaboration and Data Accessibility for AI in a Decentralized Blockchain-based Marketplace }, author={Matthew Pisano, Connor Patterson and Oshani Seneviratne}, year={2023}, publisher={Ledger Journal}, booktitle={ChainScience 2023} }
In addition to this readme, we have also created some Sphinx documentation for our python code. This details the usage and qualities of all important functions, classes, and variables within PredictChain. This documentation is in html format and can be found at docs/sphinx/index.html or at our GitHub pages. For the best viewing experience, we recommend cloning the repository and opening up the index.html file locally in a web browser.
For each of the following cases, they will involve setting up a relevant environment then running both the Client and Oracle nodes.
First, clone this repository and enter its directory.
git clone https://github.com/AI-and-Blockchain/S23_PredictChain # Clone the repository
cd S23_PredictChain # Enter its directoryNOTE: All commands must be run from the root project directory unless otherwise specified.
There are two primary methods of building and running the project:
The following should work on all platforms.
NOTE: If using a python virtual environment, make sure all python commands are run within that environment.
Before running the program, the following software must be available. Once the main software is installed, the instructions below will detail how to install the dependencies.
-
Python 3.10 or above
- Dependencies (from requirements.txt):
- pyteal: 0.24.0
- py-algorand-sdk: 2.1.2
- flask: 2.2.3
- requests: 2.28.2
- torch: 2.0.0
- redis: 4.5.4
- web3storage: 0.1.1
- beautifulsoup4: 4.12.2
- pandas: 2.0.0
- flask-cors: 3.0.10
- sphinx: 6.1.3
- matplotlib: 3.7.1
- Dependencies (from requirements.txt):
-
NodeJs 12.22.9 (NPM v8.5.1) or above
- Dependencies (from package.json):
- axios: ^1.3.4
- firebase: ^9.19.1
- react: ^18.2.0
- react-dom: ^18.2.0
- react-firebase-hooks: ^5.1.1
- react-router-dom: ^6.10.0
- react-scripts: 5.0.1
- web-vitals: ^2.1.4
- Dependencies (from package.json):
The following software is recommended:
- Redis 6.0.16 or above
NOTE: Redis is not required for this program to run, but is recommended. Without it, a special compatability layer will be activated that will use a dictionary instead. This dictionary will not persist between runs!
NOTE: Redis does not directly support running on windows. To install on Windows, install through the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), making sure the database has started before program execution.
First, install the project dependencies using
pip install -r requirements.txtcd client/predict-chain-ui # Enter react front end directory
npm i
cd ../.. # Return to the root directoryNOTE: Before running either node, make sure the credential files have been filled out. More information fan be found in the Credentials Readme.
Next, run the client and oracle programs. This should be done within separate terminals as both processes are continuous and do not exit while the network is running.
python clientMain.pyand
python oracleMain.pyAfter these have been run, the web interface should be running on localhost:3000.
Additionally, working examples of the three core parts of the project are available in sandbox.py.
Simply comment or uncomment the desired actions inside the sandbox() function. Leave all three uncommented for
a complete, working example.
If using Linux, building and running docker containers for the program is the most straightforward method of setting up the nodes.
NOTE: Before building the container, make sure the credential files have been filled out. More information fan be found in the Credentials Readme.
First, build the container using:
docker/buildContainer.shNext, run both the client and oracle programs using:
docker/runClient.shand
docker/runOracle.shAfter these containers have been run, the web interface should be running on localhost:3000.
After launching the front end, you will be greeted by the welcome screen. This will provide you with some extra information about PredictChain and its project participants.
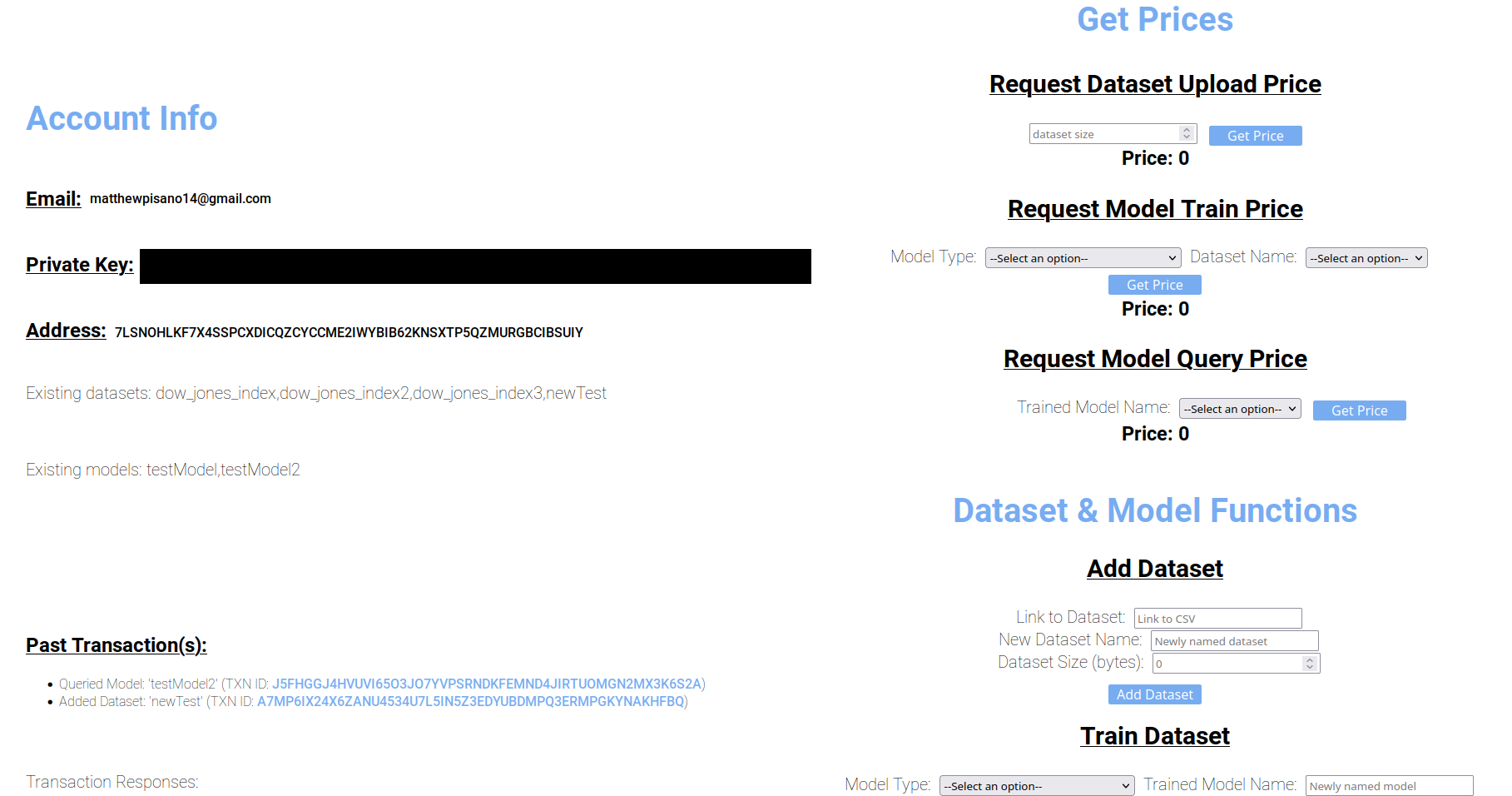
To access the functionality of the website, create an account of log in. The account management for this project is through FireBase, although, nothing has to be set up on the user end for this to work. Before you perform any transactions, it may be useful to request the pricing of each operation. This can be done on the dashboard. Simply input any request information and the front end will communicate with the oracle which will calculate the pricing and send it back to you. After this, you will be able to upload a dataset, request that a model be trained, and query trained models to check their responses. It is suggested that you upload our testing dataset for the best results. It can be found here.
Users can interact with this system through a variety of ways. Users can choose to upload datasets of their own, train one of the base models on any previously uploaded dataset, or query any of the trained models for a specific result.
There will be several types of models available for use. These include:
- Multi-layered Perceptrons
- Recurrent Neural Networks
- Long Short-term Memory Networks
- Gated Recurrent Unit Networks
The capabilities of these different methods varies greatly. To save on costs, users with simple classification tasks can opt for models that are cheaper, but will still provide good results. Alternatively, users looking to analyze more complex relations can select the more complex models at a higher cost. Users are incentivized to balance cost and performance as they will be rewarded for better performing models.
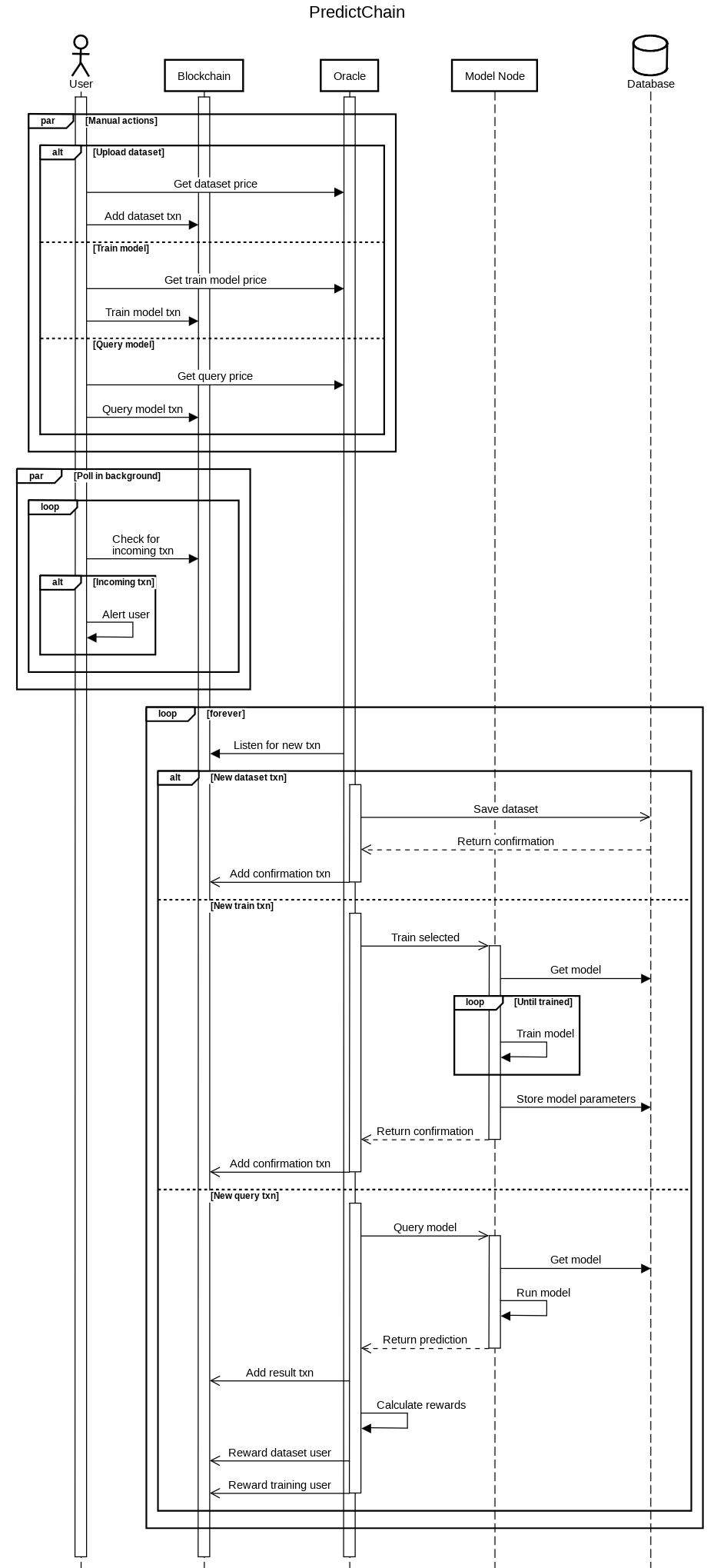
The oracle is a privileged node that helps the blockchain keep up to date with the outside world. It can help get information out of the blockchain and to a programmatic API, or it can gather information from the outside world and inject it back into the blockchain. For example, it would listen for the outcomes of user-predicted events, return those results to the users, and update those who submitted the dataset.
Communication between the blockchain and the oracle is facilitated by transactions. When a message needs to be sent between the two parties, the sending party creates a transaction with a note attached. This note contains a JSON-encoded form of the arguments for the operation being requested. These arguments are then received and interpreted by the target of the transaction. Using this form for communication ensures an unbroken, public record of all of PredictChain's functions.
Payments and incentives help to turn this project into a functioning system. They are each calculated using a fixed equation that is open to all users to view. Each reward and incentive is also subject to a multiplier. This can be raised or lowered by the oracle at any point. To ensure there is a constant log kept in the blockchain, the id of this modifying transaction will be saved and returned to any user upon request.
-
Any user will be able to query previously trained models for predictions of real-world events. Each time this is done, these users will make a small payment to the system. This fee is based off of the complexity of the requested model.
-
Users who upload their own datasets will also have to pay a small fee. This fee is based off of the size of the dataset that they plan to upload.
-
Users who choose to request that a base model be trained on a particular dataset will also be charged with a small fee. This fee is based off of a variety of factors including the complexity of the model and the size of the dataset.
To compensate for the payments that users make to the system, they will also be rewarded in the right circumstances. Each of the below events are triggers when a user queries the model for some event.
-
Dataset uploading users will be rewarded both when a model is trained on their dataset and when that trained model makes a correct prediction.
-
Model training users will be rewarded whenever their model makes a correct prediction.