Terraform confiuration for automatic deployment of applications to Google Cloud Platforms' Kubernetes engine
This repository is part of a bachelor thesis done by four students at NTNU.
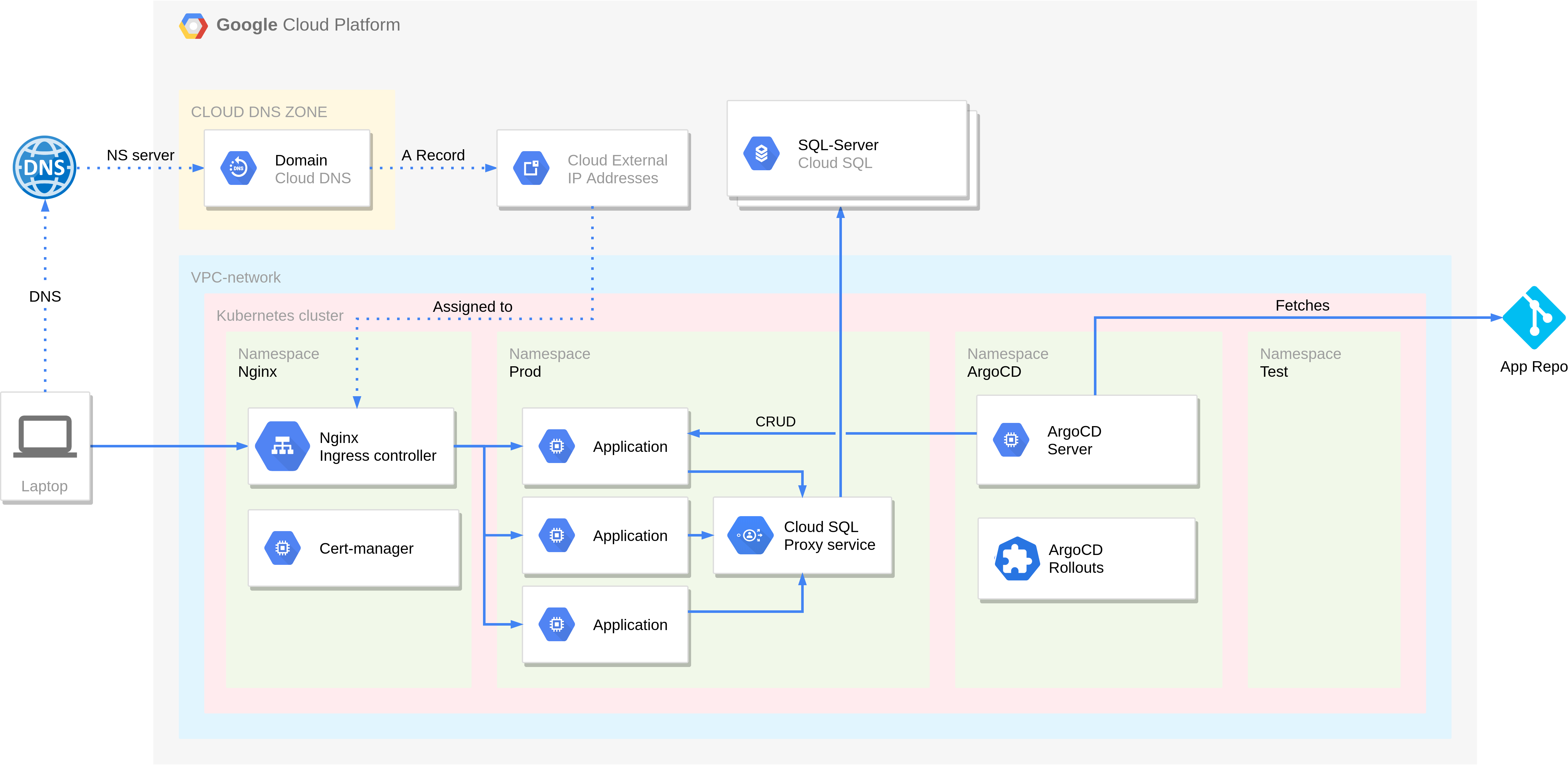
The repo aims to automate deployment of complex applications to Google Kubernetes Engine. To that end, it also automates the deployment of the infrastructure required for it. It uses Terraform to deploy infrastructure and Argo CD to do continuous deployment of applications. Some additional supporting survices, such as a Cloud SQL database, are also provided.
-
A Google Cloud Platform project with a suitable funding solution.
-
A GCS bucket to remotely store the Terraform state. Change the name of the bucket in terraform/dev/backend.tf to the name of your bucket.
-
Service account with the following roles:
- Kubernetes Engine Admin
- Editor
- Project IAM Admin
Download the credentials for the service account in json format, rename the file "credentials.json" and place it in under terraform/dev. This service account is used to authenticate the remote backend in GCS and as credentials for the various Google providers in the repository.
-
If using Cloud SQL, a service account with the role Cloud SQL Client is required. Download the credentials for the service account in json format, rename the file "proxyCreds.json" and place it under terraform/dev. This service account is used to authenticate the Cloud SQL Proxy.
- Clone this repository.
- Ensure prerequisites are fulfilled.
- Set the variables in terraform/dev/terraform.tfvars to the desired values.
- Run the terraform/scripts/tf-init.sh script to initialize the Terraform configuration.
- Run the terraform/scripts/tf-apply.sh script to apply the Terraform configuration.
- Run the terraform/scripts/tf-destroy.sh script to destroy the Terraform configuration.
The Terraform configuration can be configured to deploy the following:
- An autoscaling GKE cluster
- A managed SQL database with connection from GKE cluster via cloudsql proxy deployed as a service.
- Cloud DNS zone with domain
- A NGINX ingress controller with domain pointing to the controller via A record
- Cert-Manager with Let's Encrypt issuer
- ArgoCD along with Argo Rollouts for CD of applications
- Online Boutique (formerly known as "Hipster Shop") as a demo application
To interact with the infrastructre, terraform init, apply and destroy should be used in the terraform/dev directory.
Each of the scripts in terraform/scripts may also be used. They simplify interactions with the infrastructure, for example by automatically supplying the var-file. Each of the main scripts (tf-init.sh, tf-apply.sh and tf-destroy.sh) has a help command which explains basic usage.
When only interacting with parts of the infrastructure (such as a single module), the -target option should be used.
After deploying the infrastructure, the deployed Argo CD should be used for continuous deployment of the applications.
In order to interact with Argo CD, you have to connect to the ArgoCD server. To do so, you can expose the argocd-server or use the following command to use port-forwarding instead:
kubectl port-forward svc/argo-cd-argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443It may then be accessed on localhost:8080. The default username is admin, and the default password is the name of the pod running the Argocd server.
Argo CD can used either through a CLI or web UI.
For more information regarding Argo CD, see the documentation.
In order to set the domain, the hardcoded values (example.com) mentioned in the TODOs must be changed aswell.
A Cloud SQL proxy is deployed as a service in order to allow applications in the cluster to connect to the Cloud SQL database. Connection information is exported as the Kubernetes secret db-secrets. It contains the following (the secret keys are in parentheses):
- Host (DB_HOST)
- Port (DB_PORT)
- Username (DB_USER)
- Password (DB_PASSWORD)
- Database name (DB_NAME)
- SSL mode (DB_SSLMODE)
deployments/test-rest/test-rest.yaml shows these being passed to an example application as environment variables.
- ArgoCD TLS ingress currently has the domain hardcoded in the K8s ingress manifest (terraform/modules/argo/k8s/argocd-ingress.yaml).
- Uptime check uses hardcoded domain (terraform/modules/argo/main.tf).
- Change from default admin password(argocd-server podname) and store somewhere secure (terraform/modules/argo/main.tf).
Erlend Fonnes, Johan Selnes, Aksel Baardsen, Knut Jørgen Totland
During the project, we used Vscode liveshare. The commits are therefore not directly attributable to the author.