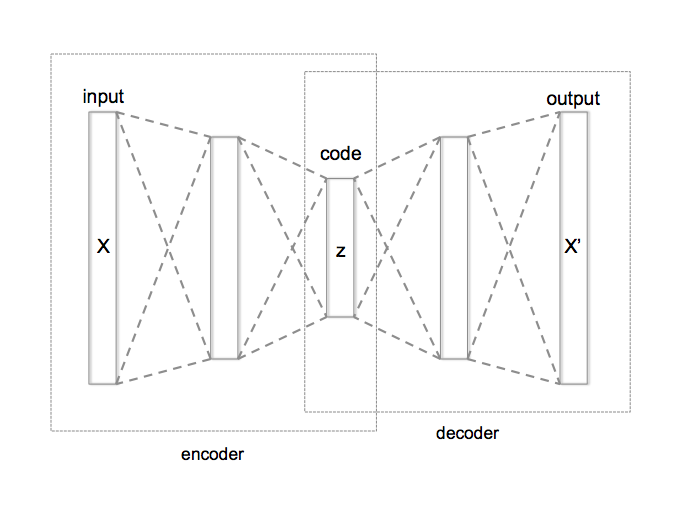
Autoencoders are an unsupervised learning technique in which we leverage neural networks for the task of representation learning. We pass the input through a neural network which compresses it into a low dimensional latent code, by passing through bottle neck and then we reconstruct an output using the compressed latent code by another neural network.
It consists of two networks:
- Encoder network: It translates the original high-dimension input into the latent low-dimensional code. The input size is larger than the output size.
- Decoder network: The decoder network recovers the data from the code, likely with larger and larger output layers.
The encoder network essentially accomplishes the dimensionality reduction, just like how we would use Principal Component Analysis (PCA) or Matrix Factorization (MF) for. In addition, the autoencoder is explicitly optimized for the data reconstruction from the code. A good intermediate representation not only can capture latent variables, but also benefits a full decompression process.
The model contains an encoder function (g) and a decoder function (f). The low-dimensional code learned for input x in the bottleneck layer is z and the reconstructed input is x'
The parameters for the encoder and decoder function are learned together by minimizing a loss function(or reconstruction error) to output a reconstructed data sample which is then used for various purposes such as reconstruction, denoising, generation of new images etc