Federated Learning is a project which was assigned to us as a project of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Federated learning (also known as collaborative learning) is a machine learning technique that trains an algorithm across multiple decentralized edge devices or servers holding local data samples, without exchanging them. This approach stands in contrast to traditional centralized machine learning techniques where all the local datasets are uploaded to one server, as well as to more classical decentralized approaches which often assume that local data samples are identically distributed.
Federated learning enables multiple actors to build a common, robust machine learning model without sharing data, thus allowing to address critical issues such as data privacy, data security, data access rights and access to heterogeneous data. Its applications are spread over a number of industries including defense, telecommunications, IoT, and pharmaceutics.
- From Distributed Machine Learning to Federated Learning: A Survey
- Communication-Efficient Federated Learning with Compensated Overlap-FedAvg
def create_keras_model(shape , classes):
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters =32 , kernel_size =3 , activation='relu' , input_shape = [shape[0], shape[1] , shape[2] ]))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D( strides = 2,pool_size=2))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters = 32, kernel_size = 3 , activation = 'relu' ))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(strides = 2, pool_size =2))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten())
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units = 128 , activation = 'relu'))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.25))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units = 128 , activation = 'relu'))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.25))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units =classes ,activation ='softmax'))
return model
Firstly initialize the local models weights by global model weights. In each communication with global model , local models are created ,fitted and the weights are scaled then append in a list. After all clients have trained ,take average of weights and update global weights.
#commence global training loop
for comm_round in range(comms_round):
# get the global model's weights - will serve as the initial weights for all local models
global_weights = global_model.get_weights()
#initial list to collect local model weights after scalling
scaled_local_weight_list = list()
#randomize client data - using keys
all_client_names = list(clients_batched.keys())
client_names = random.sample(all_client_names, k=10)
# print(client_names, len(client_names))
random.shuffle(client_names)
#loop through each client and create new local model
for client in client_names:
local_model = create_keras_model(build_shape, classes)
local_model.compile(loss=loss,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=metrics)
#set local model weight to the weight of the global model
local_model.set_weights(global_weights)
#fit local model with client's data
local_model.fit(clients_batched[client], epochs=1)
#scale the model weights and add to list
scaling_factor = 0.1#weight_scalling_factor(clients_batched, client)
scaled_weights = scale_model_weights(local_model.get_weights(), scaling_factor)
scaled_local_weight_list.append(scaled_weights)
#clear session to free memory after each communication round
K.clear_session()
#to get the average over all the local model, we simply take the sum of the scaled weights
average_weights = sum_scaled_weights(scaled_local_weight_list)
#update global model
global_model.set_weights(average_weights)
#test global model and print out metrics after each communications round
for(X_test, Y_test) in test_batched:
global_acc, global_loss = test_model(X_test, Y_test, global_model, comm_round)
global_acc_list.append(global_acc)
global_loss_list.append(global_loss)
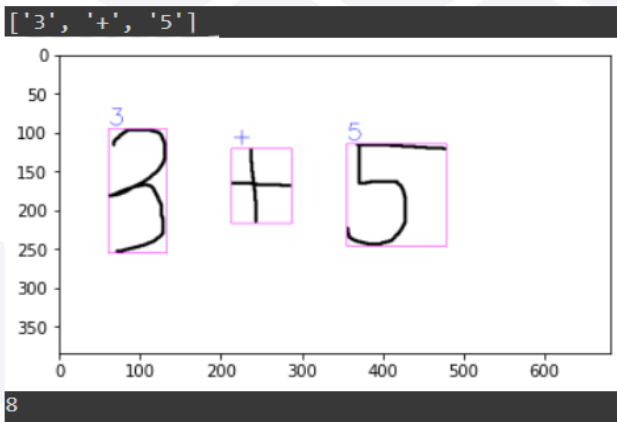
Using OpenCV's finding contours and bounding box to find the region the digits and then cropping the image to 45x45.
Cropped image are sent for single prediction.
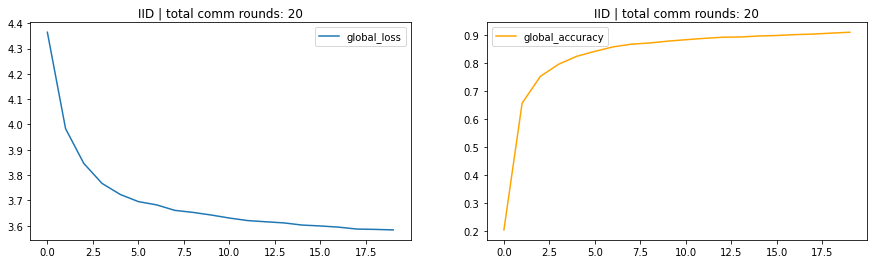
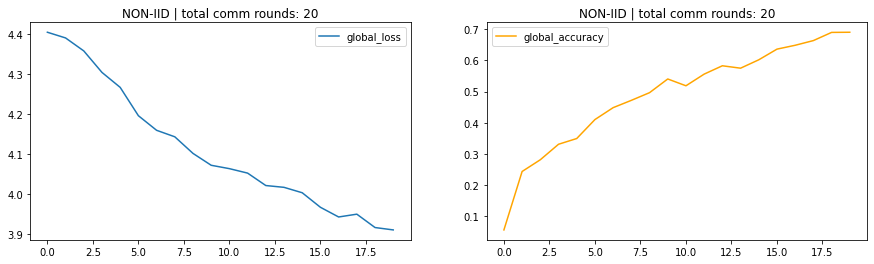
- IID -> Identical and Indepenent Distribution. Dataset are equally distributed to each clients.
- Non-IID ->Dataset are unequally distributed.
IID
- @AadityaSubedi[PUL075BCT001]
- @Arpan Pokharel [PUL075BCT015]
- @Saugatkafley[PUL075BCT099]