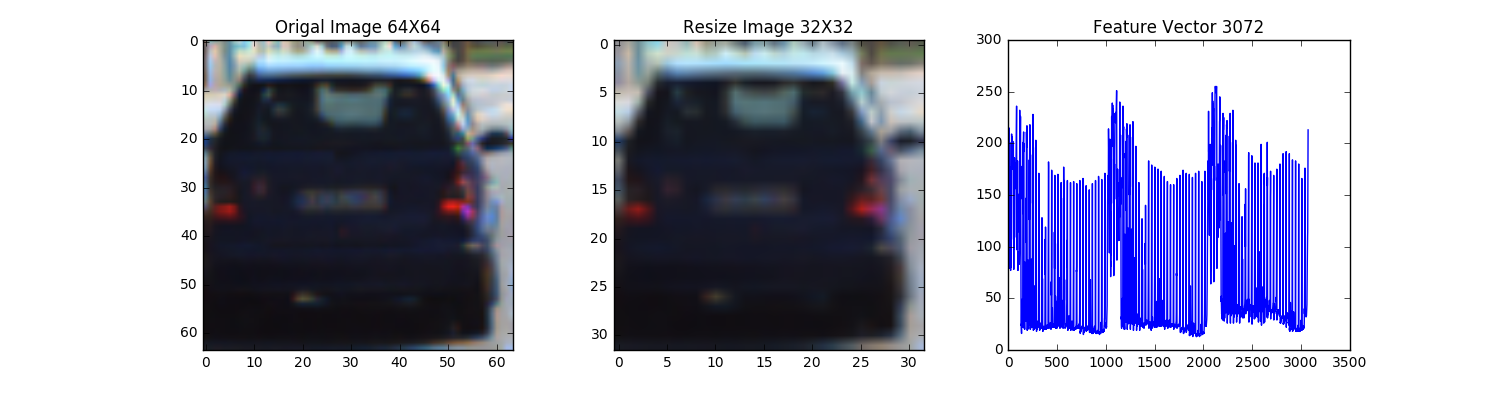
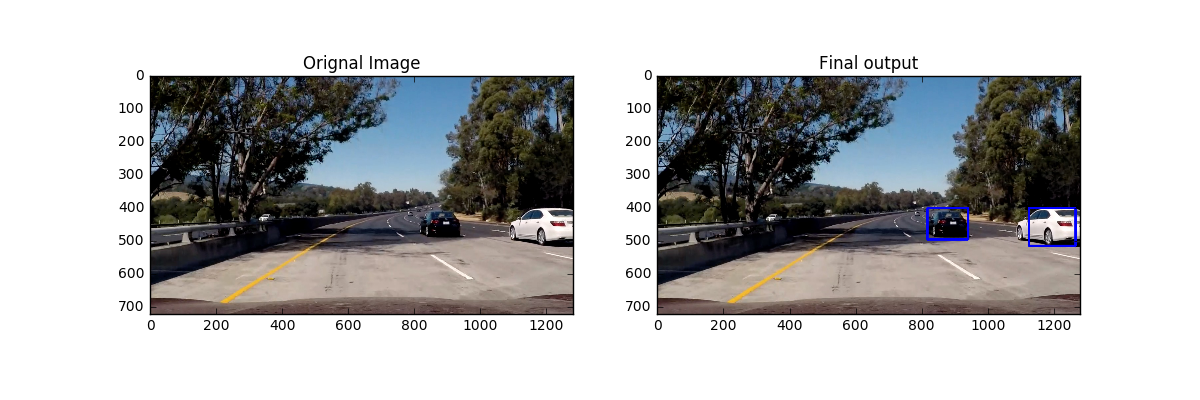
Vehicle Detection Project
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Perform a Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) feature extraction on a labeled training set of images and train a classifier Linear SVM classifier
- Optionally, you can also apply a color transform and append binned color features, as well as histograms of color, to your HOG feature vector.
- Note: for those first two steps don't forget to normalize your features and randomize a selection for training and testing.
- Implement a sliding-window technique and use your trained classifier to search for vehicles in images.
- Run your pipeline on a video stream (start with the test_video.mp4 and later implement on full project_video.mp4) and create a heat map of recurring detections frame by frame to reject outliers and follow detected vehicles.
- Estimate a bounding box for vehicles detected.
Two of the imported files are vehicles and the other is non-vehicles. vehicles for car datas and non-vehicles for notcar datas. This file doesn't have training dataset, The training dataset provided for this project ( vehicle and non-vehicle images) are in the .png format.
- Number of car datas: 8792
- Number of notcar datas: 8968
- Train Data shape: (64, 64, 3)
The following are Car image and Not Car image:
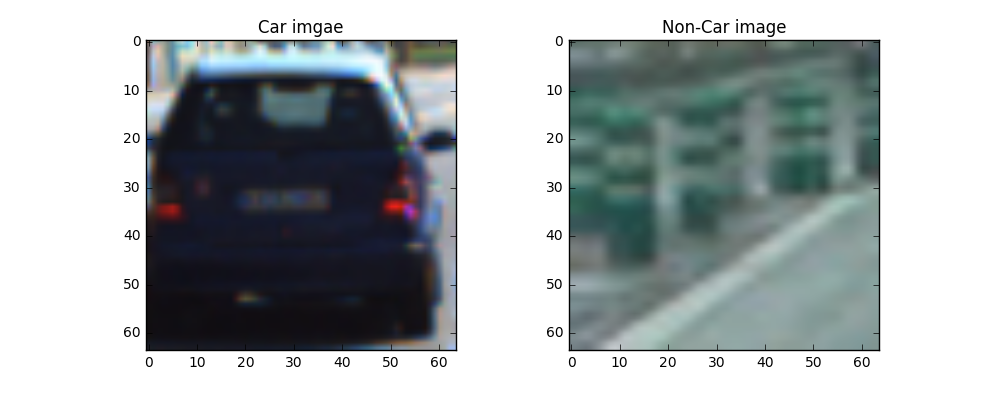
The first feature can get form image consists of raw color value, Color features The color feature can be distinguished from the surrounding color environment. The second import feature is Color Histogram which detect color, but those just auxiliary tool for vehicle detection.
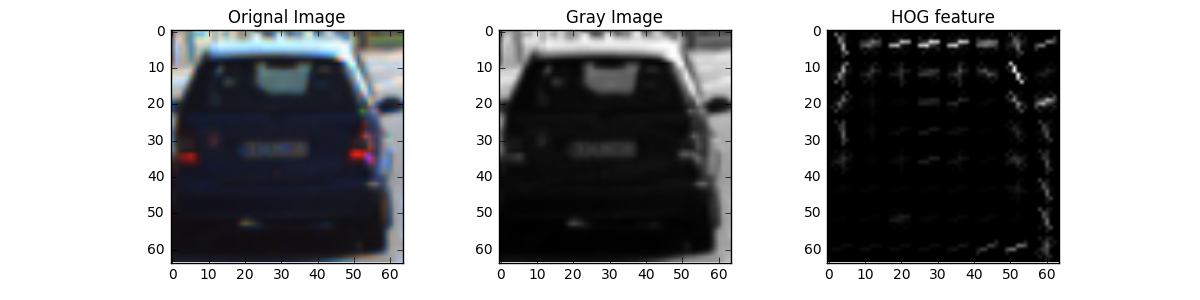
The histogram of oriented gradients (HOG) is a feature descriptor used in computer vision and image processing for the purpose of object detection. The technique counts occurrences of gradient orientation in localized portions of an image. This method is similar to that of edge orientation histograms, scale-invariant feature transform descriptors, and shape contexts, but differs in that it is computed on a dense grid of uniformly spaced cells and uses overlapping local contrast normalization for improved accuracy.
As shown in the figure below, the hog feature can judge the outline of the vehicle.
Different color space has great influence on the training machine, In order to get better results, I will adjust the parameters to facilitate future SVM to use.
# setting test parmeters
orient = 8
pix_per_cell = 8
cell_per_block = 2
hist_bins = 16
spatial_size = 16
# Turning parameters, to find which could be better
color_pars = ['RGB', 'HSV', 'LUV', 'HLS', 'YUV', 'YCrCb']
hog_channel_pars = [0,1,2,'ALL']
spatial_feat_pars = [True, False] # Spatial features on or off
hist_feat_pars = [True, False] # Histogram features on or off
hog_feat_pars = [True, False] # HOG features on or off
# Debug Paramters
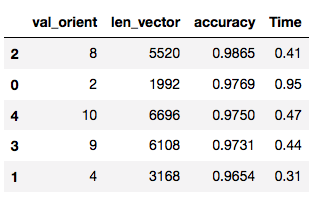
pars_orient = [2,4,8,9,10]
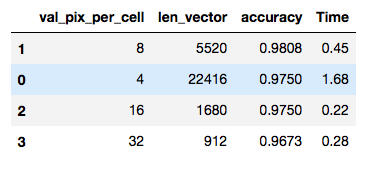
pars_pix_per_cell = [4,8,16,32]
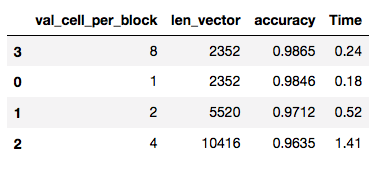
pars_cell_per_block = [1,2,4,8]
pix_per_cell = 8
cell_per_block = 2
hist_bins = 16
spatial_size = 16
color_space = 'YCrCb'
hog_channel = 'ALL'
spatial_feat = True # Spatial features on or off
hist_feat = True # Histogram features on or off
hog_feat = True # HOG features on or off
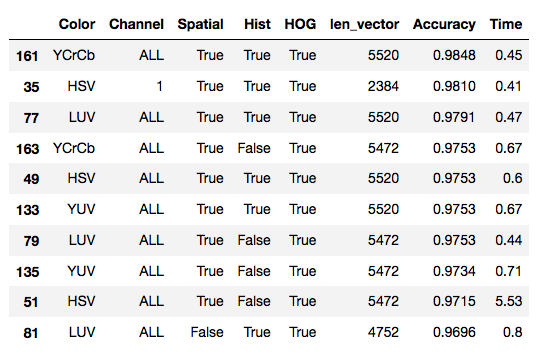
Using this method may be able to find good paramters. However, it was found that the results of each run were different. In multiple tests, the following results appeared the most, and here are my final parameters:
color_space = 'YCrCb' # Can be RGB, HSV, LUV, HLS, YUV, YCrCb
orient = 8 # HOG orientations
pix_per_cell = 8 # HOG pixels per cell
cell_per_block = 2 # HOG cells per block
hog_channel = 'ALL' # Can be 0, 1, 2, or "ALL"
spatial_size = 16 # Spatial binning dimensions
hist_bins = 16 # Number of histogram bins
spatial_feat = True # Spatial features on or off
hist_feat = True # Histogram features on or off
hog_feat = True # HOG features on or off
Need to normalize data before training data, sklearn package provides you with the StandardScaler() method to accomplish this task.
# Fit a per-column scaler
X_scaler = StandardScaler().fit(X_train)
RandomizedSearchCVimplements a “fit” and a “score” method. It also implements “predict”, “predict_proba”, “decision_function”, “transform” and “inverse_transform” if they are implemented in the estimator used.RandomizedSearchCV implements a randomized search over parameters, where each setting is sampled from a distribution over possible parameter values.
Using: 8 orientations 8 pixels per cell and 2 cells per block
Feature vector length: 5520
177.4 Seconds to train SVC...
Test Accuracy of SVC = 0.9859
classification_report(y_true, y_pred):
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.99 0.98 0.99 1768
1.0 0.98 0.99 0.99 1784
avg / total 0.99 0.99 0.99 3552
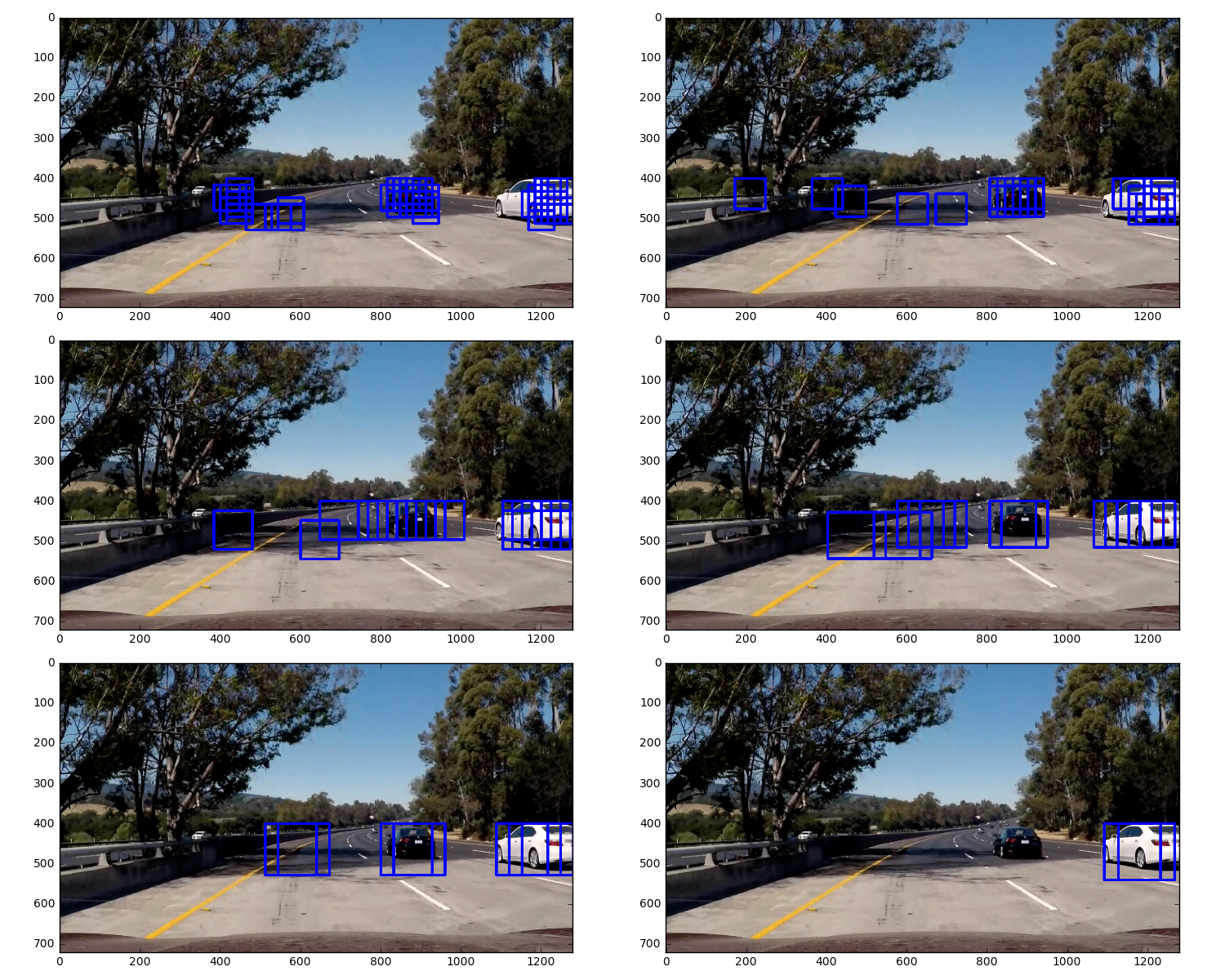
Here I used Hog Sub-sampling Window Search, this method just only to extract the Hog feature once, it's more efficient for doing the sliding window approach. I also defined pix_per_cell=8, scalers = [1, 1.2, 1.5, 1.8 ,2, 2.2] Each window is defined by a scaling factor that impacts the window size. The scale factor can be set on different regions of the image.
I used cells_per_step = 2 this would result in a search window overlap of 75%(2 is 25% of 8, so we move 25% each time, leaving 75% overlap with the previous window).
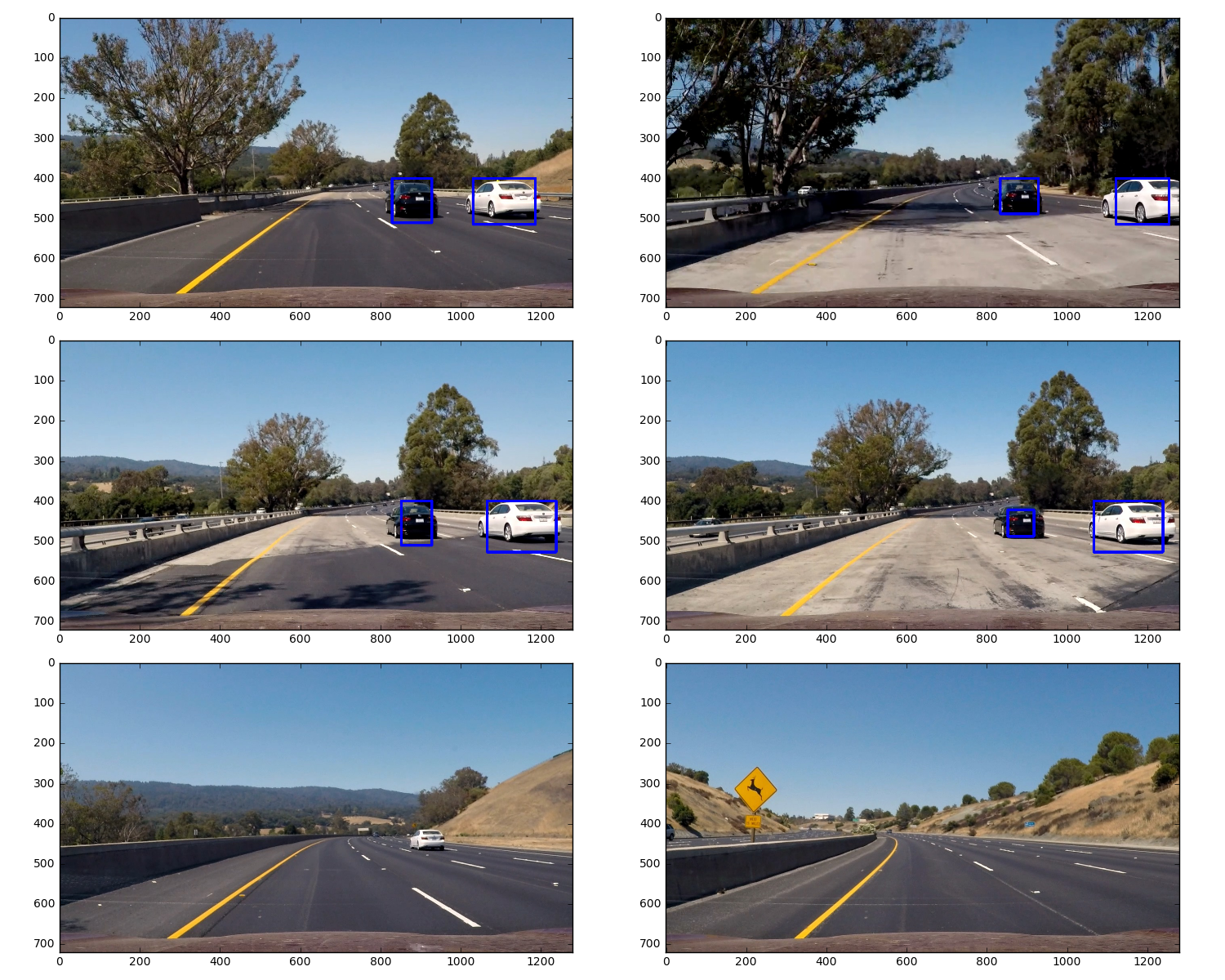
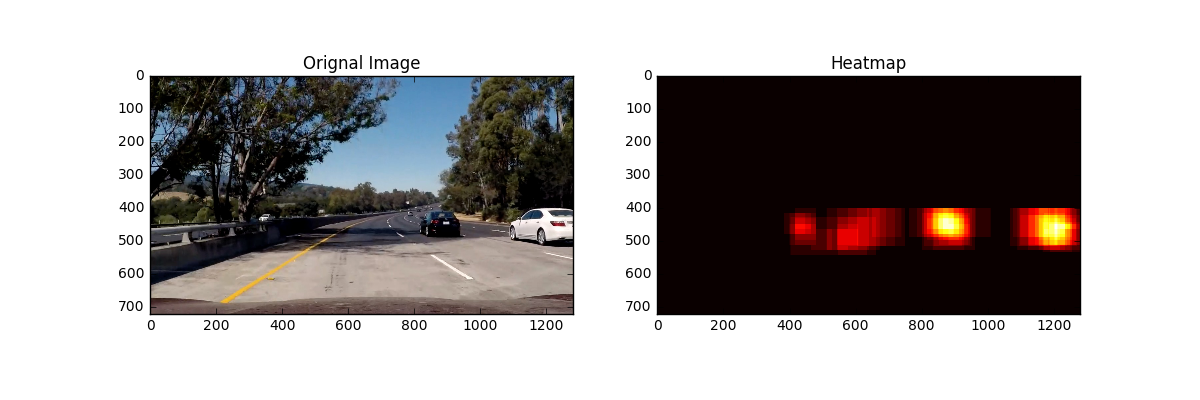
Here are the results of images, However, there are some False Positives on those images
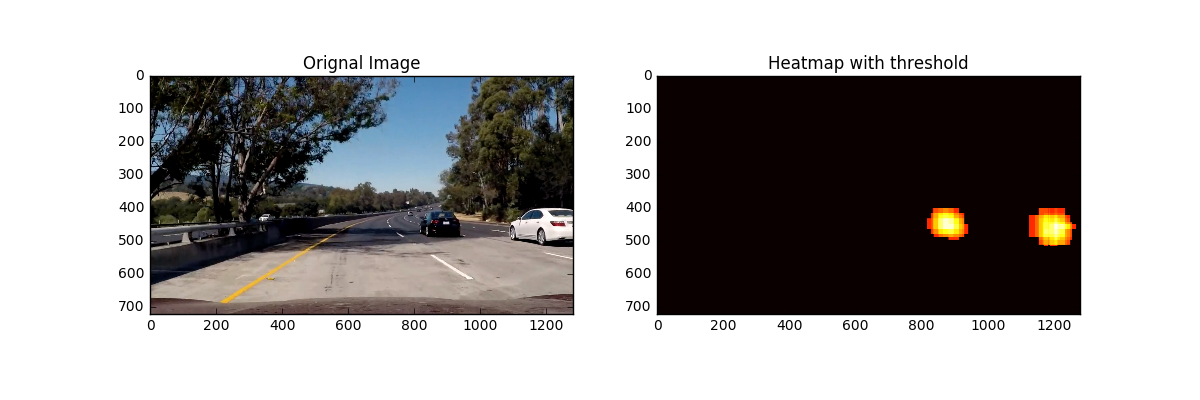
To make a heat-map, to add "heat" (+=1) for all pixels within windows where a positive detection is reported by classifier. Setting a threshold reduces false positive. The heat-maps for the above images look like this:
Through the above experiments, svm is very slow in operation and not very efficient. At the same time, identification on the classifier also has the problem of identification errors.Maybe YOLO can solve this problem, but due to the time problem can only be implemented in the follow-up time.