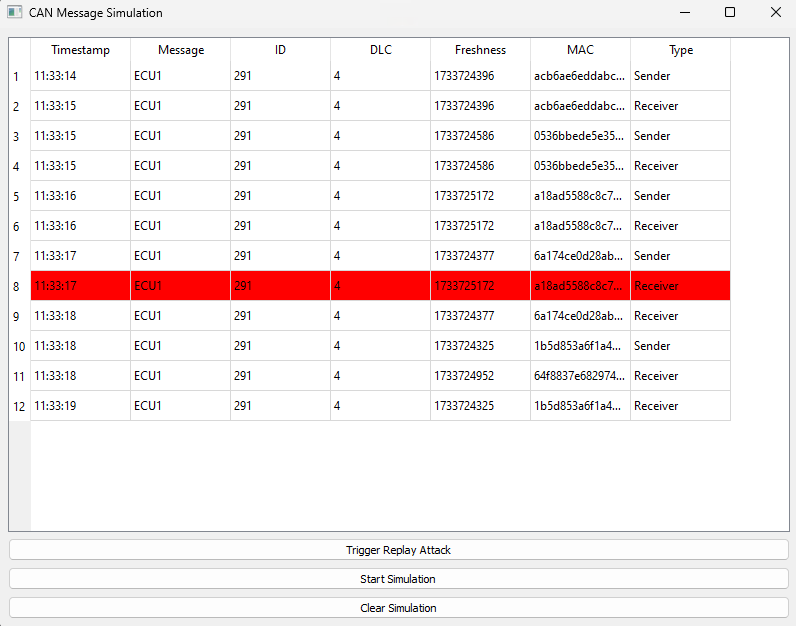
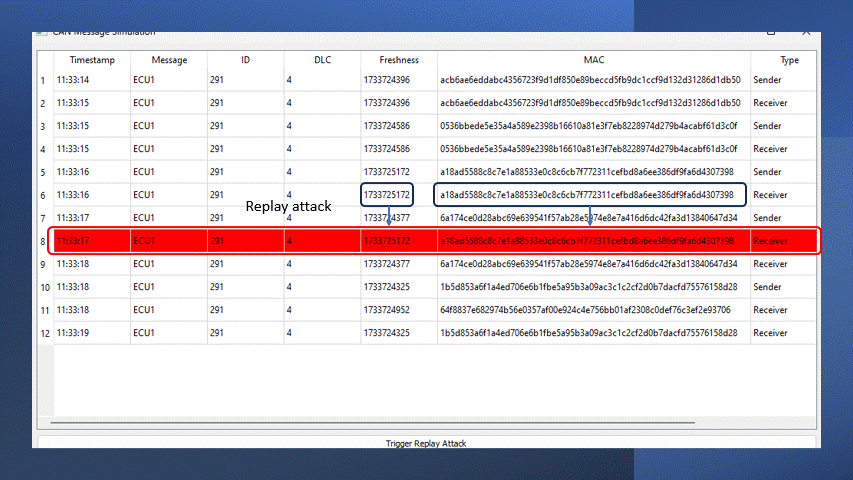
This is a Python-based simulation of the Secure On-Board Communication (SecOC) protocol, which is designed to ensure secure communication within an ECU network, such as for automotive applications. This simulation mimics two ECUs (Electronic Control Units) that send and receive messages over a simulated CAN bus while implementing basic security features such as Message Authentication Code (MAC) and freshness checks to prevent replay attacks.
- Message Authentication: Uses HMAC with SHA256 to ensure message integrity and authenticity.
- Replay Attack Detection: Implements freshness timestamps to detect replay attacks based on stale message freshness.
- Key Rotation: Periodically rotates the secret key used to generate MACs to enhance security.
- CAN Bus Simulation: Simulates the transmission of messages between sender and receiver ECUs over a queue that mimics a CAN bus.
- Logging: Displays simulation logs in the console to track the communication and security checks (e.g., successful authentication, replay attacks).
- Python 3.6 or higher
- PyQt5 (for UI in case of GUI implementation, but can be removed if not needed)
queue(Python standard library)
This simulation features two main components:
Sender ECU: Simulates an ECU that sends a message over the "CAN bus" (represented by a queue). Each message is accompanied by a Message Authentication Code (MAC) and a freshness timestamp. Receiver ECU: Simulates an ECU that receives the message, verifies the MAC and freshness timestamp, and checks if the message is valid or if a replay attack is detected. The system will log:
Successful authentications Detected replay attacks Key rotations Any errors or malformed messages Key Components: MAC Generation: Uses HMAC with SHA256 to generate a unique authentication code for each message. Freshness Check: Compares the freshness (timestamp) of each message to the last received one to prevent replay attacks. Key Rotation: The secret key is periodically changed to enhance security, preventing attacks that exploit key reuse.
To run the SecOC simulation, follow these steps:
Clone this repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/SecOC-Simulation.git
cd SecOC-SimulationRun the simulation:
python secoc_simulation.pyLogs During the simulation, you'll see logs printed to the console indicating:
When a message is sent or received. If the MAC is verified successfully. If a replay attack is detected due to freshness issues. When the key is rotated to ensure ongoing security.
Here is an example of the ECU log output:
[ECU 1] Sent: 0x123|12|EngineTemperature:85|1618001234|abc123...
[ECU 2] Received: 0x123|12|EngineTemperature:85|1618001234|abc123...
[ECU 2] Message authenticated: EngineTemperature:85 (ID: 0x123, DLC: 12, Freshness: 1618001234)
[ECU 2] Replay attack detected! Freshness is too old.
- Start/ Stop Simulation
- Clear Simulaiton
- Trigger Replay Attack
Testing with Vector SIL Kit