The project deals with creating a recommendation engine of movies to the users.
The project involves performing ETL on data based on Movie_Metadata , Movie_genre , Movie_Casting and the CPI index for the time the movies were released.
Using the information derived from the dataset, the system would be able to answer typical question like
Which are the top 5 movie genres based on the average rating of the movie?
Does casting particular people help increase the popularity of the movie?
Finding out if releasing the film at a particular time - in a particular month might affect the revenue?
Which are the top 5 genres based on the CPI index?
The system uses data from 2 different sources : -
-
The movies , genre and cast data is based on the following Kaggle dataset.
There are multiple files containing the data for movies , genre and cast data. These files contain metadata for all 45,000 movies listed in the Full MovieLens Dataset. The dataset consists of movies released on or before July 2017. Data points include cast, crew, plot keywords, budget, revenue, posters, release dates, languages, production companies, countries, TMDB vote counts and vote averages. This dataset also has files containing 26 million ratings from 270,000 users for all 45,000 movies. Ratings are on a scale of 1-5 and have been obtained from the official GroupLens website.
-
The CPI (consumer Price Index) Data is collected from the below source.
This dataset contains Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: Admission to Movies, Theaters, and Concerts in U.S. City Average
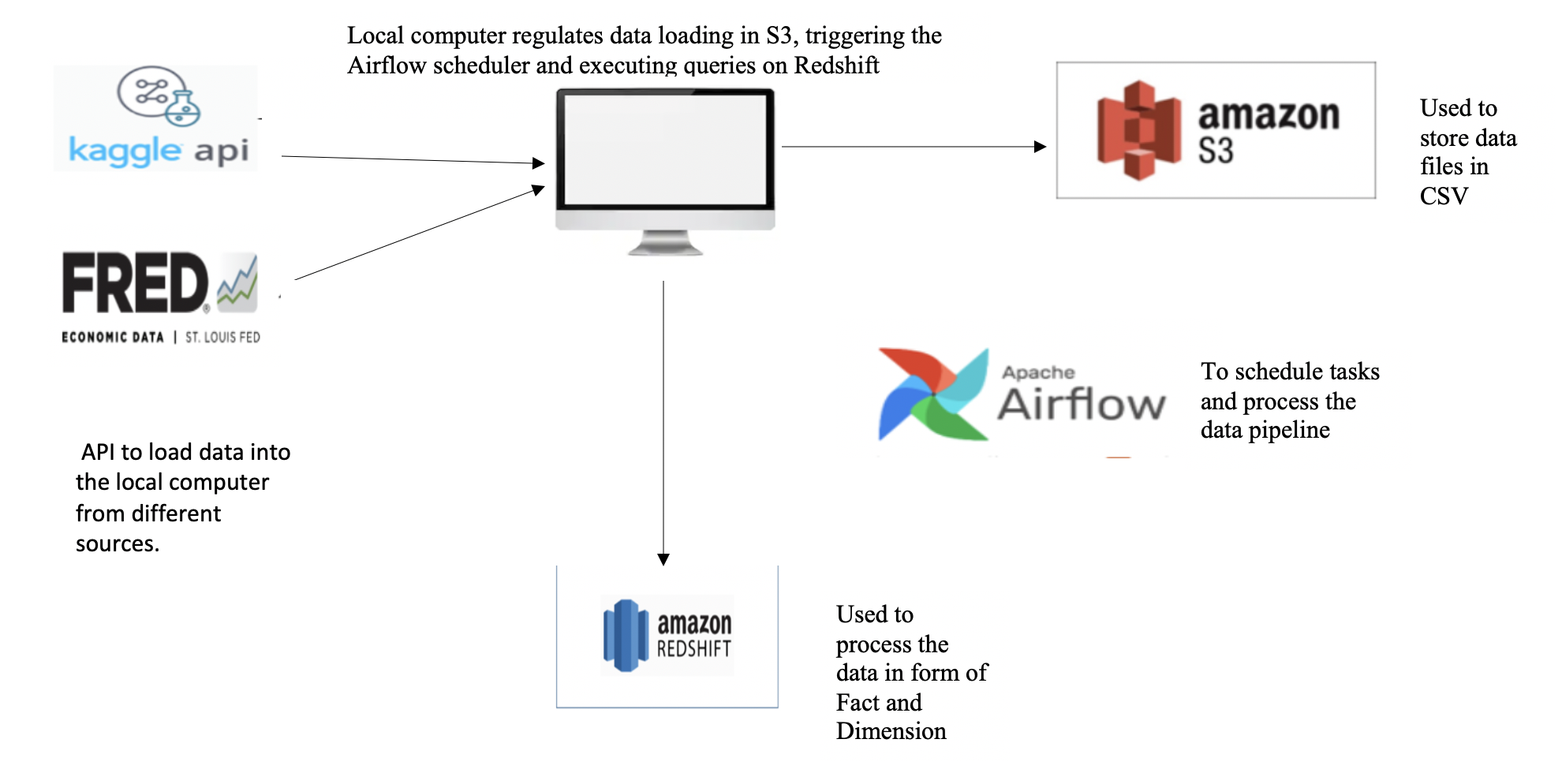
a. The above mentioned APIs are used to load data into the local system. This data is in form of a bunch of CSV files. Amongst those, the following are staged on the S3 bucket - credits.csv - movies_metadata.csv - ratings.csv - CPI.csv
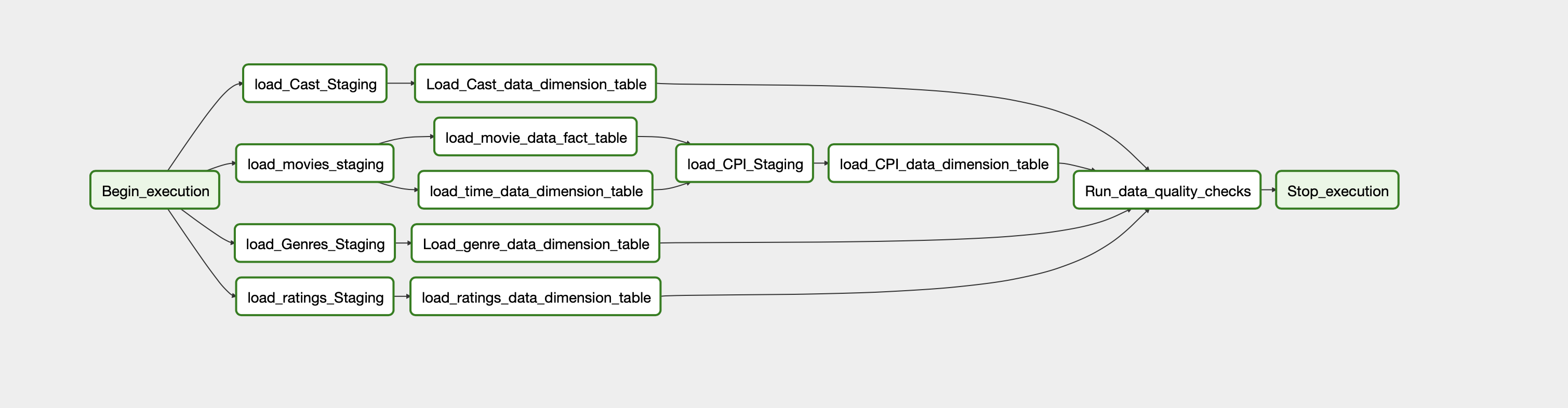
b. Data is then staged from these files into the Staging tables in redshift using the COPY command. Further this staged data is converted into Dimension and Fact tables on redshift itself. This is done using the Airflow scheduler where in each task is executed in a particular order. The Architecture is as shown below.
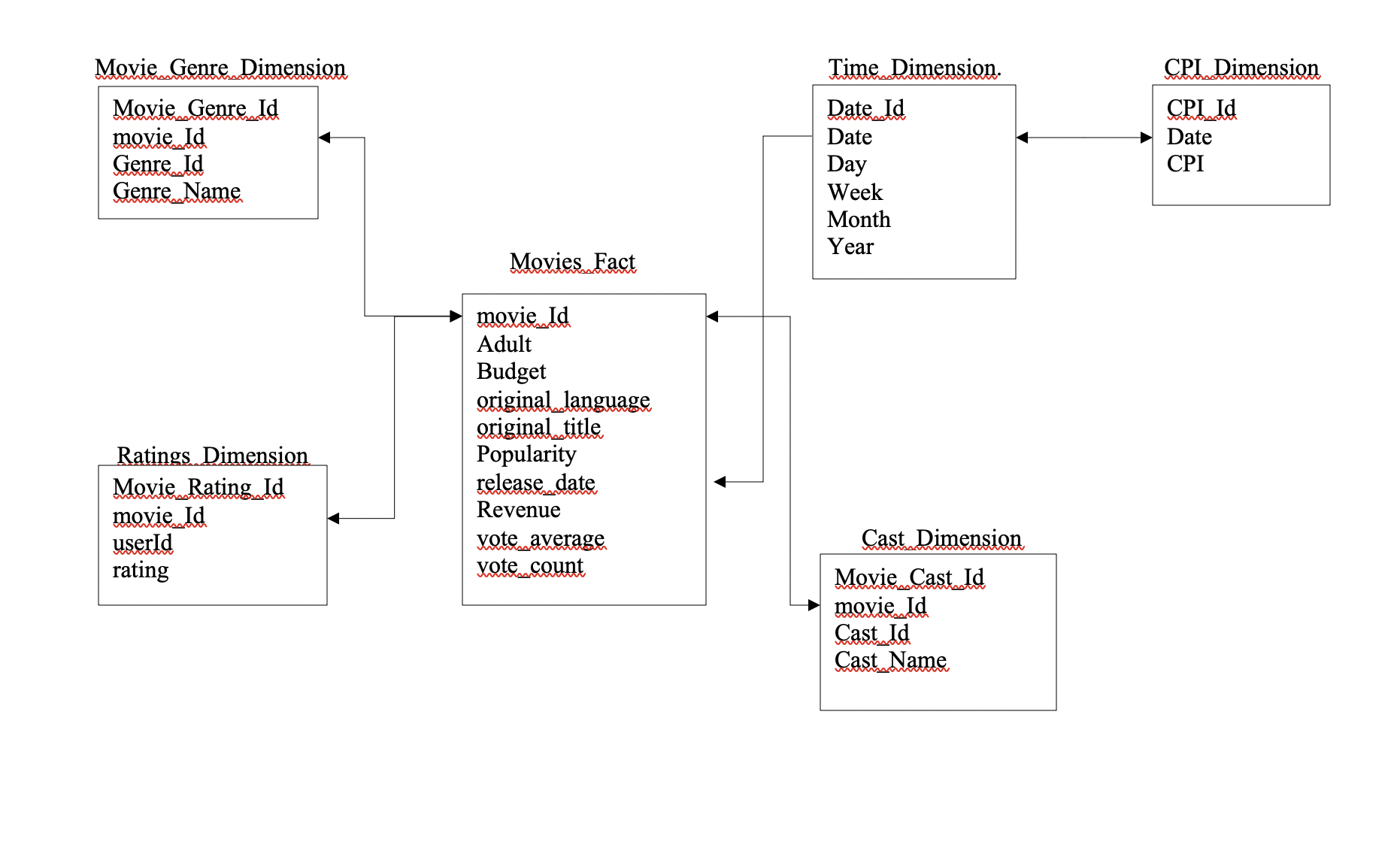
The Schema for the facts and dimensions is as shown below.
c. For a staging the “Cast_staging “and the “Genre_staging” tables , some preprocessing is done on the data. This is cause the data is in form of a comma separated JSON structure. For eg, the genre column looks like this - '[{"id": 10749, "name": "Romance"}, {"id": 18, "name": "Drama"}, {"id": 9648, "name": "Mystery"}]'
So to dump this into genre table, ‘LoadGenreStagingOperator’ first ports in the Genre data from the S3 bucket.
Then it filters on the Genre_id and Genre_name and stores it in a dataframe object. This is then converted into a csv object
This csv object is further processed to enter the Genre_Data into the Staging table.
The Cast data is processed by ‘LoadCastStagingOperator’ in similar way to form the Cast_Staging table.
- The data-pipelining is done as follows. The data is ported from S3 into staging and then into Dimension/Fact tables. The tables are created earlier itself.
- Further, we update the tables whenever new set of data is ported in based on the scheduler.
- We also run the quality checks on fact and dimension tables after every cycle is complete.
- Currently the DAG schedules the pipeline only once, but depending upon the requirement we can trigger it periodically everyday.
1. Top 5 genres of movies based on a “avg_rating”
select
movie_genre_dimension.genre_name,
TRUNC( avg(ratings_dimension.rating) , 2) as "avg_rating"
from ratings_dimension
inner join movies_fact on ratings_dimension.movie_id = movies_fact.movie_id
inner join movie_genre_dimension on movies_fact.movie_id = movie_genre_dimension.movie_id
group by movie_genre_dimension.genre_name
order by "avg_rating" Desc
limit 5;
2. The casting of the most popular films
select
cast_dimension.cast_name,
avg (movies_fact.popularity ) as "popularity"
from movies_fact
inner join cast_dimension on movies_fact.movie_id = cast_dimension.movie_id
where movies_fact.popularity is NOT null
group by cast_dimension.cast_name , popularity
order by "popularity" DESC
3. Finding out if releasing the film in a particular month might affect the revenue.
select
sum(movies_fact.revenue) as "total_revenue",
time_dimension.month
from movies_fact
inner join time_dimension on movies_fact.release_date = time_dimension.date
group by time_dimension.month
order by total_revenue desc
What if data is increased by 100x?
Currently the processing is done on local system. If we need faster processing, then we can employ much faster EC2 instances to handle the load.
Also, we can use SPARK clusters if required to process this faster. Also, we can program the DAG to take only the subset of data at a time rather than in bulk.
What if data pipeline needs to be run by 7am daily?
We can trigeer the DAG to run at any time daily. Also, currently, the DAG runs of local system. If this was running on an EC2 instance, the DAG would itself run
at every regular interval without any disturbance.
What if the database needs to be accessed by 100+ users?
Redshift would be able to handle this load properly. Also, In order to optimize this further the tables can be redesigned / schema can be changed based on most common queries.
Aggregated data tables can be provided beforehand to make queries more and more efficient.
These instructions will get you a copy of the project up and running on your local machine for development and testing purposes.
- Clone this repo
- Install the prerequisites
- Run the service
- Check http://localhost:8080
- Install Docker
- Install Docker Compose
- Following the Airflow release from Python Package Index
Run the web service with docker
docker-compose up -d
# Build the image
# docker-compose up -d --build
Check http://localhost:8080/
docker-compose logs- Displays log outputdocker-compose ps- List containersdocker-compose down- Stop containers
The project user 2 hooks in particular. The first one is the postgres hook.
To set it up , fist run the build using Docker Compose. Then, Go to Admin -> Connections and create "redshift" postgress connection with following values.
- Conn Id:
redshift. - Conn Type:
Postgres. - Host: {redshift.xxxx.us-west-2.redshift.amazonaws.com:5439
- Schema: database name
- Login: user id
- Password: password
- Port:
5439
The second one is the 'AWS, hook to access the bucket data. Go to Admin -> Connections and create "aws_credentials" AWS connection with following values.
- login - ['AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID']
- password - ['AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY']
- Udacity for providing all the related contect.
- I was originally inspired from this - https://github.com/alanchn31/Movalytics-Data-Warehouse