The Web technology materials and resources of the 2018/19 Web and Database Technology course at TU Delft are listed here. ~900 students follow the course, the course setup reflects that.
The database materials are not included here!
- Responsible instructors
- Web technology course book
- Tooling
- Course grading
- Course topics
- Sample exams
- Assignments
- Demo application
- Interactive web technology exercises
- Twitter accounts to follow
- Web development resources
- Lecture material types
- Web lectures
The responsible instructors are Associate Professors Claudia Hauff and Alessandro Bozzon.
The course book for the web technology part is Learning Web App Development by Semmy Purewal. This book covers HTML, CSS, JavaScript and Node.js/Express - exactly the technologies we cover in this course. The book is written for learners without any prior knowledge in these technologies.
Visual Studio Code is the strongly recommended development environment for this course. It is a free and open-source IDE available for all major operating systems. It was originally designed to support Node.js programmers (a server-side JavaScript framework we use in this class), but now has extensions for many programming languages. Best of all, Visual Studio Code itself is written in JavaScript! It has integrated source control with git support out of the box - making it easy to program in pairs. It als has a Live Share extension, which allows you to code in pairs without the need for tools like git.
VS Code offers many extensions. You can find a guide on how to browse and install them here. A list with all kinds of "delightful" extensions can be found here. Since this may be a bit overwhelming, we made a short list of the extensions we recommend to install for this course:
- ESLint, the most popular linting utility for JavaScript (a linter is a tool that analyzes source code to flag potentially poor code such as unused variables) - use it to improve your code.
- Bracket Pair Colorizer does what the name suggests.
- Quokka.js - a great tool to try out JavaScript snippets without hassle.
- VS Live Share - a collaborative real-time coding extension (especially useful if a student team works mostly remotely).
- Material Icon Theme to make finding the file you are after in your app directory a bit easier.
- If you like to add TODOs to your code, try Todo Tree, it makes sure you don't overlook any of your TODOs!
- Finally, a good theme for your IDE to make coding more enjoyable is also not a bad idea. Dracula is a popular one. Cobalt2 is also nice. If you want to pick based on visuals, head over to https://vscodethemes.com/.
If you need to be convinced about why Visual Studio Code is a great IDE to use, check out this podcast by Wes Bos and Scott Tolinski on this very topic.
Browser developer tools: they are built into all modern browsers; familiarize yourself with the developer tools of your favorite browser. For Firefox (my personal choice), you can find an elaborate description of the developer tools at MDN.
If you are new to team programming, and want to use VSC's features efficiently, read our guide.
The latest stable version of Node.js.
Two modern web browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc. to test your project code across browser implementations.
Telnet (for Assignment 1): if you use a Linux derivative (e.g. Ubuntu, older versions of Mac OS), open a terminal and you are good to go; for new Mac OS versions you may need to install telnet yourself. If you are a Windows user please use the Windows Subsystem for Linux or use a Virtual Machine. You can also use Windows alternatives to telnet such as Putty.
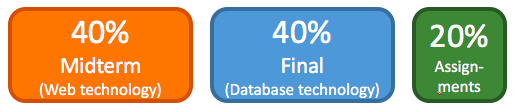
Passing requirements: the overall grade must be 5.8 or higher AND the midterm grade must be at least a 5 AND the final exam grade must be at least a 5 in accordance with TU Delft's exam regulations.
Assignments are done in pairs of two students and are graded by student assistants in a binary manner (pass or fail). There are six assignments in total, three cover web programming topics and three cover database topics. While the assignments together make up only 20% of the final grade and are not required, we strongly recommend to tackle the assignments - they cover a lot of exam materials in a practical manner!
We have two assessment moments: one for the Web technology assignments and one for the Database technology assignments. The assessment is interview-based. The assessment session can yield anything between 3x pass and 3x no-pass. The grading is conducted per student.
The table below shows how the number of passes (maximum 6: 3x web and 3x database) are converted to the assignment grade:
| Number of passes | Grade |
|---|---|
| 6 | 10.0 |
| 5 | 8.3 |
| 4 | 6.7 |
| 3 | 5.0 |
| 2 | 3.3 |
| 1 | 1.7 |
| 0 | 0.0 |
| Week | Monday | Thursday | Friday |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | HTTP | HTML5 | --- |
| 2.2 | JavaScript | Node.js | --- |
| 2.3 | CSS | Node.js (advanced) | --- |
| 2.4 | Cookies and sessions | Web security | --- |
| 2.5 | --- | Midterm exam | --- |
| 2.6 | Introduction to databases | Data models | --- |
| 2.7 | RDBMS: SQL DML 1 | RDBMS: SQL DML 2 | --- |
| 2.8 | NoSQL: document stores | NoSQL: graph stores | --- |
| 2.9 | NoSQL: key-value stores | SQL/NoSQL (advanced) | --- |
| 2.10 | --- | --- | Final exam |
Until (and including) the 2017/18 edition, the web and database (DB) topics were interwoven (usually 1 lecture of web and 1 lecture of DB topics per week) and thus for most years, the midterm and final exams also contain questions on both topics.
Exam topics are all topics covered in the lectures and the required readings. Content of the recommended activitivies/readings that goes beyond what is covered in the lectures/course book is not exam material.
- Midterm 2015/16 (with answers)
- Final 2015/16 (with answers)
- Midterm 2016/17
- Final 2016/117
- Midterm 2018/19 (with answers)
- Midterm Resit 2018/19 (with answers)
There are six assignments in total.
Assignments are worked on in teams of 2 students. We do not allow larger teams; we do not allow teams of 1.
The first three assignments cover web technology topics.
Assessment: the three web assignments are assessed in a single interview session with a TA; the interview lasts 20-30 minutes. Each of the three assignments can be passed or failed (binary judgment, there are no grade levels) on an individual basis. The assessment rubric is available here.
A demo board game application (a word guesser) is available as well. It has has been implemented along the lines of the assignments.
The demo app, just as listed in this year's board game project, consists of two screens, a splash screen:
and a game screen:
Students who do not have a lot of prior knowledge often struggle to get started. Here is a list of useful interactive exercises and how they match up with each lecture. Each of these exercises is small, taking just a few minutes (sometimes less than a minute) to solve.
Twitter is a great resource to hear the latest and greatest about the web stack. Here is a list of accounts we recommend to follow
- Franziska Hinkelmann, working on Node.js at Google
- Lin Clark makes technical challenges accessible to the wider public for Mozilla
- V8, Google's JavaScript engine
- JavaScript Daily, does exactly as the name suggests
- AmsterdamJS, local JavaScript community
- Node.js (of course)
- Axel Rauschmeyer, an author of popular JavaScript books
- Addy Osmani, working on Google Chrome and well known for his JavaScript design patterns book
- Wes Bos, a popular teacher of the web stack
- Mozilla Hacks, official Mozilla account for web developers
- Visual Studio Code (of course)
- JavaScript Conference Series - look out for their conference talks, usually posted on YouTube
- Chrome DevTools, tips and tricks of the dev tool trade
- Syntax, podcasts for web developers
The practical assignments of this work often require looking up Web development specifics. Two good resources, in general, for Web engineering are Mozilla's MDN portal and Google's Web Fundamentals.
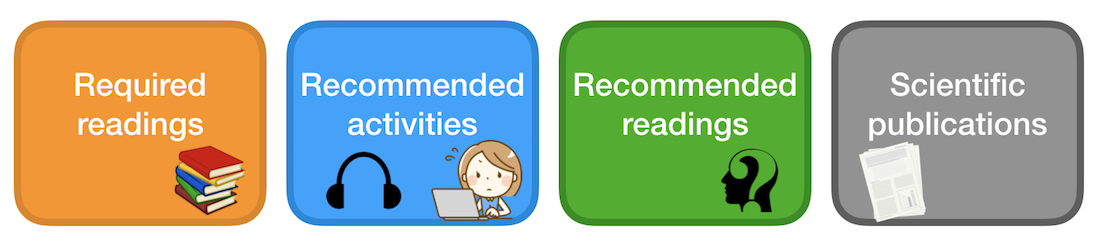
For each lecture we provide a range of materials:
- Required readings: most of the required readings are book chapters of the web course book. The book introduces each technology from scratch. The lectures go beyond what is covered in the book and assume that you have read the corresponding book chapter(s) before the lecture.
- Recommended activities: activities that we think will help you get a better grasp of the different web technologies. Activities are either programming exercises or podcasts (there are some great ones out there!). Don't see those as a complete list to work through, that is impossible given the time!
- Recommended readings: these may be tweets, blog posts or book chapters that help you understand some of the introduced concepts better; again, do not attempt to read all of the materials.
- Relevant scientific publications: we are often asked why this kind of course is part of the computer science curriculum. Isn't this "just" programming? To showcase how web technologies are researched, we here list a number of scientific publications that contribute to our understanding of (the use of) web technologies.
If you are interested in knowing what other universities teach in terms of web technologies, take a look at this list of courses with a web focus.
All lecture transcripts and assigments (which were developed in Markdown) were automatically converted to PDF format, for those students preferring PDFs. Warning: due to the automatic conversion not all pages will look great. You cann find them in the generatedPDFs folder here on GitHub.
The lecture covers HTTP (transcript, course intro slides and lecture slides).
- Required readings: none
- Recommended activity:
- 🎧 Listen to this podcast on how to learn new things quickly in the Web technology world.
- 📺 A short video (in Dutch) by CWI (Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica) to celebrate 30 years since the Netherlands was connected to the public Internet!
- Recommended readings:
- 📕 Chapters 1, 2 and 3 of HTTP: The Definite Guide (O'REILLY 2002).
- MDN overview of HTTP.
- Developer tools overview of your favorite web browser (e.g. Firefox or Chrome).
- A brief history of HTTP.
- Browser fingerprinting showcases how seemingly innocuous data can identify users.
- A crash course on HTTP and DNS by Mozilla (among other things).
- Relevant scientific publications:
- Ihm, S. and Pai, V.S., 2011. Towards understanding modern web traffic. In Proceedings of the 2011 ACM SIGCOMM conference on Internet measurement conference (pp. 295-312). ACM.
- Naylor, D., Finamore, A., Leontiadis, I., Grunenberger, Y., Mellia, M., Munafò, M., Papagiannaki, K. and Steenkiste, P., 2014. The cost of the S in HTTPS. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM International on Conference on emerging Networking Experiments and Technologies (pp. 133-140). ACM.
- Falaki, H., Lymberopoulos, D., Mahajan, R., Kandula, S. and Estrin, D., 2010. A first look at traffic on smartphones. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM SIGCOMM conference on Internet measurement (pp. 281-287). ACM.
This lecture covers web design and HTML5 (transcript and lecture slides).
- Required readings:
⚠️ Chapter 2 of the web course book.⚠️ Introduction to HTML forms (ignore the section on Basic form styling, we will cover CSS in a later lecture) and Sending form data (up to and including the section on Viewing HTTP requests).
- Recommended activity:
- 🎧 Listen to this podcast with Tom Dale discussing modern web applications and the move from web sites to web apps and an almost native experience.
- Recommended readings:
- 📕 Chapter 3 of the Definite Guide to HTML5.
- Web Fundamentals by Google.
- Examples of what modern web technologies can achieve in Chrome (if you use another browser, not all examples may work as expected).
- Relevant scientific publications:
- Fernandez, A., Insfran, E. and Abrahão, S., 2011. Usability evaluation methods for the web: A systematic mapping study. Information and Software Technology, 53(8), pp.789-817.
- Sonderegger, A. and Sauer, J., 2010. The influence of design aesthetics in usability testing: Effects on user performance and perceived usability. Applied Ergonomics, 41(3), pp. 403-410.
This lecture covers client-side JavaScript (transcript and lecture slides).
- Required readings:
⚠️ Chapter 4 of the web course book.
- Recommended activities:
- Interactive exercises for Lecture 3.
- 🎧 Listen to this podcast by Wes Bos and Scott Tolinski on debugging.
- JavaScript30: 30 day vanilla JS coding challenges
- Recommended readings:
- 📕 Learning JavaScript design patterns, in particular the sections on the constructor pattern and the module pattern.
- MDN's introduction to JavaScript objects.
- The dynamic nature of JavaScript makes optimization tricky (blog post).
- Why do we need all those fancy tools for JavaScript development nowadays? (blog post).
- Learn how to debug with Firefox devtools.
- Array.prototype.sort is now stable in V8 (tweet): shows that even basic mechanisms like sorting are still being changed in mature implementations.
- Tooling and conventions are vital in the fast-paced world of JavaScript.
- The State of JavaScript 2017.
- Relevant scientific publications:
- Charland, A. and Leroux, B., 2011. Mobile application development: web vs. native. Queue, 9(4), p. 20.
- Mowery, K., Bogenreif, D., Yilek, S. and Shacham, H., 2011. Fingerprinting information in JavaScript implementations. In Proceedings of W2SP (Vol. 2, No. 11).
- Ratanaworabhan, P., Livshits, B. and Zorn, B.G., 2010. JSMeter: Comparing the Behavior of JavaScript Benchmarks with Real Web Applications. WebApps, 10, pp.3-3.
- Lin, J., 2018. Computing without Servers, V8, Rocket Ships, and Other Batshi*t Crazy Ideas in Data Systems. In Proceedings of DESIRES. A quote ... "So, the future is. . . JavaScript? Once we get beyond the fact that JavaScript is an undeniably shitty language on which to build an interlingual execution platform, there is at least some so-crazy-it-might-actually-work appeal to this idea."
- Patra, J., Dixit, P.N. and Pradel, M., 2018, May. ConflictJS: finding and understanding conflicts between JavaScript libraries. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Software Engineering (pp. 741-751). ACM.
This lecture covers Node.js (transcript and lecture slides).
- Required readings:
⚠️ Chapters 5 & 6 of the web course book.
- Recommended activities:
- Recommended readings:
- Relevant scientific publications:
- Chaniotis, I.K., Kyriakou, K.I.D. and Tselikas, N.D., 2015. Is Node.js a viable option for building modern web applications? A performance evaluation study. Computing, 97(10), pp.1023-1044.
This lecture covers CSS (transcript and lecture slides).
- Required readings:
⚠️ Chapter 3 of the web course book.
- Recommended activities:
- 📺 Watch this talk by Rachel Andrew to learn more about the long (and painful) history of CSS.
- 📺 Watch this talk by Mandy Michael on text effects in CSS. Data attributes and pseudo-elements are a powerful combination!
- 🎧 Listen to this podcast by Wes Bos and Scott Tolinski on the present and future of CSS.
- Recommended readings:
- 📕 Chapters 1-4 and chapter 13 of The Book of CSS3: A developer's guide to the future of web design by Peter Gasston (2nd edition, 2014).
- To make sense of CSS positioning, take a look here.
- If you want to look behind the scenes, read Mozilla's blog post on their CSS engine Quantum CSS.
- Relevant scientific publications:
- Meyerovich, L.A. and Bodik, R., 2010, April. Fast and parallel webpage layout In Proceedings of the 19th international conference on World wide web (pp. 711-720). ACM.
This lecture covers advanced Node.js concepts (transcript and lecture slides).
- Required readings: none
- Recommended activities:
- An interactive ejs playground can be found here.
- Recommended readings:
- To learn more about ejs, take a look at its GitHub repository.
- To learn more about middleware and Express, take a look at the Express documentation.
- An overview of best practices in Node.js.
- Slide deck on High Performance JS in V8.
- Relevant scientific publications:
- Fard, A.M. and Mesbah, A., 2013, September. JSNose: Detecting javascript code smells. In Source Code Analysis and Manipulation (SCAM), 2013 IEEE 13th International Working Conference on (pp. 116-125). IEEE.
- Nasehi, S.M., Sillito, J., Maurer, F. and Burns, C., 2012, September. What makes a good code example?: A study of programming Q&A in StackOverflow. In 2012 28th IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance (ICSM) (pp. 25-34). IEEE.
This lecture covers cookies and sessions (transcript and lecture slides).
- Required readings: none
- Recommended activities: none
- Recommended readings:
- 📕 Chapter 9 of Web Development with Node & Express by Ethan Brown.
- Instead of cookies to recognize a user, we can also resort to the more stealthy version of browser fingerprinting.
- Relevant scientific publications:
- Roesner, F., Kohno, T. and Wetherall, D., 2012. Detecting and defending against third-party tracking on the web. In Proceedings of the 9th USENIX conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (pp. 12-12). USENIX Association.
- Park, J.S. and Sandhu, R., 2000. Secure cookies on the Web. IEEE internet computing, 4(4), pp.36-44.
- Franken, G., Van Goethem, T. and Joosen, W., 2018. Who left open the cookie jar? a comprehensive evaluation of third-party cookie policies. In Proceedings of the 27th USENIX Security Symposium, pp. 151-168.
This lecture covers web security topics (transcript and lecture slides).
- Required readings: none
- Recommended activities:
- 🎧 Listen to this podcast on how to navigate the fast-paced Web technology industry.
- The OWASP Juice Shop is a more advanced Node.js/Express application that is intentionally insecure to train your web security skills.
- Recommended readings:
- 📕 If you want to know everything there is about security, read Ross Anderson's Security Engineering book. Chapter 21 is most pertinent to the web security lecture (warning: this is an extensive read).
- Stanford's CS155: Computer and Network Security course has a number of lectures on web security (PDFs: here, here, here and here).
- CERN's web security lecture.
- The Open Web Application Security Project provides an extensive list of practical tips, best practices and further readings on the topic.
- Node.js security best practices.
- Relevant scientific publications:
- Aggarwal, G., Bursztein, E., Jackson, C. and Boneh, D., 2010. An Analysis of Private Browsing Modes in Modern Browsers. In Proceedings of the 19th USENIX conference on Security. USENIX Association.
- Kieyzun, A., Guo, P.J., Jayaraman, K. and Ernst, M.D., 2009. Automatic creation of SQL injection and cross-site scripting attacks. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Software Engineering (pp. 199-209). IEEE Computer Society.
- Von Ahn, L., Maurer, B., McMillen, C., Abraham, D. and Blum, M., 2008. recaptcha: Human-based character recognition via web security measures. Science, 321(5895), pp.1465-1468.
- Acar, G., Eubank, C., Englehardt, S., Juarez, M., Narayanan, A. and Diaz, C., 2014. The web never forgets: Persistent tracking mechanisms in the wild. In Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security (pp. 674-689). ACM.