Command Line Interface clio is the utility for integration Creatio platform with development and CI/CD tools.
Please give clio-explorer, a Visual Studio code extension for clio a try! This extension provides user interface over clio commands.
To register clio as the global tool, run the command:
dotnet tool install clio
you can register clio for all users:
dotnet tool install clio -g
To unregister clio as the global tool, run the command:
dotnet tool uninstall clio
or for all users:
dotnet tool uninstall clio -g
More information you can see in .NET Core Global Tools overview.
clio register
clio_context_menu.mp4
clio unregister
- Download .net core for mac
- Register clio as the global tool, with the command:
dotnet tool install clio
More information you can see in .NET Core Global Tools overview.
Execute command in terminal for success check
clio help
To display available commands use:
clio help
For display command help use:
clio <COMMAND_NAME> --help
docker build -f ./install/Dockerfile -t clio .
docker run -it --rm clio help
docker run -it --rm clio reg-web-app -help
- Introduction
- Installation and features
- Content table
- Arguments
- Packages
- NuGet Packages
- Application
- Environment settings
- Development
- Packages
- NuGet Packages
- Environment settings
- Using for CI/CD systems
- GitOps
- Installation of Creatio
<PACKAGE_NAME>- package name<ENVIRONMENT_NAME>- environment name<COMMAND_NAME>- clio command name
To create a new package project, use the next command:
clio new-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME>
you can set reference on local core assembly by using Creatio file design mode with command in Pkg directory
clio new-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME> -r bin
When creating package with option -a True then an app-descriptor.json will be created.
All subsequent packages will be added to app-descriptor.json.
#To add package with app descriptor
clio add-package <PACKAGE_NAME> -a True
#To add package without app descriptor
clio add-package <PACKAGE_NAME> -a FalseTo install package from directory, you can use the next command: for non-compressed package in current folder
clio push-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME>
or for .gz packages you can use command:
clio push-pkg package.gz
or with full path
clio push-pkg C:\Packages\package.gz
for get installation log file specify report path parameter
clio push-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME> -r log.txt
install one or more applications from marketplace.creatio.com
clio push-pkg --id 22966 10096
Important
When you work with packages from Application Hub, you need use command push-app with same parameters like push-pkg. For example
clio push-app C:\Packages\package.gz
For compile package
clio compile-package <PACKAGE NAME>
//or
clio compile-package <PACKAGE NAME> -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>
To download package to a local file system from application, use command:
clio pull-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME>
for pull package from non default application
clio pull-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME> -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>
Applies to Creatio 7.14.0 and up
To delete a package, use the next command:
clio delete-pkg-remote <PACKAGE_NAME>
for delete for non default application
clio delete-pkg-remote <PACKAGE_NAME> -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>
clio download-app <APP_NAME|APP_CODE> -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>
#or
clio download-app <APP_NAME|APP_CODE> -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME> --FilePath <FILE_PATH.ZIP>clio deploy-application <APP_NAME|APP_CODE> -e <SOURCE_ENVIRONMENT_NAME> -d <DESTINATION_ENVIRONMENT_NAME>
#or omit -e argument to take application from default environment
clio deploy-app <APP_NAME|APP_CODE> -d <DESTINATION_ENVIRONMENT_NAME>To uninstall application, use the next command:
clio uninstall-app-remote <APP_NAME|APP_CODE>
x
To compress package into *.gz archive for directory which contains package folder
clio generate-pkg-zip <PACKAGE_NAME>
or you can specify full path for package and .gz file
clio generate-pkg-zip C:\Packages\package -d C:\Store\package.gz
The get-app-list command, also short alias as apps,
is used to list all the installed applications in the selected environment.
This command is useful when you want to check which applications are currently
installed in your Creatio environment.
clio get-app-list
#or
clio appsFor package from *.gz archive
clio extract-pkg-zip <package>.gz -d c:\Pkg\<package>
Restore configuration
clio restore-configuration
Restore configuration without rollback data
clio restore-configuration -d
Restore configuration without sql backward compatibility check
clio restore-configuration -f
To get packages list in selected environment, use the next command:
clio get-pkg-list
for filter results, use -f option
clio get-pkg-list -f clio
Set a specified package version into descriptor.json by specified package path.
clio set-pkg-version <PACKAGE PATH> -v <PACKAGE VERSION>
Set a specified composable application version into application-descriptor.json by specified workspace or package path.
clio set-app-version <WORKSPACE PATH> -v <APP VERSION>
// or
clio set-app-versin -f <PACKAGE FOLDER PATH> -v <APP VERSION>
The set-app-icon command is used to set the icon for a specified application
by updating the app-descriptor.json file.
clio set-app-icon [options]-p, --app-name (required): The name or code of the application. -i, --app-icon (required): The path to the SVG icon file to be set. -f, --app-path (required): Path to application package folder or archive.
Examples Set the icon for an application with a specified name:
clio set-app-icon -p MyAppName -i /path/to/icon.svg -f /path/to/app To see full description about Hot Fix mode visit Creatio Academy
# To enable hot-fix mode for a package
clio pkg-hotfix <PACKAGE_NAME> true -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>
# To disable hot-fix mode for a package
clio pkg-hotfix <PACKAGE_NAME> false -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>
List marketplace applications
clio catalog
List marketplace applications and highlight search words
clio catalog -n Data
To pack creatio package to a NuGet package (*.nupkg), use the next command:
pack-nuget-pkg <CREATIO_PACKAGE_PATH> [--Dependencies <PACKAGE_NAME_1>[:<PACKAGE_VERSION_1>][,<PACKAGE_NAME_2>[:<PACKAGE_VERSION_2>],...]>] [--NupkgDirectory <NUGET_PACKAGE_PATH>]
Default value of 'PACKAGE_VERSION' argument it's last package version.
Default value of 'NupkgDirectory' argument it's current directory.
To push NuGet package (*.nupkg) to a NuGet repository, use the next command:
push-nuget-pkg <NUGET_PACKAGE_PATH> --ApiKey <APIKEY_NUGET_REPOSITORY> --Source <URL_NUGET_REPOSITORY>
To restore NuGet package (*.nupkg) to destination restoring package directory , use the next command:
restore-nuget-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME>[:<PACKAGE_VERSION>] [--DestinationDirectory <DESTINATION_DIRECTORY>] [--Source <URL_NUGET_REPOSITORY>]
Default value of 'PACKAGE_VERSION' argument it's last package version.
Default value of 'DestinationDirectory' argument it's current directory.
Default value of 'Source' argument: https://www.nuget.org/api/v2
To install NuGet package to a web application Creatio, use the next command:
clio install-nuget-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME>[:<PACKAGE_VERSION>] [--Source <URL_NUGET_REPOSITORY>]
you can install NuGet package of last version:
clio install-nuget-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME> [--Source <URL_NUGET_REPOSITORY>]
for install several NuGet packages:
clio install-nuget-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME_1>[:<PACKAGE_VERSION_1>][,<PACKAGE_NAME_2>[:<PACKAGE_VERSION_2>],...]> [--Source <URL_NUGET_REPOSITORY>]
or you can install several NuGet packages of last versions:
clio install-nuget-pkg <PACKAGE_NAME_1>[,<PACKAGE_NAME_2>,...]> [--Source <URL_NUGET_REPOSITORY>]
Default value of 'PACKAGE_VERSION' argument it's last package version.
Default value of 'Source' argument: https://www.nuget.org/api/v2
To check Creatio packages updates in a NuGet repository, use the next command:
clio check-nuget-update [--Source <URL_NUGET_REPOSITORY>]Default value of 'Source' argument: https://www.nuget.org/api/v2
To upload licenses to Creatio application, use the next command for default environment:
clio lic <File Path>clio lic <File Path> -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>To restart Creatio application, use the next command for default environment:
clio restart-web-appor for register application
clio restart-web-app <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>For default application
clio clear-redis-dbor non default application
clio clear-redis-db <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>For compile configuration
clio compile-configurationor
clio compile-configuration <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>for compile all
clio compile-configuration --allTo set system settings value
clio set-syssetting <CODE> <VALUE>To read system settings value
get-syssetting <CODE> --GET -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>To enable feature
clio set-feature <CODE> 1To disable feature
clio set-feature <CODE> 0To specify User or Role, use SysAdminUnitName options
clio set-feature <CODE> 1 --SysAdminUnitName SupervisorTo configure a base url of a web service, in an environment use the following command. It may be useful when you need to change the base url of a web service in a development or testing environment.
clio set-webservice-url <WEB_SERVICE_NAME> <BASE_URL> -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>
Get versions of all known components
clio verGet current clio version
clio ver --clioGet current cliogate version
clio ver --gateGet dotnet runtime that executes clio
clio ver --runtimeEnvironment is the set of configuration options. It consist of name, Creatio application URL, login, and password.
Register new application settings
clio reg-web-app <ENVIRONMENT_NAME> -u https://mysite.creatio.com -l administrator -p passwordor update existing settings
clio reg-web-app <ENVIRONMENT_NAME> -u administrator -p passwordclio unreg-web-app <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>For validation existing environment setting you can use ping command
clio ping <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>For view list of all applications
clio show-web-app-listor for concrete application
clio show-web-app <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>For open selected environment in default browser use (Windows only command)
clio open <ENVIRONMENT NAME>For check options fort selected environment use next command
clio ping <ENVIRONMENT NAME>For clone environment use next command.
clio clone-env --source Dev --target QA --working-directory [OPTIONAL PATH TO STORE]The command creates a manifest from the source and target, calculates the difference between them, downloads the changed package from the source environment to the working directory (optional parameter), and installs it in the source environment.
Check application health
clio hc <ENVIRONMENT NAME>clio healthcheck <ENVIRONMENT NAME> -a true -h trueclio healthcheck <ENVIRONMENT NAME> --WebApp true --WebHost trueThis command is designed to retrieve information about the Creatio instance, version, underlying runtime and database type and product name.
clio get-info -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>
//OR
clio get-info <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>For connect professional developer tools and Creatio no-code designers, you can organize development flow in you local file system in workspace.
clio_workspaces_tutorial.mp4
Create workspace in local directory, execute create-workspace command
C:\Demo> clio create-workspaceIn directory .clio specify you packages
Create workspace in local directory with all editable packages from environment, execute create-workspace command with argument -e
C:\Demo> clio create-workspace -e demoCreate workspace in local directory with packages in app, execute create-workspace command
To get list of app codes execute clio lia -e <ENVIRONMENT>
C:\Demo> clio create-workspace --AppCode <APP_CODE>Restore packages in you file system via command from selected environment
clio restore-workspace -e demoWorkspace supports Package assembly. Clio creates, ready to go solution that you can work on in a professional IDE of your choice. To open solution execute command
OpenSolution.cmdPush code to an environment via command, then work with it from Creatio
clio push-workspace -e demoIMPORTANT: Workspaces available from clio 3.0.1.2 and above, and for full support developer flow you must install additional system package cliogate to you environment.
C:\Demo> clio install-gate -e democlio convert <PACKAGE_NAME>Execute code from assembly
clio execute-assembly-code -f myassembly.dll -t MyNamespace.CodeExecutorSet references for project on src
clio ref-to srcSet references for project on application distributive binary files
clio ref-to binExecute custom SQL script on a web application
execute-sql-script "SELECT Id FROM SysSettings WHERE Code = 'CustomPackageId'"Executes custom SQL script from specified file
execute-sql-script -f c:\Path to file\file.sqlExecute dataservice requests on a web application.
| Key | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -t | Operation Type | One of [select, insert, update, delete] |
| -f | Input filename | File in json format that contains request payload |
| -d | Output filename | File where result of the operation will be saved |
| -v | Variables to substitute | List of key-value pairs to substitute in an input file |
Execute dataservice request with variable substitution.
{
"rootSchemaName": "{{rootSchemaName}}",
"operationType": 0,
"includeProcessExecutionData": true,
"columns": {
"items": {
"Id": {
"caption": "",
"orderDirection": 0,
"orderPosition": -1,
"isVisible": true,
"expression": {
"expressionType": 0,
"columnPath": "{{IdVar}}"
}
}
}
}
}clio ds -t select -f SelectAllContacts.json -d SelectAllContacts_Result.json -v rootSchemaName=Contact;IdVar=Id
Create item in project
clio <ITEM-TYPE> <ITEM-NAME> <OPTIONS>
Add web service template to project
clio add-item service test
Add entity-listener template to project
clio add-item entity-listener testGenerate AFT model for Contact entity with Name and Email fields, set namespace to MyNameSpace and save to current directory
clio add-item model Contact -f Name,Email -n MyNameSpace -d .Generate ATF models for All entities, with comments pulled from description in en-US Culture and set ATF.Repository.Models namespace and save them to C:\MyModels
add-item model -n "<YOUR_NAMESPACE>" -d <TARGET_PATH>To generate all models in current directory
add-item model -n "<YOUR_NAMESPACE>" OPTIONS
| Short name | Long name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| d | DestinationPath | Path to source directory |
| n | Namespace | Name space for service classes and ATF models |
| f | Fields | Required fields for ATF model class |
| a | All | Create ATF models for all Entities |
| x | Culture | Description culture |
Adds cs schema to a project
clio add-schema <SCHEMA_NAME> -t source-code -p <PACKAGE_NAME>The switch-nuget-to-dll-reference command is a vital tool for managing NuGet package references,
especially in scenarios where internet access is limited or unavailable.
This command is specifically designed to convert NuGet package references into direct dll
(Dynamic Link Library) references.
switch-nuget-to-dll-reference command, is beneficial when developing a package on for installation on Creatio
instance that lacks internet connectivity. Command converts [PackageReference] into local DLLs,
This facilitates seamless package installation and operation in offline environments.
Lear more about PackageReference and Reference in Microsoft documentation.
clio switch-nuget-to-dll-reference <PACKAGE_NAME>
#or
clio nuget2dll <PACKAGE_NAME>To connect your package from workspace to local system in file design mode use command
clio link-from-repository --repoPath {Path to workspace packages folder} --envPkgPath {Path to environment package folder ({LOCAL_CREATIO_PATH}Terrasoft.WebApp\\Terrasoft.Configuration\\Pkg)}
Link all packages from repository
clio l4r -e ({LOCAL_CREATIO_PATH}Terrasoft.WebApp\\Terrasoft.Configuration\\Pkg) -p * -r .\To connect your local system in file design mode use command to workspace
clio link-to-repository --repoPath {Path to workspace packages folder} --envPkgPath {Path to environment package folder ({LOCAL_CREATIO_PATH}Terrasoft.WebApp\\Terrasoft.Configuration\\Pkg)}
To mock data for unit tests with using [ATF].[Repository] use the following command
clio mock-data --models D:\Projects\MyProject --data D:\Projects\MyProject\Tests\TestsData -e MyDevCreatio
``
# Using for CI/CD systems
In CI/CD systems, you can specify configuration options when calling commands:
clio restart -u https://mysite.creatio.com -l administrator -p password
# GitOps
To support GitOps approach clio provides yaml manifest file. This file has following structure to describes desired state of Creatio instance.
Example of manifest:
```yaml
environment:
url: https://production.creatio.com
username: admin # or use OAuth token
password: password # or use OAuth token
clientid: "{client-id}"
clientsecret: "{client-secret}"
authappurl: https://production.creatio.com/0/ServiceModel/AuthService.svc/Login
platformversion: "8.1.1"
platformtype: "NET6" # "NET6" or "NETFramework"
apps:
- name: CrtCustomer360
version: "1.0.1"
apphub: MyAppHub
- name: CrtCaseManagment
version: "1.0.2"
apphub: CreatioMarketplace
syssettings:
- name: SysSettings1
value: Value1
- name: SysSettings2
value: Value2
features:
- name: Feature1
enabled: "true"
- name: Feature2
enabled: "false"
webservices:
- name: WebService1
url: "https://preprod.creatio.com/0/ServiceModel/EntityDataService.svc"
- name: WebService2
url: "https://preprod.creatio.com/0/ServiceModel/EntityDataService.svc"
app_hubs:
- name: MyAppHub
path: "//tscrm.com/dfs-ts/MyAppHub"
- name: CreatioMarketplace
url: "https://marketplace.creatio.com/apps"
To apply manifest to your Creatio instance use the following command
clio apply-manifest "D:\manifest\myinstance-creatio-manifest.yaml" -e MyInstance
To control changes of an instance download state to manifest file and store it in Git. To download state use the following command
clio save-state "D:\manifest\myinstance-creatio-manifest.yaml" -e MyInstance
To compare two Creatio instances and show it use the following command
clio show-diff --source production --target qa
To save diff manifest to file, specify arguments file
clio show-diff --source production --target qa --file diff-production-qa.yaml
You can combine multiple commands into one scenario and execute it with
clio run-scenario --file-name scenario.yaml
Scenario consists of and steps and optional settings and/or secrets.
secrets:
Login: real-login
Password: real-password
settings:
uri: http://localhost:80
steps:
- action: restart
description: restart application
options:
uri: {{settings.uri}}
Login: {{secrets.Login}}
Password: {{secrets.Password}}See more examples in samples
Clio provides functionality to install Creatio on a local machine using a zip file or an unzipped folder.
Supported Net6 and NetFramework platforms with MsSql or PostgreSQL databases
Here's how you can do it:
To simply installation of dependencies, clio provides deployment files for Microsoft SQL, Postgres, and Redis server in your local Kubernetes cluster. To create an empty cluster, we recommend using Rancher Desktop, however there are other alternatives.
If you already have running MSSQL/PostgresSQL/Redis servers on you local machine you have to configure kubernetes services ports to avoid collisions. Reffer to services.yaml in related directories
To manage required windows features execute command
# check
clio manage-windows-features -c
# install
clio manage-windows-features -i
# uninstall
clio manage-windows-features -u
Install Rancher Desktop and configure resources
On Windows configure resources with .wlsconfig file. Sample config:
[wsl2]
memory=8GB # Limits VM memory in WSL 2 to 16 GB
processors=4 # Makes the WSL VM use 8 virtual processors
clio create-k8-filesReview files in C:\Users\YOUR_USER\AppData\Local\creatio\clio\infrastructure folder.
Things to review:
mssql-stateful-set.yaml- make sure thatresourcessection has correct values. Values will depend on your PC's hardware.mssql-stateful-set.yaml- make sure you agree with terms and conditions of Microsoft SQL Server Developer Edition.mssql-stateful-set.yaml- will try to allocate 20Gb of disk space for database files. Make sure you have enough space on your disk.postgres-stateful-set.yaml- make sure thatresourcessection has correct values. Values will depend on your PC's hardware.postgres-stateful-set.yaml- will try to allocate 40Gb of disk space for database files and 5Gb for backup files. Make sure you have enough space on your disk.
Deploy necessary components by executing a series of commands from C:\Users\YOUR_USER\AppData\Local\creatio\clio\
or execute command to open directory
clio open-k8-files
# common
kubectl apply -f clio-namespace.yaml
kubectl apply -f clio-storage-class.yaml
# redis
kubectl apply -f redis
# mssql
kubectl apply -f mssql\mssql-volumes.yaml
kubectl apply -f mssql
# postgresql
kubectl apply -f postgres\postgres-volumes.yaml
kubectl apply -f postgres
kubectl apply -f pgadminClio will set up an IIS site, configure the relevant app pool,
and then launch Creatio in your default browser.
You can override default location in of an IIS folder in appsetting.json iis-clio-root-path property.
- Enable required Windows components for NET Framework
- Enable required Windows components for .NET 6
For automated check you can execute command
clio check-windows-featuresTo get a Windows (only) context menu for .zip file execute
clio registerYou may need to close all Explorer windows and open them again. Find Creatio installation zip file and right-click on it.
You should see clio: deploy Creatio menu item. Click on the menu item and follow the prompts.
You may need Administrator privileges.
Other OS use command to install Creatio
clio deploy-creatio --ZipFile <Path_To_ZipFile>Clio will automatically determine if the zip file is stored remotely.
If the file isn't on your local machine, Clio will copy it to a predefined local working folder location,
You can change the default location in appsetting.json file creatio-products property.
To see your appsetting.json file execute
clio cfg openIf the zip file already exists in your working directory, Clio will skip this step.
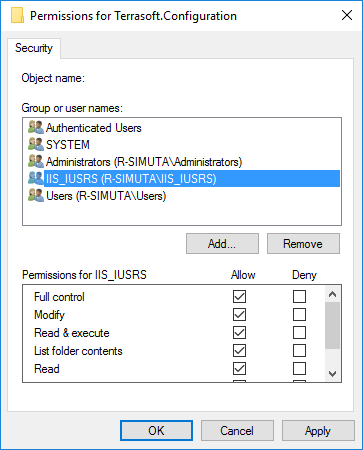
Make sure that iis working directory defined in appsettings.json file iis-clio-root-path has allow Full Control for IIS_IUSRS
Clio will extract the zip file to the same directory where the original zip file is located. If the folder already exists, Clio will skip this step.
The connection string will be generated based on your existing cluster configuration.
Initially, the backup file will be copied to a folder that is accessible by the database server.
Scripts suitable for both Microsoft SQL and Postgres deployment within a Kubernetes cluster are provided.
Clio will then search for a fitting server within the clio-infrastructure namespace in Kubernetes and
copy files as needed.
Once files are copied, Clio will proceed to restore the database.
By default, database will be available on default port
- Postgres: localhost:5432 (root/root)
- PG Admin: localhost:1080 (root@creatio.com/root)
- MSSQL: localhost:5432 (sa/$Zarelon01$Zarelon01)
Postgres - clio will create a template database, and then a real database from the template. If Database or template already exists, Clio will skip this step.
You can change port and secrets in configuration files
C:\Users\YOUR_USER\AppData\Local\creatio\clio\infrastructure
To restore database for Creatio environments, you can use the next command:
clio restore-db --db-name mydb10 --db-working-folder <DB_SERVER_FOLDER> --backup-file <BACKUP_FILE_PATH> --db-server-uri mssql://USERNAME:PASSWORD@127.0.0.1:1433
#use --force to overwrite existing database without promptYou can register db-servers in clio config file (appsetting.json) see example below
"dbConnectionStringKeys" : {
"k8-mssql": {
"uri": "mssql://username:password@127.0.0.1:1433",
"workingFolder" : "\\\\wsl.localhost\\rancher-desktop\\mnt\\clio-infrastructure\\mssql\\data"
}
}To link environment with a db server use DbServerKey property in environment settings.
You can also specify DbName and BackupFilePath properties to simplify command.
"Environments": {
"apollo-bundle-framework": {
... OTHER PROPERTIES ...
"DbServerKey": "k8-mssql",
"DbName": "mydb10",
"BackupFilePath": "D:\\Projects\\CreatioProductBuild\\8.1.2.2482_Studio_Softkey_MSSQL_ENU\\db\\BPMonline812Studio.bak"
}
},
"dbConnectionStringKeys" : {
"k8-mssql": {
"uri": "mssql://username:password@127.0.0.1:1433",
"workingFolder" : "\\\\wsl.localhost\\rancher-desktop\\mnt\\clio-infrastructure\\mssql\\data"
}
}clio resrore-db -e <ENVIRONMENT_NAME>Uninstall Creatio from your local machine by executing the following command:
clio uninstall-creatio -e <ENV_NAME>