第 11 题:将数组扁平化并去除其中重复数据,最终得到一个升序且不重复的数组
zpzxgcr opened this issue · 381 comments
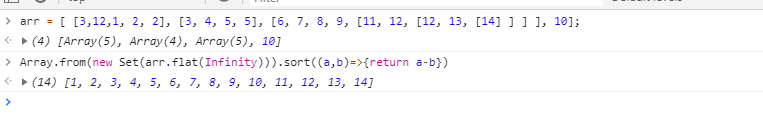
Array.from(new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))).sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b})
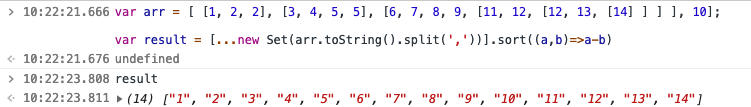
arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b})arr.toString()。split(“,”)。sort((a,b)=> {return ab})
你可能后面需要 arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b}).map(Number)
不然数组元素都是字符串 结果并没有去重 还有两个2 5和12
arr.toString()。split(“,”)。sort((a,b)=> {return ab})
你可能后面需要
arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b}).map(Number)
不然数组元素都是字符串
谢谢大佬指点,学习了
Array.prototype.flat= function() {
return [].concat(...this.map(item => (Array.isArray(item) ? item.flat() : [item])));
}
Array.prototype.unique = function() {
return [...new Set(this)]
}
const sort = (a, b) => a - b;
console.log(arr.flat().unique().sort(sort)); // [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 ]var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
function flatten(arr) {
while (arr.some(item => Array.isArray(item))) {
arr = [].concat(...arr);
}
return arr;
}
Array.from(new Set(flatten(arr))).sort((a, b) => {
return a - b
})Array.prototype.falt = function() { return [].concat(...this.map(item => (Array.isArray(item) ? item.falt() : [item]))); } Array.prototype.unique = function() { return [...new Set(this)] } const sort = (a, b) => a - b; console.log(arr.falt().unique().sort(sort)); // [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 ]
函数名应该是flat
Array.prototype.falt = function() { return [].concat(...this.map(item => (Array.isArray(item) ? item.falt() : [item]))); } Array.prototype.unique = function() { return [...new Set(this)] } const sort = (a, b) => a - b; console.log(arr.falt().unique().sort(sort)); // [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 ]函数名应该是flat
- -感谢斧正
var old_arr=[ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
// 数组拍平
var level_arr=old_arr.flat(4);
//数组去重
var Distinct=Array.from(new Set(level_arr));
// 排序
var sort= Distinct.sort((a, b) =>a - b)
console.log("new arr",sort)递归函数解法:
function spreadArr(arr=[]){
if(arr.some(ele=>Array.isArray(ele))){
let newArr = [];
arr.forEach((ele) => {
if(Array.isArray(ele)){
newArr = newArr.concat(...ele)
}else{
if(!newArr.includes(ele)) newArr.push(ele)
}
})
return spreadArr(newArr);
}
return arr.sort((a,b)=> a-b);
}
spreadArr([ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10]);利用前面的答案,修正一个没用ES6的写法:
// 1、扁平化数组
var flatArr = arr.toString().split(",");
// 2、去重
var hash = {};
for (var i = 0, len = flatArr.length; i < len; i++) {
hash[flatArr[i]] = "abc"
}
flatArr = [];
// 3、将元素字符串转化为数字、遍历hash并不能保证输出顺序
for (var i in hash) {
flatArr.push(+i)
}
// 4、排序
flatArr = flatArr.sort(function(a, b) {
return a - b
})
console.log(flatArr)
看一道面试题:
已知如下数组:var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
编写一个程序将数组扁平化去并除其中重复部分数据,最终得到一个升序且不重复的数组
答案:
var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10]
// 扁平化
let flatArr = arr.flat(4)
// 去重
let disArr = Array.from(new Set(flatArr))
// 排序
let result = disArr.sort(function(a, b) {
return a-b
})
console.log(result)
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]关于 Set 请查阅 Set、WeakSet、Map及WeakMap
本文首发于我的博客:数组扁平化、去重、排序
[...new Set(String(arr).split(','))].sort((a, b) => a - b).map(Number)
额 虽然没大佬们厉害,暂且做个记录吧
function flap(arr){
if([].every.call(arr,item=>!Array.isArray(item))){
return arr;
}
return [].reduce.call(arr,(pre,cur)=>{
if(Array.isArray(cur)){
return [].concat(pre,flap(cur));
}else{
return [].concat(pre,cur);
}
},[])
}
function removeRepeat(arr){
return [...new Set(arr)];
}
function sort(arr){
return [].sort.call(arr,(a,b)=>a-b)
}
function handle(data,...fns){
return fns.reduce((pre,cur)=>{
return cur(pre);
},data)
}
handle(arr,flap,sort,removeRepeat);arr.join(','),split(','),sort((a,b) => a - b)
拍平: const deepFlatten = arr => [].concat(...arr.map(v => (Array.isArray(v) ? deepFlatten(v) : v)));
用toString会改变数组里面的原始数据,应该会是扣分项。
Array.from(new Set(arr.toString().split(',').map(Number))).sort((a, b) => (a-b))- 拍平数组:const flatArray = arr => arr.reduce((a,b) => a.concat(Array.isArray(b) ? flatArray(b): b), []);
- 去重+排序: [...new Set(flatArray)].sort((a,b) => a-b);
var arr = [...new Set(arr.join(',').split(','))].map(v => Number(v)).sort((a,b) => a-b)
var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
var obj = {};
function arrDef(arr) {
if(arr instanceof Array){
arrforDef(arr)
}else {
obj[arr] = 1;
}
}
function arrforDef(arr){
arr.forEach( function(element, index) {
arrDef(element)
});
}
arrDef(arr);
console.log(Object.keys(obj))
var arr = [...new Set(arr.toString().split(',').map(Number).sort((a,b)=>a-b))]
const arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10]
function flat (arr) {
function toFlat (acc, current) {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(current) === '[object Array]') {
current.forEach(item => {
toFlat(acc, item)
})
} else {
if (!acc.includes(current)) {
acc.push(current)
}
}
return acc
}
return arr.reduce(toFlat, []).sort((value1, value2) => value1 - value2)
}
flat(arr)利用Array.prototype.reduce函数递归进行函数拍平去重加排序。这个咋样?
// 已知如下数组:
var arr = [
[1, 2, 2],
[3, 4, 5, 5],
[6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14]]]], 10
];
// 编写一个程序将数组扁平化去并除其中重复部分数据,最终得到一个升序且不重复的数组
// // 去扁平化
function paiping(arr){
if(Array.isArray(arr)){
let arr_ = [];
digui(arr,arr_);
return arr_;
}
}
// 递归
function digui(arr_item,arr_){
for(let i=0;i<arr_item.length;i++){
if(Array.isArray(arr_item[i])){
digui(arr_item[i],arr_);
}else{
arr_.push(arr_item[i]);
}
}
}
let res =[...new Set(paiping(arr).sort((a,b)=>a-b))];
console.log(res);
// 方法二
let res2 =[...new Set(arr.toString().split(",").map((items)=>{
return parseInt(items);
}).sort((a,b)=>a-b))] ;
console.log(res2);
原题中的Infinity是用来干什么的
[...new Set(arr.toString().split(',').map(k => +k))].sort((a, b) => a-b)
我觉得最好不要在 built-in 函数的 prototype 上直接加方法
而且有些方法命名不太规范,比如 const sort = (a, b) => a - b;,我觉得命名为 comparator 比较合理。另外,还有函数命名为 flatten,我觉得 flat 可能会更好
const arr = [[1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14]]]], 10];
Array.from(new Set (arr.toString().split(',')), val => +val).sort((a, b) => a - b)toString 用在这里确实不太合适。因为 tostring 会把数组里面的元素会变成 string 类型。比如,对象类型的数组元素({a: 1})会变成 [object Object] 以及函数类型的数组元素(new Function('a', 'b', 'return a - b'))会变成 function anonymous(a,b) {return a - b}
const arr1 = (arr + '').split(',')
[...new Set(arr1)].sort((a,b)=>a-b)const set = new Set([ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10].flat(Infinity));
const arr = Array.from(set);
arr.sort((a,b) => a - b);
总结方法就是以下几种方式:1. es6 2. reduce 3. 递归 4. toString
[...new Set(arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b}).map(Number))]
this is good
arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b})
- split()方法是把字符串分割成字符数组,所以最后的排序是根据字符串的编码来排序,输出的也是字符串数组
- 这个方法也没有去重
set方法去重,flat方法扁平化,最后把对象转化成数组:
var arry =[1,25,15,[1,2,15,5],15,25,35,1];
var set =new Set(arry.flat(Infinity).sort((a,b)=>(a-b)));
var arr= [...set];
:
console.log(arr)// [1, 2, 5, 15, 25, 35][...new Set(arr.toString().split(',').sort(function(a,b){return a-b}).map(Number))]
Array.from(new Set(arr.toString().split(',').sort((a, b) => { return a - b }).map(Number)))
1、.toString().split(',') 扁平化数据;
2、sort() 排序数据;
3、map(Number) 转数字;
4、Array.from(new Set()) 去重;
为什么没有人提 利用 apply 做数组降维 呢?
简单实现,不考虑 depth=Infinity 的情况
const flat = function(ary, depth) {
let flatedAry = ary
while(depth > 0) {
flatedAry = [].concat.apply([], flatedAry)
depth--
}
return flatedAry
}再结合 Set 去重、sort 排序。 美滋滋呢~
另外, toString 的降维方式并不认同,原因是不严谨。
[...arr.join().split(',')].sort(a,b)
join() 数组转为字符串
split 字符串 转为数组
[...]去重
我个人觉得这个是最简单的
[...new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))].sort((a,b) => a-b)
Array.from(new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))).sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b})
这里的 sort 里面的排序函数可以省略,直接使用 sort, 默认就是升序排列
Array.from(new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))).sort()
const arr = [[1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14]]]], 10];
const flat = (array) => [].concat(...array.map(i => Array.isArray(i) ? flat(i) : [i]));
const unique = (array) => [...new Set(array)];
const sort = (array) => array.sort((a, b) => a - b);
const compose = (...fns) => value => [...fns].reduceRight((prev, fn) => prev = fn(prev), value);
compose(sort, unique, flat)(arr);
@BaconZhang 为啥不用 reduceRight?因为我觉得 reduceRight 比 reduce 更符合语义
@liuliangsir 感谢指正,这里使用reduceRight比reverse加reduce更简洁
@inJs apply 作用是用来降维?apply 之所以能够用来降维,是因为你借用 concat 函数吧
@BaconZhang 其实我觉得代码还是有点问题,compose(sort, unique, flat)(arr); 这种写法不太符合 pipe 理念,而且 (prev, fn) => prev = fn(prev) 这里有点问题,不需要把 fn(prev) 重新赋给 prev,可以参考 reduce 或者 reduceRight 的实现
这是我实现的 compose
function compose(...funcs) {
return function (...args) {
return funcs.reduceRight((prev, func) => Array.isArray(prev) ? func(...prev) : func(prev), args);
};
}@liuliangsir compose 和 pipe 是两种思路。pipe(flow)是从前到后,compose是从后到前。
var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
arr.toString().split(",").filter((item,index,arrs)=>(arrs.indexOf(item) === index)).sort((a,b)=>a-b);@liuliangsir 相反。 concat 可以被替换, apply 是必须的。 这个方法的缺点是有点绕,不好理解。但是兼容性好。
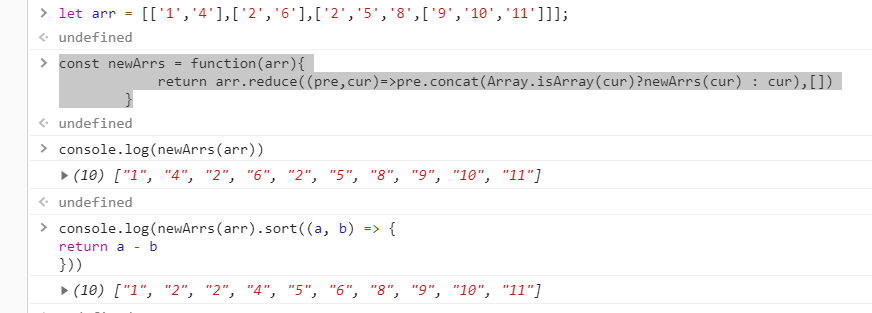
const flat = (arr) => { return [...new Set(arr.reduce((prev, curr)=>{ return prev.concat(Array.isArray(curr) ? flat(curr) : curr) }, []))].sort((a,b)=>{return a-b}) }
这样也是可以的:
Array.from(new Set(arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b}))).map(Number)
原题中的Infinity是用来干什么的
flat 参数,来判定需要去重的层数。
var arr = [[1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14]]]], 10];
function flatArr(arr, hash = {}) {
var newArr = [];
for (var i = 0, len = arr.length; i < len; i++) {
if (arr[i].constructor === Array) {
newArr.push(...flatArr(arr[i], hash));
} else {
if (!hash[arr[i]]) {
newArr.push(arr[i]);
hash[arr[i]] = 1;
}
}
}
newArr.sort((a, b) => a - b);
return newArr;
}
console.log(flatArr(arr));
var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
var resArr = [];
function dealArr(arr) {
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
var item = arr[i];
if (Array.isArray(item)){
dealArr(item);
}else{
if (resArr.indexOf(item) === -1){
resArr[resArr.length] = item;
}
}
}
}
dealArr(arr);
for (var i = 0; i < resArr.length - 1; i++) {
for (var j = i + 1; j < resArr.length; j++) {
if (resArr[i] > resArr[j]){
var key = resArr[i];
resArr[i] = resArr[j];
resArr[j] = key;
}
}
}
console.log(resArr);
arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b})
这个想法可以
[...new set(arr.flat())].sort((a,b) => a - b)
[...new Set(arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b) => a-b).map(Number))]
function flat(arr) {
let result = [];
function fn(arr) {
if (Array.isArray(arr)) {
arr.forEach((item)=> {
fn(item);
})
} else {
result.push(arr);
}
}
fn(arr);
return [...new Set(result)].sort((a, b) => { return a - b; });
}arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b})
这种会丢失原来的数据类型吧
[...new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))].sort((a, b) => a -b )
function arrayFlat(list = []) {
return [...new Set(function (arr) { //去重
const newArr = Array.prototype.concat.apply([], arr) //扁平化
return newArr.some(Array.isArray) ? arguments.callee(newArr) : newArr; //递归
}(list))]
.sort((a, b) =>a - b) //排序
const arr = [[1, 3, 13, 1, 14], [2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 6, 7, 8, [10, 11, 21, [14]]]];
function flatArr(arr, nodelist = []) {
return arr.reduce((total, item) => {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
flatArr(item, total);
} else {
total.push(item);
}
return total;
}, nodelist)
}
const newArr = [...new Set(flatArr(arr))].sort((a, b) => a - b);
[...new Set(arr.flat(Infinity)].sort((a, b) => a-b);[...new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))].sort((a, b) => a - b)
var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
var map = {};
var res = []
function depth (arr) {
arr.forEach(item => {
if (item instanceof Array) {
depth(item)
} else {
map[item] = item
}
})
}
depth(arr)
for (let key in map) {
res.push(parseInt(key))
}
res = res.sort((a, b) => a - b)
console.log(res)
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10]; var map = {}; var res = [] function depth (arr) { arr.forEach(item => { if (item instanceof Array) { depth(item) } else { map[item] = item } }) } depth(arr) for (let key in map) { res.push(parseInt(key)) } res = res.sort((a, b) => a - b) console.log(res) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
const flatten = arr => arr.reduce((acc, item) =>
acc.concat(Array.isArray(item) ? flatten(item) : item), [])
const sw = arr => Array.from(new Set(flatten(arr))).sort((a, b) => a - b)
const arr = [[1,21],3,[40,5,[6,[7,8,[90,10]]]]]
console.log(sw(flat))
// [1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 21, 40, 90][...new Set(JSON.parse(`[${arr}]`).sort((a, b) => a - b))]如果重复的数都是连着的
JSON.parse( `[${`${arr}`.replace(/\b(\d+),\1/g, '$1')}]`).sort((a, b) => a - b)原题中的Infinity是用来干什么的
目测是用来指定要扁平化数组的层数
原题中的Infinity是用来干什么的
flat() 方法会按照一个可指定的深度递归遍历数组,并将所有元素与遍历到的子数组中的元素合并为一个新数组返回。 参数是 要提取嵌套数组的结构深度,默认值为 1。
这个题面试的时候真的遇到了,用递归写了。
考虑到元素可能不止数字,排序时候稍微改下
[...new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))].sort((a,b)=>+(a>b)||+(a===b)-1)var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
var obj = {};
function deepClone(arr) {
var attr = [];
arr.forEach(function (v) {
if (v.constructor === Array) {
attr = attr.concat(deepClone(v));
} else {
if (obj[v] === undefined) {
obj[v] = v;
attr.push(v);
}
}
});
return attr;
}
console.log(deepClone(arr).sort(function (a, b) {
return a - b;
}))
let arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
let tempArray = arr.flat(); // 保存每次flat后的数组
while(checkArrayItemHasArray(tempArray)) {
tempArray = tempArray.flat();
}
tempArray = Array.from(new Set([...tempArray])); // 去重
tempArray = tempArray.sort((a, b) => a - b); // 排序
console.log(tempArray);
// 判断数组项是否有数组类型
function checkArrayItemHasArray(arr) {
let result = false;
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (Array.isArray(arr[i])) {
result = true;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
function flattern(arg){
if(!Array.isArray(arg)) return false;
const arr = arg.reduce((prev, next)=>{
return prev.concat(Array.isArray(next) ? flattern(next) : next)
}, [])
return arr;
}
function unique(arg){
return Array.from(new Set(arg))
}
function sortArr(arg) {
const arr = arg.sort((a, b) => {
return a-b;
})
return arr
}
sortArr(unique(flattern(arr)));
第一印象写出来的,原生方法 arr.flat(arg) 参数表示要展开的层级,默认也是全部展开 Infinity 全部展开。
改进地方, 参考前面的答案可以把方法挂载到原型 Array.prototype 上,实现链式调用 var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10]; var map = {}; var res = [] function depth (arr) { arr.forEach(item => { if (item instanceof Array) { depth(item) } else { map[item] = item } }) } depth(arr) for (let key in map) { res.push(parseInt(key)) } res = res.sort((a, b) => a - b) console.log(res) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
用了递归扁平,hash去重,冒泡排序,打开讨论区大吃一惊
var arr = [[1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
var res = [];
var obj = {};
//扁平时去重
function flattenDeep(arr){
var target;
var i = 0;
for(;i < arr.length;i++){
target = arr[i];
if(Array.isArray(target)){
flattenDeep(target);
}else{
//用对象来过滤重复的数据(空间换时间)
if(!obj[target]){
obj[target] = target;
res.push(target);
}
}
}
}
flattenDeep(arr);
console.log(res.sort(function(a,b){return a - b}));
[...new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))].sort((a,b)=>a-b)
`var arr = [
[1, 2, 2],
[3, 4, 5, 5],
[6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14]]]],
10
];
const arrHandel = arr => [...new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))].sort((a, b) => a - b);
console.log(arrHandel(arr));`
[...new Set(arr.toString().split(','))].sort((x, y) => x - y)
// 扁平化数组方法
function formatArr(arr) {
return arr.reduce((result, item) => {
return result.concat(item instanceof Array ? formatArr(item) : item)
}, [])
}
// 数组去重
function noRepeat(arr) {
var obj = {}
var newArr= []
arr.forEach((item, key) => {
if( !obj[item]){
newArr.push(item);
obj[item] = true
}
})
return newArr;
}
var arr = [[1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14]]]], 10];
// 将相关方法统一
function unionArr(arr){
var arr1 = formatArr(arr);
var arr2 = noRepeat(arr1);
arr2.sort((a, b)=>{
return a - b
})
return arr2;
}
console.log(unionArr(arr))
[... new Set(arr.toString()。split(','))]。sort((x,y)=> x - y)
这样变成字符串了哈,加了一步
[...new Set(arr.toString().split(','))].map(val => Math.floor(val)).sort((x, y) => x - y)
var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
let Array = Array.from(new Set(arr.join(',').split(',').sort((a,b) => {return a-b}))).map(Number)
前面的答案都是直接来这些高级方法,其实我是面试官,可能更愿意看到:
sort,你能直接写个快排
扁平化,知道使用递归
去重,知道set结构并且自己实现一个set
最后,用函数式把这些串起来
这才perfect呀
// 实现:
const flat = (data) => data.reduce((acc, val) => Array.isArray(val) ? acc.concat(flat(val)) : acc.concat(val), [])
const unique = data => data.reduce((acc, val) => acc.indexOf(val) > -1 ? acc : acc.concat(val), [])
const sort = (data, order) => data.sort((a, b) => order === 'desc' ? b - a : a - b)
const compose = (...fns) => fns.reduce((f, g) => (...args) => f(g(...args)))
const bindRight = (fn, thisObj, ...values) => (...args) => (len = fn.length - values.length, fn.apply(thisObj, args.slice(0, len > 0 ? len : 0).concat(values.reverse())))// 数据:
const arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];// 验证:正序
console.log(compose(sort, unique, flat)(arr))// 输出:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]// 验证:倒序
console.log(compose(bindRight(sort, null, 'desc'), unique, flat)(arr))// 输出:
[14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]一种方法:[...new Set(arr.toString().split(','))].sort((a, b)=>{return a-b}).map(Number)
还有:[...new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))].sort((a,b)=>{return a- b})[... new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))].sort((a,b)=>a-b)
arr.toString()。split(“,”)。sort((a,b)=> {return ab})
你可能后面需要
arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b}).map(Number)
不然数组元素都是字符串 结果并没有去重 还有两个2 5和12
[... new Set(arr.toString().split(",").sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b}).map(Number))]
// 递归方式 数组扁平化
var arr = [ [1, 2, 2], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14] ] ] ], 10];
function flat(arr) {
let _arr = Array.from(arr);
let res = [];
_arr.map(el => {
if (el instanceof Array) {
res = res.concat(flat(el))
} else {
res.push(el)
}
})
return res
}
答案为: [...new Set(flat(arr))].sort((a,b)=>{return a - b})
Array.from(new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))).sort((a,b)=>{ return a-b})
这个目前低版本浏览器是不支持的 需要es7 babel支持
Array.from(new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))).sort((a, b) => a - b)发一个不是很成熟的解决方法 :
function flat(arr) {
let result = [];
arr.forEach(a=>{
if(Array.isArray(a)) {
result = [...result,...flat(a)]
} else {
result.push(a);
}
})
return [...new Set(result)].sort((a,b)=>a-b)
}@zpzxgcr 测试结果,如果将Array1.flat(Infinity)替换为:Array2.toString().split(',') #能省300多ms
arr.flat(Infinity)
.sort((a, b) => a - b)
.filter((item, index, arr) => index == 0 || arr[index-1] != item)