SONetworking
NSURLSession network abstraction layer, using Codable and Decodable for response and Encodable for request.
Project Folder and File Structure
Data
├── ServiceConfig
├── DataTransferService
│ ├── DataTransferService
│ ├── ResponseDecoder
│ ├── DataTransferErrorLogger
│ └── DataTransferErrorResolver
├── NetworkService
│ ├── NetworkService
│ ├── NetworkSessionManager
│ ├── NetworkCancellable
│ ├── NetworkError
│ └── NetworkErrorLogger
│── Endpoint
│ ├── Requestable
│ ├── ResponseRequestable
│ ├── HTTPMethodType
│ └── Endpoint
└── Extensions
......
High Level Overview
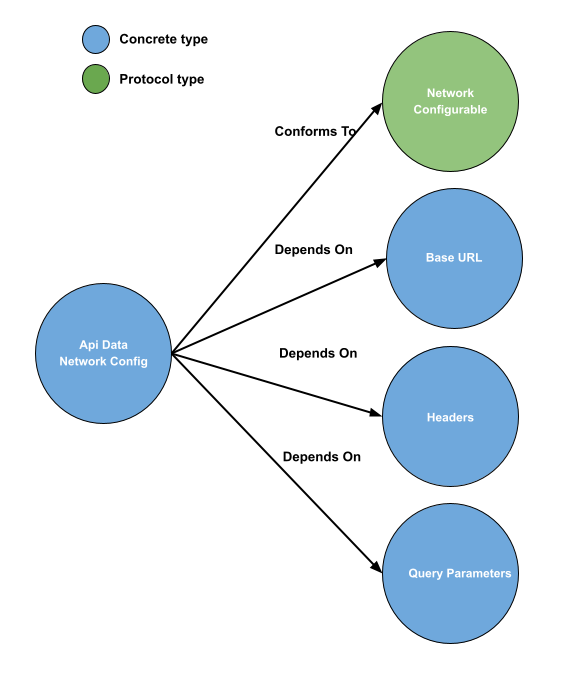
ServiceConfig
The configuration file holds the base URL, headers, and query parameters that can be utilized as an interceptor for any instance.
The NetworkConfigurable protocol defines a set of properties that can be used to configure a network request.
- baseURL: Represents the base URL for the network request.
- headers: A dictionary of key-value pairs representing the headers to be included in the network request.
- queryParameters: A dictionary of key-value pairs representing the query parameters to be included in the network request.
This protocol can be implemented by a struct or a class that needs to provide these configurations to other components that make network requests. The actual implementation of this protocol will depend on the requirements of the specific application.
public protocol NetworkConfigurable {
var baseURL: URL { get }
var headers: [String: String] { get }
var queryParameters: [String: String] { get }
}DataTransferService
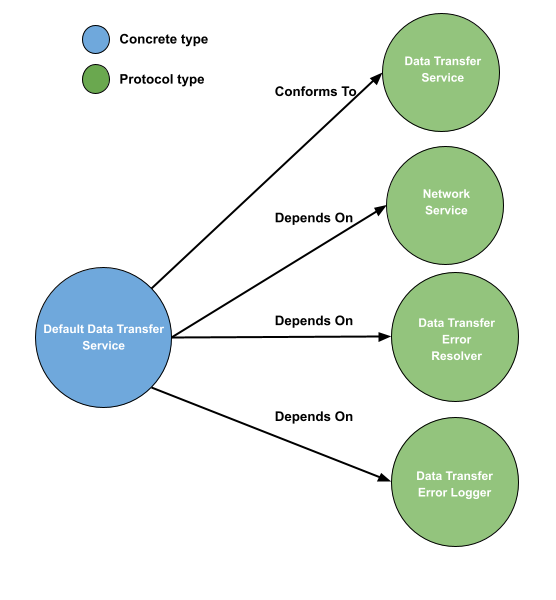
The DataTransferService protocol defines a blueprint for a service that handles data transfer between the application and a remote server. It provides two methods for making network requests, request and request.
public protocol DataTransferService {
typealias CompletionHandler<T> = (Result<T, DataTransferError>) -> Void
@discardableResult
func request<T: Decodable, E: ResponseRequestable>(with endpoint: E,
completion: @escaping CompletionHandler<T>) -> NetworkCancellable? where E.Response == T
@discardableResult
func request<E: ResponseRequestable>(with endpoint: E,
completion: @escaping CompletionHandler<Void>) -> NetworkCancellable? where E.Response == Void
}The first method request is used for making network requests that expect a response from the server. The response will be decoded into an object conforming to the Decodable protocol. The method takes two parameters:
- endpoint: An object conforming to the ResponseRequestable protocol that defines the endpoint to make the request to.
- completion: A completion handler that returns a Result object. If the request was successful, the Result object will contain the decoded response, otherwise it will contain an error of type DataTransferError.
The second method request is used for making network requests that don't expect a response from the server. The method takes two parameters:
- endpoint: An object conforming to the ResponseRequestable protocol that defines the endpoint to make the request to.
- completion: A completion handler that returns a Result object. If the request was successful, the Result object will contain Void, otherwise it will contain an error of type DataTransferError. Both methods return an object conforming to the NetworkCancellable protocol, which allows the network request to be cancelled if necessary.
The DataTransferErrorResolver protocol defines a blueprint for objects that are responsible for resolving network errors. The protocol requires the implementation of a single method resolve, which takes a NetworkError object and returns a Error object.
public protocol DataTransferErrorResolver {
func resolve(error: NetworkError) -> Error
}The resolve method is called when a network error occurs during a data transfer operation. The method takes a NetworkError object as its input, which represents the network error that has occurred. The method returns a Error object, which represents the resolved error that should be propagated to the calling code.
By implementing the DataTransferErrorResolver protocol, objects can provide a custom error resolution process that is appropriate for their needs. This allows for a flexible and modular error handling system that can be adapted to different error types and requirements.
The DataTransferErrorLogger protocol defines a blueprint for objects that are responsible for logging errors that occur during data transfer operations. The protocol requires the implementation of a single method log, which takes an Error object and logs it.
public protocol DataTransferErrorLogger {
func log(error: Error)
}The log method is called whenever an error occurs during a data transfer operation. The method takes an Error object as its input, which represents the error that has occurred. The method is responsible for logging the error in a way that is appropriate for the implementation.
By implementing the DataTransferErrorLogger protocol, objects can provide a custom error logging process that is appropriate for their needs. This allows for a flexible and modular error logging system that can be adapted to different logging requirements and technologies.
NetworkService
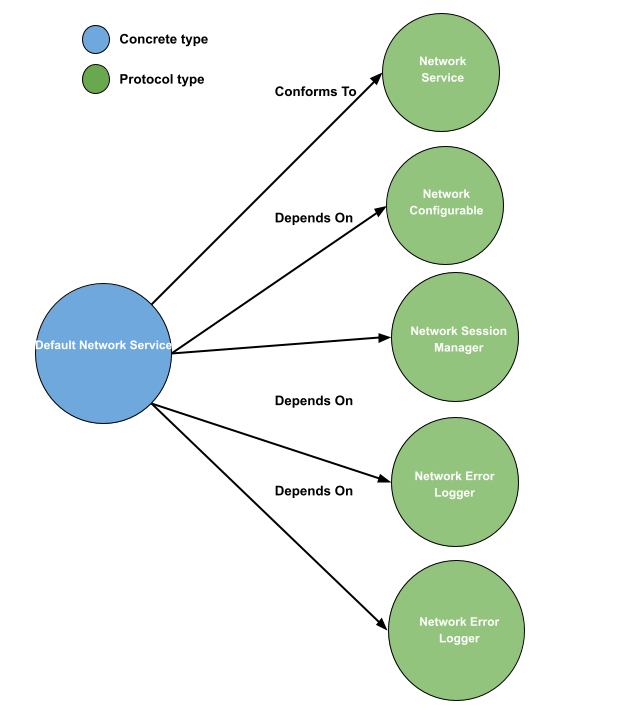
The NetworkService protocol defines a blueprint for objects that are responsible for making network requests. The protocol requires the implementation of a single method request, which takes a Requestable endpoint and a completion handler and returns a NetworkCancellable object.
public protocol NetworkService {
typealias CompletionHandler = (Result<Data?, NetworkError>) -> Void
func request(endpoint: Requestable, completion: @escaping CompletionHandler) -> NetworkCancellable?
}The request method is called to initiate a network request to a specified endpoint. The method takes two parameters:
- endpoint: An object conforming to the Requestable protocol, which defines the details of the network request to be made.
- completion: A closure that will be called when the network request completes, either with data or with an error. The method returns a NetworkCancellable object, which can be used to cancel the network request if desired.
The completion handler is a closure that takes a Result object as its parameter. The Result object is an enumeration that represents the outcome of the network request, either with data (if the request was successful) or with a NetworkError object (if the request failed).
By implementing the NetworkService protocol, objects can provide a custom network request implementation that is appropriate for their needs. This allows for a flexible and modular network layer that can be adapted to different network technologies and requirements.
The NetworkSessionManager protocol defines a blueprint for objects that are responsible for managing network sessions and executing network requests. The protocol requires the implementation of a single method request, which takes a URLRequest object and a completion handler and returns a NetworkCancellable object.
public protocol NetworkSessionManager {
typealias CompletionHandler = (Data?, URLResponse?, Error?) -> Void
func request(_ request: URLRequest,
completion: @escaping CompletionHandler) -> NetworkCancellable
}The request method is called to execute a network request using a URLRequest object. The method takes two parameters:
- request: A URLRequest object that defines the details of the network request to be executed.
- completion: A closure that will be called when the network request completes, either with data, a URL response, or an error. The method returns a NetworkCancellable object, which can be used to cancel the network request if desired.
The completion handler is a closure that takes three parameters:
- Data: The data returned from the network request, if any.
- URLResponse: The URL response from the network request, if any.
- Error: The error from the network request, if any. By implementing the NetworkSessionManager protocol, objects can provide a custom network session management implementation that is appropriate for their needs. This allows for a flexible and modular network layer that can be adapted to different network technologies and requirements.
The NetworkErrorLogger protocol defines a blueprint for objects that are responsible for logging network errors. The protocol requires the implementation of three methods for logging various aspects of a network request and response, and it also defines a logEnabled property that can be used to control whether or not logging is enabled.
public protocol NetworkErrorLogger {
var logEnabled: Bool {get set}
func log(request: URLRequest)
func log(responseData data: Data?, response: URLResponse?)
func log(error: Error)
}- logEnabled: A boolean property that can be used to control whether or not logging is enabled.
- log(request: URLRequest): A method that logs the details of a network request.
- log(responseData data: Data?, response: URLResponse?): A method that logs the details of a network response, including the data returned and the URL response.
- log(error: Error): A method that logs the details of an error that occurred during a network request. By implementing the NetworkErrorLogger protocol, objects can provide a custom error logging implementation that is appropriate for their needs. This allows for a flexible and modular logging layer that can be adapted to different logging requirements.
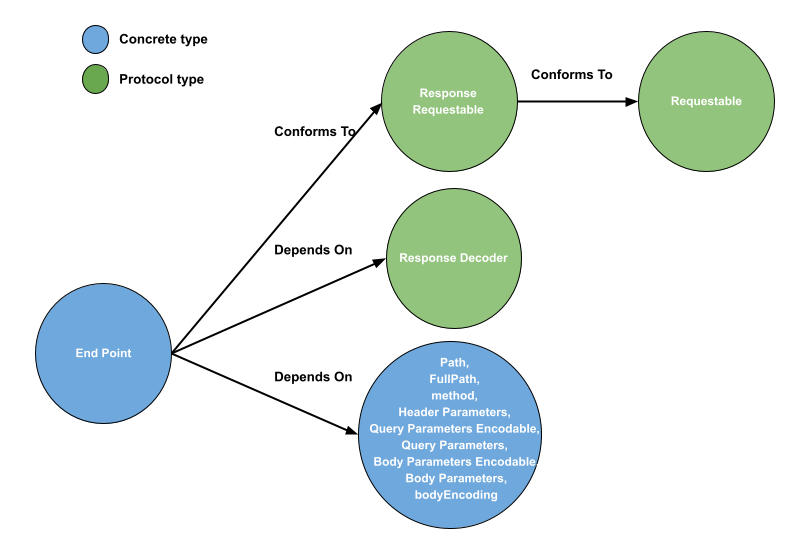
Endpoint
Transform the path into a URL request with a specified method, header, body, and query.
The Requestable protocol defines the properties and methods necessary to make a network request. It requires a path property for the URL path, a method property for the HTTP method type, headerParamaters for the headers, and properties for query and body parameters. It also requires an implementation of the urlRequest method which creates a URLRequest with the given NetworkConfigurable instance.
The protocol extension provides a default implementation for the url and urlRequest methods which prepare the URL and the request with the headers and body parameters.
The ResponseRequestable protocol extends the Requestable protocol and adds an associated type Response and a responseDecoder property. The associated type defines the expected response type, and the responseDecoder property is used to decode the response data.
public protocol Requestable {
var path: String { get }
var isFullPath: Bool { get }
var method: HTTPMethodType { get }
var headerParamaters: [String: String] { get }
var queryParametersEncodable: Encodable? { get }
var queryParameters: [String: Any] { get }
var bodyParamatersEncodable: Encodable? { get }
var bodyParamaters: [String: Any] { get }
var bodyEncoding: BodyEncoding { get }
func urlRequest(with networkConfig: NetworkConfigurable) throws -> URLRequest
}
extension Requestable {
/// prepare the url by appening the base url and query parameters.
private func url(with config: NetworkConfigurable) throws -> URL { }
/// prepare the Request by adding headers and bodyParamaters.
public func urlRequest(with config: NetworkConfigurable) throws -> URLRequest { }
}
public protocol ResponseRequestable: Requestable {
associatedtype Response
var responseDecoder: ResponseDecoder { get }
}Installing
SONetworking is available through CocoaPods. To install it, simply add the following line to your Podfile:
pod 'SONetworking'SONetworking is also available through Carthage. To install it, simply add the following line to your Cartfile:
// TODO SONetworking is also available through Package Manager. To install it, simply add the following line to your Package Manager:
// TODO 👨🏻💻 Author
- Created by Ahmad AlSofi
- Ahmadalsofi, alsofiahmad@yahoo.com
❤️ Contributing
Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub
P.s not mine, but I used to customize it and add some layers