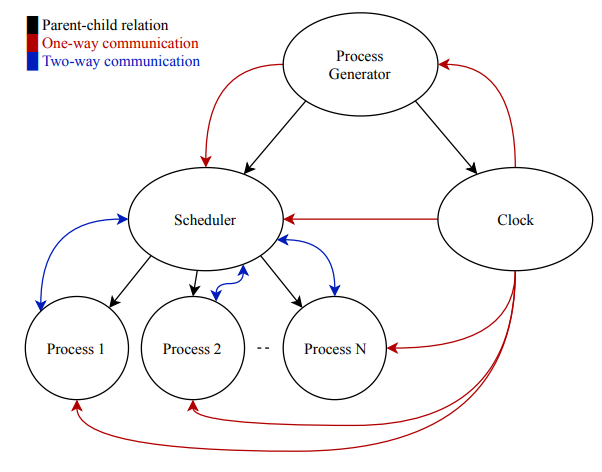
A CPU scheduler determines an order for the execution of its scheduled processes; it decides which process will run according to a certain data structure that keeps track of the processes in the system and their status.
A process, upon creation, has one of the three states: Running, Ready, Blocked (doing I/O, using other resources than CPU or waiting on unavailable resource).
OS for 1 CPU and fixed memory size 1024 byte
- First Come First Serve
- Shortest Job First
- Preemtive Highest Priority First
- Shortest Remaining Time Next
- Round Robin
- First Fit
- Next Fit
- Best Fit
- Buddy System Allocation
- No process can arrive at 0 (this causes inconsistency as the program requires time to initialize)
- In phase 2 RR, If a process cannot be allocated (insufficient memory) it proceeds to the next process and if it is at the end it wraps around.
- In phase 2, If 2 or more processes have the same everything except memory size it does NOT get sorted by the memory size. We just get the same order of the process generator.
- The compiled programs is .out (not .o). it matters as we are calling them by name in the code.
You can use this snippet for compiling the program.
PS: the -lm argument while compiling scheduler is necessary.
gcc process_generator.c -o process_generator.out
gcc clk.c -o clk.out
gcc scheduler.c -lm -o scheduler.out
gcc process.c -o process.out - Faster is
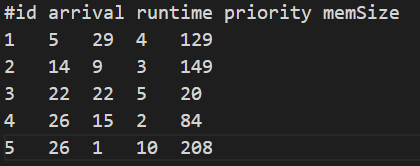
make run- See the scheduler results on this testcase sample
- Scheduling Algorithms with the First Fit Memory Allocation here
- Scheduling Algorithms with the Next Fit Memory Allocation here
Contributions are what make the open source community such an amazing place to be learn, inspire, and create. Any contributions you make are greatly appreciated.
- Fork the Project
- Create your Feature Branch (
git checkout -b AmazingFeature-Feat) - Commit your Changes (
git commit -m 'Add some AmazingFeature') - Push to the Branch (
git push origin AmazingFeature-Feat) - Open a Pull Request
headers.hcontains clk functions, it should be included anywhere the clock functions are used.- To get time call: getClk();
- If you added a file to your project add it to the build section in the Makefile
- Always start the line with a tab in Makefile, it is its syntax