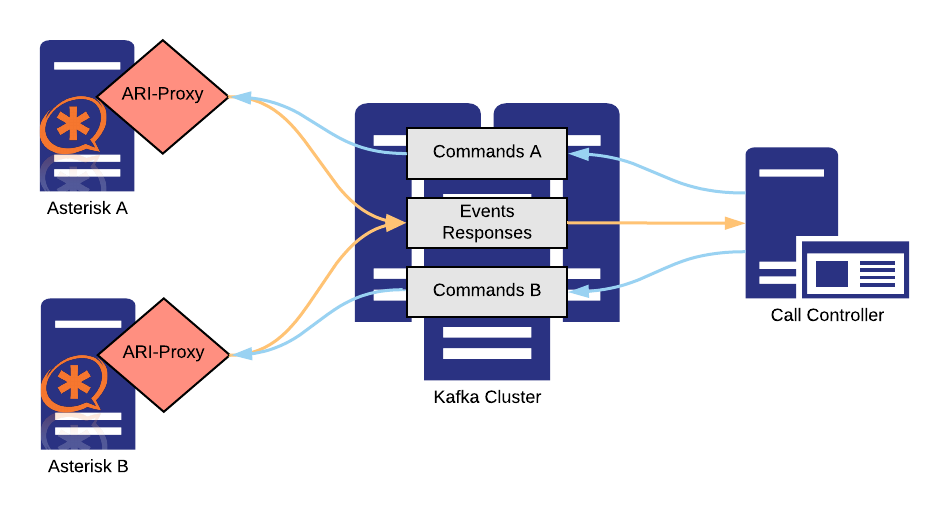
Ari-proxy connects Asterisk, an open source communication server, to the Apache Kafka distributed streaming platform.
- Abstract
- Getting started
- Metrics
- Compatibility
- Contributing & feedback
- Credit & License
- Acknowledgements
The motivation to create ari-proxy arose from the need to build distributed and resilient telephony services scaling up to millions of active users. Ari-proxy makes use of Kafka’s built-in routing concepts to ensure consistency of message streams and proper dispatching to the call-controller, the application implementing the service logic.
Please see docs/concepts.md for details on the concepts of message routing and session mapping.
In order to operate ari-proxy, make sure you have a running instance of both Asterisk and Kafka server.
ari-proxy is written in Java, so you should install and setup Java before continuing. The project is managed by maven, which requires you to install maven as well.
Build the fat jar in target/:
mvn packageari-proxy expects the following configuration files, which should be passed to the jvm when running the fat-jar:
| config | optional | purpose |
|---|---|---|
| service.conf | no | configure the service, see our template: service.conf.sample |
| log4j2.xml | yes | configure logging (if not specified, a bundled config will be used logging to STDOUT only) |
| jolokia.properties | no | configure jolokia agent properties, see our template: jolokia.properties.sample |
Run the fat jar:
java -Dconfig.file=/path/to/service.conf [-Dlog4j.configurationFile=/path/to/log4j2.xml] -jar target/ari-proxy-1.3.0-fat.jarThere are two ways to persist the in-memory data storage (Asterisk Object ID -> Kafka Routing Key).
First there is Redis (default). The redis needs to be configured in service.conf file in order to be able to connect. Also a keyspace needs to be configured. Second possibility to store the data is Cassandra. This is a more robust but more complex configuration as it provides HA and better scalability. You need to configure the Cassandra nodes in the "datastax" section of "service.conf"
In order to choose one option you need to enable the one or the other backend by set the parameter persistence-store to one of these values:
-
"io.retel.ariproxy.persistence.plugin.CassandraPersistenceStore"
-
"io.retel.ariproxy.persistence.plugin.RedisPersistenceStore"
In case you want to use Cassandra you need to create a keyspace and table in Cassandra. This snippet might help to create one. (please adapt replication factor and names according your setup)
CREATE KEYSPACE retel with replication = {'class':'SimpleStrategy','replication_factor':1};
USE retel;
CREATE TABLE retel (
"key" text primary key,
"value" text
);Hint: do not forget some kind of housekeeping by adding TTL or a cleanup job.
Ari-proxy provides service specific metrics using the micrometer framework which are available via JMX.
| mbean | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| metrics:name=CallSetupDelay.* | Timer | Measures the duration between a StasisStart event and the first response to an ari-command |
| metrics:name=CallsStarted | Counter | Increases for every StasisStart event |
| metrics:name=CallsEnded | Counter | Increases for every StasisEnd event |
Note: JMX data may be exposed via HTTP using the jolokia jvm agent (see: debian/ari-proxy@.service).
We aim for compatibility with the latest stable release of
- Java OpenJDK 8
- Asterisk
- the utilized Akka Modules
To report a bug or make a request for new features, use the Issues Page in the ari-proxy Github project. We welcome any contributions. Please see the Developer Guidelines for instructions on how to submit changes.
ari-proxy is maintained by the folks at sipgate and licensed under the terms of the AGPL license.
Maintainers of this repository:
Please refer to the Git commit log for a complete list of contributors.
ari-proxy is not the first of its kind. This project was inspired by the concepts underlying both go-ari-proxy by N-Visible as well as ari-proxy by CyCore Systems.