DaisyRec-v2.0 is a Python toolkit developed for benchmarking top-N recommendation task. The name DAISY stands for multi-Dimension fAirly compArIson for recommender SYstem. Note that the preliminary version of DaisyRec is available here, which will not be updated anymore. Please refer to DaisyRec-v2.0 for the latest version. (Please note that DaisyRec-v2.0 is still under testing. If there is any issue, please feel free to let us know)
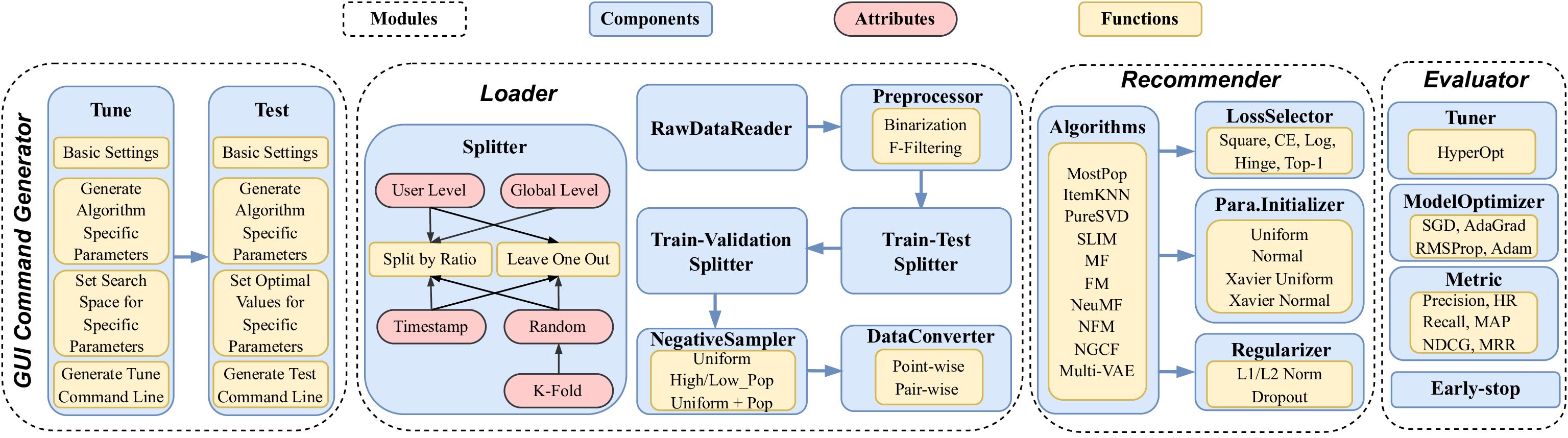
The figure below shows the overall framework of DaisyRec-v2.0.
To get all dependencies, run:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Before running, you need first run:
python setup.py build_ext --inplace
to generate .so or .pyd file used for further import.
Make sure you have a CUDA enviroment to accelarate since the deep-learning models could be based on it.
-
The GUI Command Generator is available here.
-
Please refer to DaisyRec-v2.0-Tutorial.ipynb, which demontrates how to use DaisyRec-v2.0 to tune hyper-parameters and test the algorithms step by step.
The documentation of DaisyRec-v2.0 is available here, which provides detailed explainations for all commands.
Below are the algorithms implemented in DaisyRec-v2.0. More baselines will be added later.
- Memory-based Methods
- MostPop, ItemKNN
- Latent Factor Methods
- PureSVD, SLIM, MF, FM
- Deep Learning Methods
- NeuMF, NFM, NGCF, Multi-VAE
You can download experiment data, and put them into the data folder.
All data are available in links below:
- MovieLens 100K, MovieLens 1M, MovieLens 10M, MovieLens 20M
- Netflix Prize Data
- Last.fm
- Book Crossing
- Epinions
- CiteULike
- Amazon-Book/Electronic/Clothing/Music (ratings only)
- Yelp Challenge
-
Please refer to ranking_results for the ranking performance of different baselines across six datasets (i.e., ML-1M, LastFM, Book-Crossing, Epinions, Yelp and AMZ-Electronic).
- Regarding Time-aware Split-by-Ratio (TSBR)
- We adopt Bayesian HyperOpt to perform hyper-parameter optimization w.r.t. NDCG@10 for each baseline under three views (i.e., origin, 5-filer and 10-filter) on each dataset for 30 trails.
- We keep original objective functions for each baseline (bpr loss for MF, FM, NFM and NGCF; squre error loss for SLIM; cross-entropy loss for NeuMF and Multi-VAE), employ the uniform sampler, and adopt time-aware split-by-ratio (i.e., TSBR) at global level (rho=80%) as the data splitting method. Besides, 10% of the latest training set is held out as the validation set to tune the hyper-parameters. Once the optimal hyper-parameters are decided, we feed the whole training set to train the final model and report the performance on the test set.
- Note that we only have the 10-fiter results for SLIM due to its extremely high computational complexity on large-scale datasets, which is unable to complete in a reasonable amount of time; and NGCF on Yelp and AMZe under origin view is also omitted because of the same reason.
- Regarding Time-aware Leave-One-Out (TLOO)
- We adopt Bayesian HyperOpt to perform hyper-parameter optimization w.r.t. NDCG@10 for each baseline under three views (i.e., origin, 5-filer and 10-filter) on each dataset for 30 trails.
- We keep original objective functions for each baseline (bpr loss for MF, FM, NFM and NGCF; squre error loss for SLIM; cross-entropy loss for NeuMF and Multi-VAE), employ the uniform sampler, and adopt time-aware leave-one-out (i.e., TLOO) as the data splitting method. In particular, for each user, his last interaction is kept as the test set, and the second last interaction is used as the validation set; and the rest intereactions are treated as training set.
- Note that we only have the 10-fiter results for all the methods across the six datasets.
- Regarding Time-aware Split-by-Ratio (TSBR)
-
Please refer to appendix.pdf file for the optimal parameter settings and other information.
- Tables 16-18 show the best hyper-parameter settings for TSBR
- Table 19 shows the best hyper-parameter settings for TLOO
- A more friendly GUI command generator
- Improve the efficiency of the negative sample process
- Optimize the part of building candidate set
- Improve the modularity and scalability of the code (e.g., initializer, optimizer, loss function)
- Reconstruct convert_npy_mat() and UAEData class in Multi-VAE
- A more flexible way to pass parameters
- Implement 5-core and 10-core
- Reduce too much CPU usage in dataloader
- Check Item2vec (add predict interface)
- Add ∞-AE (with code) and EASE algorithms
- Reconstruct DaisyRec with a new framework (YD's team to do)
- Simplify SLIM and KNN-CF (YD's team to do)
- A new GUI to generate results without any command (YD's team to do)
- Update SVDpp, WRMF with torch, torch.linalg.solve
Please cite both of the following papers if you use DaisyRec-v2.0 in a research paper in any way (e.g., code and ranking results):
@inproceedings{sun2020are,
title={Are We Evaluating Rigorously? Benchmarking Recommendation for Reproducible Evaluation and Fair Comparison},
author={Sun, Zhu and Yu, Di and Fang, Hui and Yang, Jie and Qu, Xinghua and Zhang, Jie and Geng, Cong},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems},
year={2020}
}
@article{sun2022daisyrec,
title={DaisyRec 2.0: Benchmarking Recommendation for Rigorous Evaluation},
author={Sun, Zhu and Fang, Hui and Yang, Jie and Qu, Xinghua and Liu, Hongyang and Yu, Di and Ong, Yew-Soon and Zhang, Jie},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.10848},
year={2022}
}
We refer to the following repositories to improve our code:
- SLIM and KNN-CF parts with RecSys2019_DeepLearning_Evaluation
- SVD++ part with Surprise
- NGCF part with NGCF-PyTorch